Slave to the Game
Online Gaming Community
ALL WORLD WARS
USSR NAVY
by Division of US Naval Intelligence, 1943
Part I
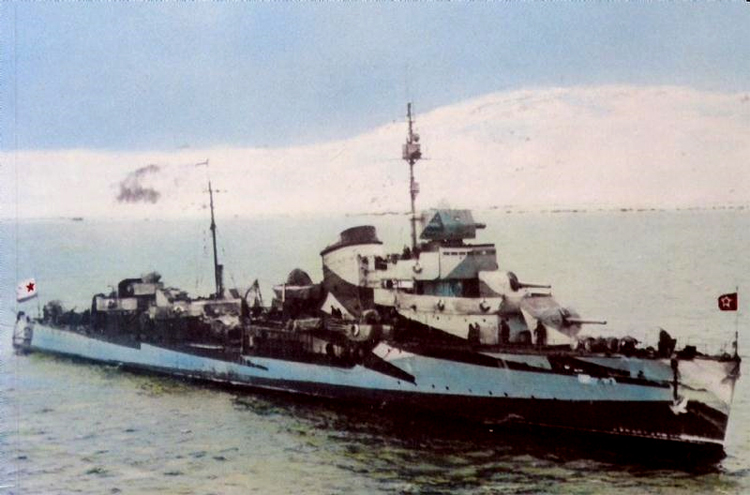
Russian North Fleet Destroyer GORDY Class, circa 1942
EASTERN EUROPEAN DIVISION
DIVISION OF NAVAL INTELLIGENCE
30 NOVEMBER 1943
N.N.I. 96—1943
ISSUED BY THE INTELLIGENCE DIVISION
OFFICE OF CHIEF OF NAVAL OPERATIONS
NAVY DEPARTMENT
INTELLIGENCE REPORT
This serial contains all pertinent information concerning the Navy of the U.S.S.R available in the Division of Naval Intelligence. It covers the organization of the Soviet Navy, naval policy, personnel, tactics and operations, naval ordnance, an estimate of the strength and disposition of the various fleets and descriptions of the units which comprise them, descriptions of all known naval bases and yards, of the naval air force and of coast defense.
This serial supersedes OM-6-F-5 serials 41-42 and 45-42, all copies of which should be destroyed.
Information contained herein is necessarily incomplete and unconfirmed, as the Soviet Government hasxr^rely given detailed information concerning its Navy or permitted accrediteaTU.S. naval representatives to visit naval bases or units.
CHAPTER I. ORGANIZATION
A. Organization in General
On December 30, 1937, the People's Commissariat of the Navy was organized; prior to that time the Navy was a mere sub-section of the Red Army, forming a part of the Peopled Commissariat for Defense, together with the Red Army and Air Force.
The People's Commissariat of the Navy trains navy personnel, administers the naval fleet, and naval bases, and land establishments ! of the nation; it is responsible for the training and administration | of naval aviation, coast defense^ coast guard, and marine corps. The navy is responsible for all coastal and port defenses, including antiaircraft defense. It shares with the People's Commissariats of Munitions^ and of the Shipbuilding Industry the responsibility for the construction of warships and naval bases. It is responsible for the distribution of naval supplies, although the procurement and production of these supplies is under the People's Commissariat of Munitions, which function in these matters under local naval inspectors. Naval war plans are the responsibility of the Soviet Naval Staff.
Little is known of the present-day organization of the Soviet Navy. The chart oh the following page shows its organization as of 1 December, 1940; however, since the outbreak of the Russo-German War in June, 1941, many changes must necessarily have taken place.
The People's Commissar for the Navy, Admiral N.G.Kuznetsov, is the Supreme Commander of the Naval Forces of theTU.S.S.R. under the 1936 Constitution. He is aided by the Deputy People's Commissar, Admiral L. M. Galler, and by the Chief of the Naval Staff, Admiral I. S. Isakov. Under the Chief of the Naval Staff, come the Commanders-in-Chief of the 4 fleets; The Baltic Fleet, Admiral V. F. Tributs; The Black Sea Fleet, Vice Admiral Vladimirski; The Pacific Fleet, Admiral I. S. Yumashev; and The Northern Fleet, Vice Admiral A. A. Golovko, as well as the Commander of the Caspian Flotilla and of the flotillas of various inland waterways, notably the Amur and Volga Rivers. The actual command, however, lies in Joseph Stalin, absolute dictator and supreme commander of all Soviet military forces.
Prior to the outbreak of the Kusso-German War, Soviet naval policy was dictated by the Politburo; decisions of this bureau were put into effect by the Supreme Naval Council. This council probably is no longer in existence, but it formerly consisted of 11 members. It decided on questions regarding the disposition of the fleets, naval construction, naval aviation,, coast defense, coast guard, marine corps, and naval policies. Its membership included M. Zhdanov, Communist Party executive of Leningrad, the Commissar of the Navy, 4 Vice-Commissars, of whom 2 were political appointees, the Chief of the Naval Staff, and the 4 Chiefs of Naval Administration, i.e., armament, supplies, aviation, political. There was a subsidiary naval council attached to each fleet; they controlled all fleet activities within the district. In general, these subsidiary councils were composed of the 2 highest ranking naval political officers and the party secretary or executive of the district.
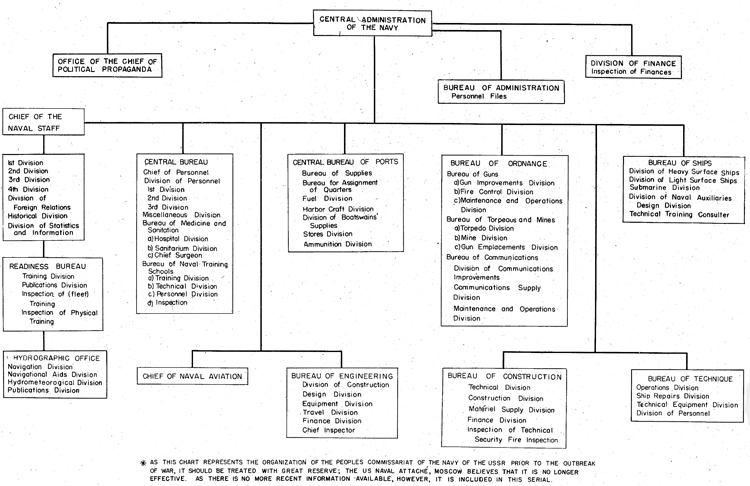
CHART OF THE ORGANIZATION OF THE NAVY COMMISSARIAT OF THE U.S.S.R. AS OF I JANUARY 1940
B. Political Intervention
At the end of the Russian Civil War in 1922, the Soviet Government found that the outstanding majority of its naval officers had bee:i inherited from the Imperial Regime, All officers who did not immediately fall in line with the new government were, of course, ettier exiled or executed. There were, however, a fairly large number of naval officers who were retained; they formed the nucleus for ihe young Soviet Navy, On the other hand, the party officials in . $bssow were not entirely certain of the political feelings of these menl and therefore set up what is now known as the "Politico" system. Under this system, each officer having command, whether of an entire fleet or a motor torpedo boat, was assigned at least one political officer, a member of the Communist Party, who looked after the political education of the men under his command, as well as making certain that the commanding officer .would commit no act which would hurt the Soviet Government. As time went on, these "Politicos" assumed more and more power, so that at the time of the Russo-Finnish Wax, no decision, either of political or operational importance, could fe made by the commanding officer without the approval of his senior politico5 in fact, the political officer was equal in rank to the commander, if not superior to him. In September, 1941, there were no less than 9 political officers assigned to the 8,000-ton heavy cruiser VOROSHILOV. This system, which existed for the sole purpose of compelling officers to adhere to the rules set down by the Cppmmunist Party, made for great inefficiency at sea.
i In order to meet, in part, the shortage of officers produced by heavy casualties and expansion, and to promote efficiency, discipline, and comradely cooperation among officers, the commissar system was, ostsnsibly, at least, abolished, both in the army and navy in 1943. Political commissars, formerly constituting as high as 1/5 of officer personnel, have been enrolled as regular naval officers, in which capacity they will, no doubt, continue to exert strong party influence upon military personnel, although without the power to countersign the orders of the commander.
CHAPTER II. SOVIET NAVAL POLICY AND POST WAR CONSTRUCTION
A. Basic Policy
The geographic position of the USSR compels a naval policy which is necessarily different from those of other nations. Instead of having one principal fleet which can be shifted from place to place as necessity dictates, the USSR must have five separate fleets i.e. Baltic, Black Sea, Pacific, Northern, and Caspian.
The Soviet authorities have done what they could to combine these fleets as much as possible. In the late thirties, the Stalin Canal was completed-connecting, to a certain degree, the Baltic and Northern Fleets. Unfortunately, however, this canal is not sufficiently large to permit the passage of capital ships, or even of cruisers, but 3,000 ton destroyers and under could be shifted between the Baltic Sea and the Arctic Ocean with comparative ease, prior to the outbreak of the Russo-German War.
Because of the opening of the Northern Sea Route, naval units, for the short period of two or three months a year, can be transferred from the Pacific Fleet to the Arctic and Baltic Fleets and visa versa; this is not entirely satisfactory, however, and exposes ships to the perils of ice and bad weather, as well as taking a minimum of 1-1/2 -2 months.
Many attempts have been made to connect the Black Sea with the Caspian Sea. Prior to the outbreak of the war, construction on a canal between the Volga and Don Rivers was underway, but this would not have been of much naval value because of the shoals in the area of the mouth of the Volga. Even with constant dredging of a 25-mile strip, the depth of the river at this point is only 10 feet.
The possibility of digging out the dried-up Manych Canal, which crosses the Caucasus Peninsula, and allowing the water of the Sea of Azov to flow into it has been considered. The drawback of this plan is due to the fact that water in the Black Sea below a depth of 200 meters contains poisonous gases which would ruin the fisheries, first in the Sea of Azov, and later in the northern Caspian Sea.
Naturally, there is absolutely no possibility of connecting the Black and Caspian Seas with the Baltic—Arctic—Pacific group.
The necessity of maintaining strong fleets in each of her seas was amply illustrated during the Russo-Japanese War of 1904-05, when it was seen that by the time the Imperial Fleet (Baltic) reached the Far East, it was of limited operational value, due to insufficient logistic support.
Consequently, in 1907 the first large-scale building program started. It was followed by the Naval Law of 1912, which provided for the following strength of the Baltic Fleet by 1930: (No information is at hand on programs for the other fleets, but it is presumed that they were to be of similar magnitude) 24 battleships, 12 battle cruisers, 24-light cruisers, 108 destroyers, 36 submarines.
At the outbreak of the World War in 1914, this program was well on its way. Seven dreadnought battleships were commissioned by
1917 and one more was still building; four battle cruisers were still building, eight pre-dreadnought battleships were in commission in addition to four obsolete battleships. Six armored cruisers and eight protected cruisers ?rere built by 1914, and ten light cruisers were still under construction in 1917; also, two-pre-dreadnought battleships and one protected cruiser were returned to Russia by Japan after the war was well under way. In 1914, the Imperial Fleet also consisted of about 120 destroyers and 20 more building as well as about 40 submarines and 30 more building.
Due to the World War, the Russian Civil War, Allied intervention and post-war scrapping, the Russian Fleet in 1922 consisted of four dreadnoughts, one of which was never restored, one armored cruiser, which disappeared about 1925-26, and eight uncompleted light cruisers only 3 or 4 of which were eventually commissioned (1927-1930), as well as about twenty destroyers and twenty submarines.
During the reorganization of the Hussion Navy by the Bolsheviks, two schools of thought existed regarding the strategical basis upon which changes should be made. A large number of former Czarist naval officers then still serving, supported the theory of "command of the seas", basing their ideas of new construction and-technical evolution of the future development of a powerful Soviet riavy on the lines of the western capitalist powers.
A second school of thought, headed by Trotsky, claimed that the naval theories of imperial days were wrong and bore no relation to Russia's geographic and economic conditions, and that a "defensive fleet" only should be built. This was brought about by an attempt to give a reason for the realization that the Russian shipyards were in such a state that not even the smallest building program, much less the construction of a battle fleet, could be launched for many years to come.
In formulating this policy, there was no profound naval thinking involved as the fundamental reason for the existence of a navy, to gain or dispute command-of the sea, was completely disregarded. No "defensive navy" ever has or ever, will fulfill this function. Therefore, it became apparent at the very offset that this policy was dictated by political expedi icy coupled with economic necessity* and that it would be discarded as soon as the reconstruction of industry pelmitted.
Consequently, prior to 1937 the USSR concentrated on the building of submarines and small surface craft. Submarines are used extensively for patrol and home defense purposes by the Russians and are not considered as purely offensive weapons. In 1937, the only new units which had been added to the Soviet Fleet since the World War were: 1 2900-ton destroyer leader, about 30 torpedo boats 600-800 tons each, and 60 or 70 submarines.
B. Reversal of Soviet Naval Policy (1936 to 1939)
The first indication of a change in naval policy came during the latter part of 1936 when Fleet Flagman of the First Rank (Admiral of the Fleet) Orloff, Chief of the Naval Forces, announced "a new building program which would include ships of all classes and of the most up-to-date design.1! The Third Five-Year .Plan, which began in 1937,provided for a large increase in the size of the navy.
It is hard to say whether this change of policy was brought about by careful thinking and a conviction of the necessity for employing it, or whether it was the result of a desire for achievement on the part of the Dictatorship of the Proletariat and demonstration bo the world that the U.S.S.R. can produce a fleet equal if not superior to that of a first-class naval power.
Probably Admiral Orloff was too slow to see the change in the minds of the ruling clique; in addition, Soviet shipbuilding yards were not equipped to meet any such increase in the demands made upon them. Therefore, in 1937,the purge of the Navy took place. It was the most far-reaching purge ever instituted, and when it was over, every high-ranking officer with the exception of Admiral Galler had been "liquidated". This included three Supreme Commanders of the Naval forces, the Commanders-in-Chief of three fleets and their chiefs of staff, the commanding officer of the flagship "Marat", the superintendent of the Naval Academy, and many others. The photograph shows the Naval High Command of 1936: all of these men with the exception of Admiral Galler were eventually executed or disappeared. This purge probably, because of its far-reaching results, and because it followed so closely on the heels of the purge of the Red Army, was not officially announced until August, 1938.
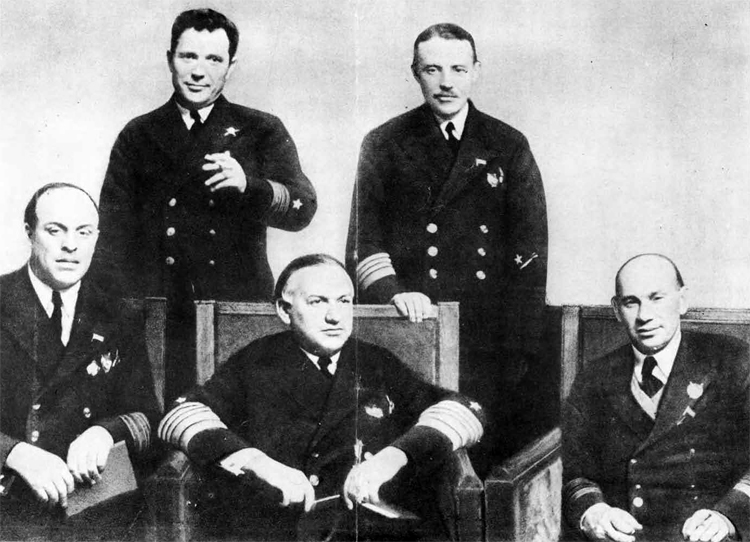

Left to right: (sitting) Fleet Flagman of the first rank (Admiral of the Fleet) M.V. Victorov; Fleet Flagman of the first rank (Admiral of the Fleet) V. M. Orlov, Chief of the Naval Forces of the Workers' and Peasants' Red Army; Fleet Flagman of the first rank (Admiral of the Fleet) I. K. Kozhanov; (standing). Fleet Flagman of the second rank (Admiral) K. I. Dushenov; Fleet Flagman of the second rank (Admiral) L. M. Galler
The first steps taken to build up the Soviet Navy were to reconstruct existing shipbuilding yards and to build new ones. Progress along these lines were found to be far from satisfactory, and so in July, 193&, M. I. Kalinin, President of .the U.S.S.R., made a speech at the Ordzhonikidze Shipbuilding Yard at Leningrad, and blamed this state of affairs not only on "the work of traitors" but also on the inefficiency of the workers themselves.
In order to give high-ranking naval officers more freedom of action, the first Commissariat of the Navy was organized in December, 1937; prior to that time, the navy was administered as a part of the Commissariat of Defense, along with the army and air forces.
In an attempt to help along this building program, Vice Admiral Isakoff, Vice Commissar of the Navyj was sent to the United States in January, 1939, as chief of a naval mission for the purpose of placing an order for the construction of one or two capital ships in this country: due to various reasons, this mission failed.
In March, 1939, at the XVIII Communist Party Congress, three new men appeared, who have since played a large role in the formation of naval policy: the first of these was Rear Admiral N. G. Kuznetsoff, then Commander-in-chief of the Pacific Fleet, who shortly afterward became People's Commissar of the Navy at the age of 37, which position he still holds to the present day. The second was P. Tevosyan, Peopled Commissar of the Shipbuilding Industry, and third was Captain I. D. Papanin, Chief of the Northern Sea Route Administration. The first two stated that the building program according to the dictates of the third Five-Year Plan was well on its way and would be met, if not exceeded. Captain Papanin declared that because of the success attained in opening the Northern Sea Route and because of the Stalin Canal, the,Baltic, Northern, and Pacific Fleets could now be considered as one.
Because of the outbreak of the war in June, 1941 ship construction did not follow according to plan; however, at the time of the German attack, there were either built or building: 2 or 3 44,000-ton battleships building, 5 8,000-ton cruisers built, and 5 more building, as well as a lrage number of smaller craft.
C. Post War Construction
(I) Submarines. The first submarines built were those of the "D" (Dekabrist) Class; the first of these were commissioned in 1927. They have an overall length of about 240 feet and a beam of 24 feet. Their normal surface displacement is 920 tons, submerged 1150 tons. They were designed to have a surface full speed of 15 knots and submerged speed of 8 knots. They have 6-21" torpedo tubes forward and 2 aft and carry a total of only 10 torpedoes.
These were not a very popular type of submarine, so they gave way to the "Ln (Linenaya Lodka) class. These are similar to the "D" class except that they are slightly larger (1300 tons normal surface displacement, 1500 submerged 266 feet long overall) and that they were fitted for minelaying, carrying 20 contact moored mines. Their torpedo tubes were placed similar to those of the "D" class, but they carried twice as many torpedoes. As these two types of submarines were not considered to be entirely satisfactory, construction on them was stopped on the "D" class in 1934 and on the "L" class in 1937.
In 1934, the first 'SCHCH" (SCHCHUKA) class submarine was completed. It turned out to be highly satisfactory as a type of medium-sized boat and was still, at the outbreak of the war in June, 1941, being constructed with but few variations; it is possible that boats of this type are still being built. They have a normal surface displacement of 660 tons, submerged 820 tons, and an overall length of 200-225 feet; they have a full surface speed of 14 knots and are designed to have a full submerged speed of 8 1/2 knots; on the surface, they have a cruising radius of 5000 miles at 10 knots and submerged an 80-mile cruising radius at 5 knots. They have a total of
6 torpedo tubes, 4 forward and 2 aft, and carry a total of 10 torpedoes. It has been reported that some of these boats are fitted for
minelaying, but there is no confirmation of this fact. The main difficulty appears to be that only 2 of the forward torpedo tubes can be fired simultaneously; perhaps this has been altered on newer models. These boats are generally popular, are easy to handle even in a rough sea, but are apt to be a "little lively" on the surface.
Obviously seeing the need for a smaller type of submarine, which, could patrol the Russian coasts near the shore, construction " was started on the "M" (Malutka) class at about the same time that the "Schch" class were being built; the first of these boats were commissioned in 1935. They have a standard surface displacement of 185-204 tons and a submerged displacement of up to 256 tons; they are about 140 feet long and have a beam of 10-11 feet. They have 2 18" or 21" torpedo tubes and carry 2 torpedoes. These boats present a rather strange silhouette, with a disproportionately large conning tower taking up about l/5 of the entire visible length of the hull.
During this period, the Russians v/ere also constructing larger submarines. In 1935, the first "P" (PRAVDA) class boat was completed; these boats, because of their being not entirely satisfactory, were replaced by the "K" (improved Pravda) class in 1938. Little is known about these classes, but from their external appearances, their design shows Italian influence. It is believed that: they have a standard surface displacement of 1500 tons, submerged 1800 tons; they are about 280 feet long and have a beam of about 22 feet. They have a full surface speed of 18 knots and have a cruising radiiats of 7000 miles at 9 knots; submerged they have a full speed of 8-1/2 knots and a cruising radius of 125 miles at 5 knots. They have a total of 8 torpedo tubes, but the number of torpedoes carried is not known; they may be fitted for minelaying. These are the largest submarines yet designed and constructed under the Soviet Regime. The chief difference between the "P" and "K" classes appears to be in the shape of the conning tower; there are possibly other variations in dimensions and armament. The tonnage of the "K" class may be slightly more than that of the "P" class. They are said to be qxiite successful boats, capable of rapid diving.
The latest type of submarine to be constructed under the Soviet Regime is the "S" x(Stalinets) class; they may have, been intended to take the place of the "D" class. They have a normal surface displacement of 750 tons, submerged' 1000 tons. They have a full surface speed of 22 knots, and have a cruising radius of 9000 miles at 11-1/2 knots; submerged they have a maximum radius of 108 miles at 9 knots. They have U torpedo tubes forward and 2 aft and carry a total of 12 torpedoes; these boats are not equipped for minelaying. They have simple, easily understood operational characteristics and are fully capable of keeping the sea and are well fitted out. The bridge and conning tower are very small and the decks very free from obstruction; the overall silhouette is considered excellent.
(II) Surface Craft. The first construction on -surface craft of any Importance undertaken by the U..S.S.R. was on the, SHTORM class torpedo boats; the first of these craft was completed in 1932. They have a normal displacement of 800 tons and an overall length of 251 feet; their, beam is 2J+ feet. They have a designed full speed of 25 knots, and had a mean speed on trials of 21 knots. They carry 2 J+u guns and 3 3" high altitude guns with a maximum range of 27,900 yards; they have 3 18B broadside torpedo tubes in a single turret. They carry 50 mines and 4 D.C.T. These boats are excessively armed for their size; they are reported as being poorly constructed and roll heavily, owing to excessive top hampers.
The Leningrad class destroyer leader represents the first
attempt of the U.S.S.R. in larger ship construction; the first unit
of this class was completed in 1935• They had a standard displace
ment of 2900 tons, a length of 400 feet, and their beam was 38 1/2
feet. They have 5 5.1 inch-guns and 2 3 inch anti-aircraft guns and
2 1.4-6 anti-aircraft guns. Their construction is said to have been
supervised and influenced by French technical experts and are quite
unsatisfactory; they are reported to be poor seaboats, very wet for
ward. Despite this fact, however, additional units are still probably being built.
In 1936 an order was placed by the U.S.S.R. at the Odero-Terni-Orlando Yards, in Leghorn (Italy) fora destroyer leader. All subsequent types of Soviet destroyers reflect this design. The first destroyers built by the U.S.S.R. were the Gordi Glass, which were first laid down in 1937. They have a standard displacement of 1600 tons, a length of 375 feet, and a beam of 33 l/2 feet. Their armament is similar to that placed on the Leningrad Class. More recently, probably not before 1938, an improved type of these destroyers was laid down. They are slightly larger, and have a standard displacement of about 1800 tons. Their main difference in silhouette is that they have two separate raking, squat, flat-sided stacks instead of one. They are indicative of the latest turn in Soviet destroyer construction.
In 1935, construction was first begun on cruisers, namely,
the KIROV class... 5 units of this class have already been completed
and constructionon 5 more was started before the outbreak of the
war, but it is doubtful whether any progress can be made on them at
the present time. These ships have a standard displacement of about
8,000 tons and a length of 613 l/2 f eet. : Their beam is 58 feet.
They have 9 7.1 inch guns in triple turrets, 6 3*9 inch guns and 4
1.4.6 inch anti-aircraft guns. They normally carry 3 aircraft which
are launched by: means of a catapult. Depth charges; are released by
means of 2 depth charge rails.. They have a designed full speed of
34- knots. The design and technical advisor of the construction of
these, units is said to have been furnished by ANSALDO. They are
lightly built, but well laid out.
Although considering the possibility, no action was taken on the possible construction of battleships until/fairly recently. After the ORLOV theory had more or less been accepted, plans were laid for the construction of large units. To this end in 1937 one battleship (and perhaps a second) was laid down at Leningrad, and in 1938 another one at Nikolaev. These units were to have a displacement of 44,190 tons, to be 794V, overall length, 119! in beam, and to have a mean draft of 29f10"5 they were to carry 9 16" guns, 12 5.9" guns and 12 3.9" guns. By the time that the Germans captured Nikolaev the battleship under construction there was about 40% completed. Since the outbreak of the war, further construction at Leningrad has been impossible.
Chapter III.
PERSONNEL
A. Efficiency
The general efficiency of the Soviet naval forces is rather below that of the navies of the western capitalist powers.
As a result of the "purge", the Navy suffers from a surfeit of youth and inexperience. The average age of Commanders-in-Chief of Fleets is 40), while commanding officers of the larger units are rarely more than 35, destroyers in many cases being commanded by lieutenants of only three or four years seniority. The officers, on the whole, are a poor lot; they are drawn from all grades of society and enter the Naval Schools with an indifferent education. They appear, however, to learn much by experience when they are afloat.
Ratings are generally extremely well set up, well-disciplined and exceptionally tough. Petty Officers exert considerable authority, and are given every ehcciaragement to improve their education.
Although the personal appearance of Red sailors is far below
the standard of other western navies, it is much cleaner and neater than
that of the soldiers of the Red Army.
Individual ship efficiency is generally good. Vessels are always well kept and, considering the inexperience of the officers, quite well handled1 Organization and staff work are generally on a very low level. Little is known of Fleet and Squadron efficiency, but it is probably very backward. Reports indicate that this is particularly" so with destroyer flotilla work, and submarine attacks on battle fleets. The whole Navy is maintained on a full commission basis, much sea iime is put in and everyone is kept'hard at work, often on useless tasks; The strain on the whole organization is very great, dockyards fail [to carry out refitting programs, and individual ships very often do not
complete their own annual practices. Tims, although there are a large number of unit s fully commissioned, it is unlikely that such a large proportion is suitable for active service as in case of other European Powers.
The submarine service, on the other hand, is not only strong numerically, but, in quality, has attained a fairly high standard. It is considered as the "Corps d'elite" of the Soviet Navy. Although, as stated above, it is unlikely that flotilla work is particularly efficient, there is no question that submarines individually are efficiently handled.
"To sum up, given good organization and experienced leaders, much could be made of the Soviet Navy, and a considerable improvement may be expected now that political control has once more been relegated to the background.
B . Psychology and Beliefs
The present Russians, especially those in positions of authority, are above all, Soviet Russians. This connotes that they are products of the Revolution. The extreme youth of Soviet naval officers means that they have all grown to manhood since the Revolution. None of them have any more than the faintest recollection of conditions under the Tsarist regime. Therefore, they attribute all the advancement and the technical development of their country to Soviet rule. It should be borne in mind that, while they have never experienced the food, the luxuries, and the broad education of western countries, they hardly know this because they have no past experience on which to compare their present standard of living. Among sailors, there is the stolidity of character that is attributable to peasant birth. Among the. officers who have seen western navies with all their technical developments and the civilization behind those developments, it is evident a kind of an inferiority complex has arisen from the feeling that perhaps their things are not as good as those of the outside world. This has resulted in a fundamental feeling of suspicion, which the Russians have toward foreigners. It is perhaps explicable by the fact that the Soviet Russians have to have something to cover up for this kind of inferiority feeling. Consequently, foreigners are very much distrusted by the Soviet Russians, because Soviet Russians have been taught that outside nations are all imperialist powers which have no real sympathy for the Soviet Union. This teaching adds fuel to the fire of suspicion which the Russians have towards foreigners.
It should be kept in mind that the rapid development of the Soviet Union to its present economic and political form was accompanied by drastic methods. Soviet citizens are supposed not at any time nor in any circumstance to forget the rigid rules for which punishment is severe and far reaching. A rule is in effect prohibiting the acceptance of foreign decorations by Soviet citizens in general, but it has been released on occasions as the recent rewarding of U. S. Navy Crosses and Distinguished Service Medals to outstanding officers and men of the Soviet Navy. It is obvious that the Soviet Russians will be reserved in what they say or do. It is a mistake to persuade them to weaken from their position, much as we are not in agreement with it, or to draw them into conversation on subjects which they are endeavoring to avoid. Political and religious matters should be avoided in discussion. In fact, the Soviet Russian is more likely to listen than to speak; he has a thirst for knowledge of his profession.
It should be kept in mind that in the early days of the Soviet Unionit was deemed essential by the Bolsheviks to secure the political safety of the state. Men were chosen for positions of responsibility pn the basis of their adherence to the official political program rather
than for their particular training or capabilities. The curriculum of
all educational establishments was drastically curtailed by the Bolsheviks and only subjects pertaining to the professions were included in such abbreviated courses as there existed. The lack of training as distinguished from education in the case of many was feverishly made good in order that these people could be used in building up the industry of the Soviet Union and preserve its existence from what the Soviets regarded as the hostile reactionary world.
As a result of this pattern^ the Soviet citizen is lacking in general knowledge and conscious understanding of the finer subjects, and gives the impression that he is coarse and not intellectual. This impression is one which all American and British pfficers experience in their contacts with Soviet officers. The fact that the average Soviet < naval officer does not present himself as possessing outward refinement, or what we associate with being educated in the ways of theworld, does not mean that the Soviet officer lacks interest in the finer things of life. Nevertheless, the material side of life inthe U.S.S*R. takes precedence and is reflected in the appearance and conduct of the Soviet Russian of today. Russian naval personnel are specialists in tlie "technical type", that is, their training resembles more a technical rather than an educational course. This is particularly evident in the curriculum of the Soviet Naval Academy, which emphasizes very practical subjects and offers no "cultural" courses, as distinguished from the curriculum of the U. S. Naval Academy which has both practical and cultural subjects in its curriculum.
There have been a few cases where U. S. naval officers have actually been on Soviet men of war for periods of several weeks as liaison officers. These U. S. naval officers have reported their observations of the problems of joint operations. The Soviet Russian seems to have a one-track mind which is slow to act and its coordination is delayed. This is explainable by the fact that he has learned only one mechanical or technical routine.
First hand experience with Soviet Russian naval officers by U. S. naval officers has shown that the Soviet Russians in general are heavy-handed and ^nept to tools. They have two speeds, "full speed and stop". Their generalized mechanical sense is much inferior to that of U. S. personnel. They are not deliberately careless about cleaning, oiling, painting, and protecting from corrosion, for example,the many precision instruments on board a modern warship. They simply do not know any better.
In general, their operations seem to be "hit or miss" affairs. They like very much to make elaborate prearranged plans which they never follow. This is due perhaps to the fact that the Bolshevik indoctrination is filled with making plans for the future. Their literature, in almost every field of knowledge, emphasizes plans.
It should be pointed out, however, that in spite of the many weaknesses and inefficiencies of the Soviet Navy in its operations, it should be kept in mind that the £igM3£gspirit of the officers has been found to be strong. Althouglrthere Ts'good discipline and morale prevailing among both officers and men, extreme measures are sometimes taken to Insure the execution of orders at critical times. It is possible that this happens more in the Army than in the Navy. It has been rumored that, in order to guarantee the holding of the front when demanded by the tactical situation, N.K.V.D. troops have been stationed at the rear. While the Commissar system has been abolished in the Navy as well as the Army, naval personnel are constantly aware of the "secret police" which is every alert to report on their actions.
Even in spite of this, the propaganda system has been very successful in indoctrinating ideas of patriotism and invincibility in the minds of military and naval personnel. It is becoming more apparent that the fighting personnel is so imbued with these beliefs, that they go into the most daring operations with almost a spirit of recklessness.
C. Morale. Discipline. Customs and Practises
One of the most striking features of the Soviet military organizationtoday is the current revival of old imperialistic traditions. In 1940, special Bolshevistic designations of rank were abolished, and ranks were made to conform with those of other navies; the main changes were in the designations of flag rank. Also, the titles of Engineer Lieutenant through Engineer Admirals as existed in the Imperial Nay^werereihtroduced. Military titles of Major General and Coionei General of Coast Defense were also introduced. The dirk for all bfficers other than commissars was reintroduced in 1940 and at the same time full dress uniforms similar to those of preRevolu-tionary days were authorized for Soviet flag officers.
In 1942, an old naval custom was resurrected by restoring , to the Navy the honor of naming "Ships of the Guards"; "Guards Regiments11 were recreated in the Army. Perhaps one of the most coveted marks of honor is the Guards badge, which is worn by all officers and men who belong to a Guards ship or regiment. This badge is in the form of a small silver clasp, in which is threaded the black and yellow ribbon of the former Imperial Order of St. George. The wearing of these Imperial colors for valor is, no doubt, especially appreciated, since in generations gone by, black and yellow ribbons were to be seen on the sword hilts of officers who have been decorated for valor in the
field.
On the whole, officer and enlisted personnel are fairly smartly turned out. In the early part of 1943, Army and Navy officers were authorized to wear, as insignia of their rank, shoulder marks strikingly similar to those worn under the Tsarist regime. Great fanfare was made by the press over the revival of epaulets and the improvement in discipline expected through this change. In this connection, the omission of the N.K.V.D. troops in the restoration of epaulets is perhaps significant of a desire to minimize their importance in the eyes of the Soviet public and of other nations. At the time, "Red Star", official Army newspaper sounded the aew note in military discipline: "The introduction of epauletes must help to improve discipline in the army. Neatness and cleanliness in clothing, discipline and politeness must become the everyday qualities of a Red Army man. Everything in the Red Army man must show the culture of the Red Army, the strength of their traditions. After the changeover to epauletes a man in military service is not allowed to appear in public places, theaters, movies, etc., in a wrinkled and dirty uniform, in felt boots, or unshaven. Excluding railway stations, army men are not allowed to carry anything but a small neatly wrapped package in the left hand. They are not allowed to appear in uniform in markets or bazaars, forbidden to stand on the steps of a tramcar or bus. In cars of city transport, a Red Army man is not allowed to sit down in the presence of a senior. Not only in the rear areas, but also at the front, the wearing of shoulder marks must improve the looks,? and the behavior of men in the army. Every man at the front must understand that his duty is to achieve, as much as possible, a clean and decent appearance even under war conditions."
On August 10, 1943, the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the U.S.S.R. issued an edict reestablishing an officers1 corps in the Russian Navy; at the same time, ratings were divided into two classes— enlisted men and petty officers. The same thing had been done for the Red Army less than a month before, so its coming was not entirely unexpected. Naval officers were divided into three classes: junior officers (junior lieutenant through captain lieutenant), senior officers (captains 3rd, 2nd, and 1st ranks), and high officers (Rear Admiral, Vice Admiral, Admiral, and Admiral of the Fleet). Of special interest in this decree is the fact that a class of flag officers, equal to that of general officers, was not established, although it would have been comparatively easy to have done so. Prior to the Russian Revolution, the social position of generals was always regarded higher than that of Admirals, and it appears as if this distinction has been continued under the Soviet regime.
Soviet Admirals are allowed a young officer on their-staffs, known as "the Adjutant", who combines the duty of secretary and Flag Lieutenant. At the present time, these personal adjutants are not distinguishable as being part of the personal staff of Admirals, since they do not wear anything resembling aiguillettes, but, no doubt, the white corded aiguillette of Tsarist days will be restored to them before the war ends.
On August 11, 1943, the day following the establishment of the Naval Officers Corps, an article appeared in "Red Fleet" official organ "of the Soviet Navy stating in part ",...... ..This act has a profound meaning and significance. The designation officer raises still higher the authority and dignity of our military leaders. It is a proof of their military maturity and ability. It emphasizes their membership in their glorious and honorable class of military professionals. ..."
Pre-Revolutionary concepts of discipline have gradually been re-established in the Soviet Navy. Rank and prerogative of rank are jealously upheld. At the Baku Naval Academy, for instance, discipline in all ranks and ratings was observed to be considerably less free and informal than in the U. S. Navy. There was no fraternization or social contact between officers and men, A general snap, dash, and accuijaey were noticed, rarely found in Soviet civilian officials and in the| general run of the Soviet population. All persons encountered sought free criticism of their methods and were eager for comparison of their system with the American.
Although rank is perhaps excessively worshipped in the Soviet
system, cases often occur in which an officer senior in rank may have
as his commanding officer one who is junior to him - a paradox ex-;
plained by the fact that innumerable officers were rushed through Naval
School and commissioned directly with the rank of G ommander and Lieutenant Commander, although poorly qualified to command a vessel. At
the same time, ex-enlisted men and Merchant Marine officers were given
berths as commanding officers of ships because of their superior experience but compelled to remain in a junior rank under the regulations
requiring three years' service in each rank. Others of high rank whose
experience has not fitted them for command are former political commissars.
Very few officers seem to have been promoted from the lower
deck. It is estimated that the proportion of officers who have risen
from the enlisted personnel is not more than five percent.
The high standards of appearance officially ordered are not always adhered to. Aboard a Soviet submarine in November, 1942, the officers and men were not neat in their persons or in their dress, the former often appearing at mess unshaven and with dirty hands. The messman wore a very dirty white jacket, although some discipline was indicated by his demeanor and by the manner in which seamen asked permission to pass officers when in close quarters. Uniforms were of poor quality and ill-fitting. The generally untidy condition of the vessel indicated either an unwillingness to order work done or a reluctance to detail men to do anything in addition to serving the vessel.
The commanding officer of one submarine took great pride in the smart appearance of his ship and crew, especially when they were about to reach port, but by way of contrast took no steps to exterminate the rats which infested his ship. Engines and all working parts, however, were kept spotlessly clean and in perfect condition.
Naval personnel on duty in the U. S. practiced extended drills, to briskly shouted commands. At meals, an officer junior in rank asked permission from the senior officer present before leaving the table* The old Tsarist custom of enlisted men shouting out greetings in unison,while in formation,persisted. Although a junior officer might address a senior officer as "Tovarish Gapitan" (Comrade Captain) he stood at faultless attention, and, when dismissed, saluted with a smart about-face, and marched out. The same behavior held between an enlisted man and officer except that officers are evidently not addressed by enlisted personnel as "Comrade Lieutenant?
Medical officers aboard ship are charged with responsibility for the menu and are expected to satisfy themselves that all food is of good quality, as well as to allocate food properly. The latter duty is not always handled with competence, as preferred foods are sometimes quickly exhausted and a meager, monotonous diet then extended for long periods. A low opinion of Soviet naval medical service has been heard expressed by other officers
D. Pay and Allowances
Officers in the Soviet Navy are paid according to the position which they occupy and not according to rank. Every commanding officer of a submarine, whatever his rank, receives 2,350 roubles a month(purchasing power about $188). The divisional mechanic or flotilla engineer gets the same pay. The assistant commanding officer and the chief mechanic receive 1,900 roubles each month, the navigator 1,600 roubles, and the junior mechanic 1,200 roubles.
The commanding officer of.the heavy cruiser Voroshilcav receives 2,000 roubles a month. A man during his first year of compulsory military service receives only 57 roubles a month (purchasing power of about $4.56) and 250 roubles a month on completion of five year term. The free supply of clothing and cigarettes is quite adequate. No marriage allowance is paid, but upon a rating's death, a pension is paid to all children under 18 years of age and to their mother. This pension ceases as soon as the children reach an age at which they can earn their own living.
As is to be expected, all branches of the Soviet af|aed forces enjoy more liberal rations than any other section of the population, but still greatly inferior to those allowed our own services. Every attempt, however, is made to avoid envious comparison on the part of Soviet personnel.
E. Strength
The numerical strength of the Soviet Navy at the present time is not known; however, at the time of the outbreak of the Russo-German War in June, 1941, it was estimated at 8,000 officers and 67,000 men and 45,000 - 50,000 trained reserves.
F. Procurement
During peacetime, all male citizens of the U.S.S.R., at the age of 19, are subject to compulsory military service in the armed forces; a portion of these are allocated to the Navy. Voluntary enlistment is also possible. A volunteer may be accepted at the age of 16; however, a special authorization for waiver of age is required. The term of compulsory service in the line and in naval engineering £s five years, in coast defense, four years, and in naval aviation, three years; this applies whether the rating is a volunteer or draftee. Health, training, and preference of draftees are considered in selection and placement into the various armed services. The healthiest go into the Navy and into the Air Force. Men with many dependents are usually discouraged from these services. An enlisted man may advance from one rating to another, similar to that in the U. S. Navy; promotions are granted on the basis of study and experience. Enlisted men, who have not had the basic ten years of school, are encouraged to take special wnight courses11, which, when completed, are equivalent to a "ten year school" education.
In order to become a commissioned officer, it is necessary for either a civilian or enlisted man to graduate from a naval school; the course for officers of the line is four years, for naval engineering, five years.
An enlisted man has certain advantages over a civilian when
entering a naval school; he may enter up to 27 years of age, whereas
the age limit for civilians is 20. While at school, he receives his
regular navy pay, which is considerably higher than that of a mid
shipman.
G. Training
I. In General.
The chief difference between the U. S. Naval Academy and the Soviet Naval School at Baku is ,that while the U. S. Naval Academy turns out officers well-grounded in all the aspects of naval science and ready to receive, during the next two years, the practical experience necessary to make them useful officers, the Soviet Naval School at Baku produces deck officers who will immediately be able to carry their own weight in one of the small ships, of which the U.S.S.R. Navy is largely composed. In order to^o this, they avoid much of the mass of general information and understanding of the many skills involved in maintaining a warship, which midshipmen of the U. S. Naval Academy receive. Great emphasis is placed on practical experience. Rear Admiral Ramishvili, Director of Naval Education, substantiated this fact when he stated in an article in "Red Fleet", organ of the Soviet Navy, that "The aim of the ftaval schools is to organize practical study in order that the Fleet can receive well-trained officers, 1 ready for action, who not only know and understand the theory, but can also use their knowledge in practise".
Although there are a large number of naval schools in the U.S.S.R., it is believed that the one at Baku is the only one which produces naval officers in the sense that the U. S- Naval Academy does. This institution is called Naval School, in that Academy,
in the U.S.S.R., denotes an institution of higher learning, such as the U. S. Naval War College or the Army Staff College.
'Little information is available on the present-day activities of other naval schools. Post-graduate schools, to which officers are sent two years after graduation from the Naval School, give special courses in engineering, ordnance, torpedoes, aerology, radio, etc. There is also a Staff Academy for the training of higher officers in strategy and tactics• In addition, Naval High Schools exist at least in Baku and Moscow, and perhaps in other cities, which are definitely official in character. Student a, who intend to go into the Navy, ordinarily choose high schools which include preliminary naval subjects in their curriculum.
Prior to the outbreak of the Russp-German War in June, 1941, it was believed that the following Naval Schools existed:
(1) Four Naval Schools open to all citizens between the
ages of 17 to 22; the School for the Baltic Fleet (probably the chief
one) was located at Leningrad, for the Black Sea Fleet at Sevastopol,
for the Pacific Fleet at Vladivostok, and for the Caspian Sea Fleet
at Baku.
(2) The Naval Academy (similar to the U. S. Naval War College) at Leningrad, was open to naval officers up to 35 years of age
and command, aviation command, hydrography, and engineering were
taught,
(3) The Supreme Naval Hydrographic School in Leningrad, for
all citizens between the ages of 17 and 22; course four years.
(4) The Naval School of Coast Defense in Sevastopol, for all
citizens between the ages of 17 and 22; course three years; number of
students - 600.
(5) The Naval School of Communications in Leningrad, for
all citizens between the ages of 17 and 22; course three years; number
of students - 600.
(6) The Supreme Naval Engineering School in Leningrad, for
all citizens between the ages of 17 and 22; course five years; number
of students - 600.
(7) The Supreme Naval Construction-Engineering School in
Leningrad, for all citizens between the ages of 17 and 22, course five
years.
(8) The Naval Faculty of the 1st Leningrad Medical Institute, for all citizens between the ages of 17 and 22; course five yrs.
(9) The Naval Medical School of the Commissariat of the
Navy in Kronstadt, for all citizens between the ages of i7 and 22;
course two years.
(10) The Naval Economic School of the Commissariat of the
Navy in Peterhof (near Leningrad), for all citizens between the ages
of 17 and 22; course two years.
(11) The Naval Air School in Nikolaev, for all citizens between the ages of 17 and 22; course two years; number of students -
200. Graduates get title of Voyentechnic of 2nd rank.
(12) The Naval Air School (Stalin) in Eisk, for all citizens between the ages of 17 and 22; course two years; number of students - 200, Graduates get title of Voyentechnic of 2nd rank.
(13) The Naval Technical Air School in Perm, for all citizens between the ages of 17 and 22; course two years; number of students - 200. Graduates get title of Voyentechnic of 2nd rank.
(14) The Training Flotilla for Submarine Sailing, either in
Leningrad or Kronstadt, is more likely an independent school but possibly is attached to the Supreme Naval School.
(15) The Navy Faculty of the Military Political Academy in
Moscow, for naval officers up to 35 years of age.
(16) The Naval Political School in Leningrad, for Party members only; entrance age from 18 to 25; course two years.
(17) The 1st (Baltic) Naval Political School, for naval personnel; course one year.
(18) The 2nd (Pacific) Naval Political School, for naval personnel; course one year.
(19) The 3rd (Black Sea) Naval Political School, for naval
personnel; course one year
(20) In addition to the afore mentioned schools, during the
fall of 1940, 7 new special secondary schools were opened for the primary training of young naval men. They closely resembled our High
School Naval ROTC units and, during the summer, students spent some
time in camps or aboard training ships. These schools were located
at Moscow, Leningrad, Vladivostok, Gorki, Kiev, Odessa, and Baku.
There are two types of schools in USSR—the "7-year school" and the "10-year school". The first is comparable to our primary school. The n10-year school" is a combination of our primary grammar, and high schools. Its graduates are eligible for entrance into institutions of higher learning, i.e., universities, the Naval School, etc.
To become a Naval officer, it is necessary to have a "10-year" education before entering a Naval school. For army officer
candidates, however, the requirements are not so high—only a "7-year" education is required.
Men eligible for Naval officer training must take a competitive examination. Candidates for entrance to the Naval School are selected from those passing the competitive examination with the highest grades. Enlisted men in the Navy are subject to the same competitive / examination in selection for officer-training as are civilians.
On graduating, the cadet is commissioned either as I&isign (Junior Lieutenant, USSR Navy) or Lieut., Junior grade (Lieutenant, USSR Navy), depending upon his class standing. Upon graduation as a line officer, the officer selects the type of duty that pleases him most, i.e., gunnery, navigation, communications, mining, etc., and he is ordered to duty with the fleet. After a minimum of five years service as an officer, he is eligible for post graduate courses to further specialize in some field of particular interest to him.
II. Baku Naval School.
The school is located about 7 miles north of Baku, in an isolated position on the sloping shores of the Caspian Sea. It was transferred here from Leningrad 2 years ago, where it had been functioning in permanent installation in one form or another, since the time of Peter the Great. All buildings at the new site are of permanent gray masonry construction. There are four barracks, U stories high, housing 600 students, plus administrative offices. Classrooms are housed in two buildings similar to those housing the barracks. The messhall is housed in a one-story buildingj it seats all students simultaneously. It also contains the kitchens, scullery, and an officers1 mess for those of the officer personnel who do not dine in their own apartments. Officers' quarters are in two buildings similar to those housing the barracks, containing apartments for families and for officers without families. AL1 officers live on the reservation because of the distance to Baku and the lack of transportation. The entire installation is apparently of recent construction and is said to have been built for some purpose other than the present one. Efforts are being made to beautify the area by planting trees and flower beds, but the general aspect is rather stark and bare. The majority of the area about the buildings is covered with asphalt paving, including a large central square between the classroom and barrack buildings, which is used for mass exercises and drill. The dimensions of the reservation are estimated at 700 x 1,000 yards.
The surrounding country is dry and barren unless it is well irrigated. In nearly all respects, it is a perfect picture of south Texas, except that it is more hilly. Violent and sudden winds are common, although they are predictable 24 or more hours in advance. "Baku", in local dialect means "windy city". Winters are cool to cold, windy and very dusty. Summers are dry and exceedingly hot, necessitating a revised schedule to ease the burden of the hot afternoons. Temperatures are as follows: Jan. 38°, Feb. 39°, Mar. 43°, Apr. 50°, May 630, Jun. 71°, Jtfl- 77°, Aug. 78°, Sept. 70°, Oct. 62°, Nov. 51°, Dec. 44°• The above summer temperatures are deceptive in that the nights are quite cool, lowering the daily average considerably. Maximum summer day temperatures in the shade frequently reach 100°.
Classrooms are exceptionally clean, well-illuminated by natural light through large windows on one side. There is a separate desk and chair for each student and large blackboard space. Laboratories are very well-equipped, radio laboratories having a large variety of modern receivers and small transmitters. Torpedoes are exceptionally well demonstrated. There are many sections of parts and mechanisms plus individual parts and assemblies working under compressed air for demonstration. Ordnance material covers various types of projectiles and propellants. There are several light (about 2 inch) dual purpose guns and one 5 inch gun. Guns are mounted inside with no apparent facilities for gun or loading drills but merely for exhibition. The mine room has several types -of moored mines, but little of the detail seen in the torpedo room. The optics room covers all types from spotting glasses to 5 meter range finders. Large windows permit ranging practice on a distant island. All gear appears to be first class and in excellent working condition. It is said that all is Soviet made. Engineering material is limited, with the piece de resistance being a model high pressure boiler sliced through the middle, with gear to swing two halves apart to show the interior. There is no evidence of any instruction in practical work in machine, wood, foundry, boiler or sheet metal shops.
Practical navigation receives special attention, judging from the facilities provided. One room contains about 30 magnetic compasses mounted in conventional pinnacles and on a rotating platform, for exercises in compass compensation. In another room, students are seated at long tables. Between each two students are mounted a gyro repeater, engine room counter and clock. The instructor changes the course and speed from a control station, simulating tracking or dead reckoning exercises at high speed in close waters. Each student plots the track on his chart, taking into account the currents and winds. Fifty hours of this and related instruction is given during the course. The seamanship "P" work room contains rigged models of small boats, ground tackle, deck gear, diving apparatus, and samples of knots and splices. Buoys and lights are demonstrated in a room full of all types, full size when possible, otherwise models, complete with illuminating gear and all operating as they would in use. The gyro compass laboratory contains two Soviet-made gyros complete and a large number of component parts and assemblies broken down for demonstration. The electrical "P" work room is very similar to that in the U. S. Naval Academy, with lines of motors, lamp banks, boards for plug-in leads and meters. There are displays in showcases and on the corridor walls throughout the buildings, showing the evolution of warships, models and section of foreign and Soviet ships, plans of ships (including USS WASHINGTON), maps of the various war fronts throughout the world, with pins showing positions of the troops, signal flags, slogans, and famous sayings of contemporary and past Russian naval commanders, portraits of famous Russian admirals, and innumerable bad likenesses of Admiral Kuz-netsov, always in full dress uniform.
Small boats are used for rowing, sailing practice, and sailing drills in which the boats maneuver, tack, turn, and come alongside by use of sails alone and with the rudder unshipped. Two 2-masted 60-foot schooners are manned for periods of several weeks at a time by junior classmen for practical work in deck seamanship and in the use of the sextant. Power boats are manned by regular Red Navy personnel, with occasional midshipmen acting as bowhooks.
Students are selected from the country at large and from the ranks of the navy, candidates usually having had an education comparable to that of a graduate of a U. S. high school. The Superintendent informs the military chiefs of the various districts of USSR how many candidates will be acceptable from that region so that representation may be maintained equally from the country at large. Candidates are sent to Baku/where they are examined mentally and physically. If they fail mentally and are acceptable physically, they are sent to the ranks of the fleet to work out their term of compulsory military servicej they may choose the army instead, however, which is sometimes more desired in that the term of army compulsory service is only two years, while in the navy it is five. Candidates are received from ranks of the navy on the same basis as above, but indications are that the number is very small. The age limit for civilians is 16 - 20 and from the ranks, up to 27. Failures during the course of instruction are sent to the fleet as seamen to finish their terms of compulsory military service. An average of 30% fail during the four year course, of which the great majority fail the first year and probably not more than two or three the final year.
The Director of Naval Education, under whom this school takes jurisdiction, is Rear Admiral Ramishvili, a Georgian born in Astrakhan. He is very alert, friendly, short, round and fat, and somewhat conceited^ he speaks passable French. The Superintendent of the Naval School at Baku is Captain First Rank Suhiashvili, a Georgian by birth and in appearance; he is a heavy driaiker. Until recently, he commanded a brigade of navaXJsgiidingforce troops in the Black Sea area. He is super-tough with a shaven head, hook
nose powerful physique, and much personal charm. He is about 41 years old. Assistant to tlie Superintendent is Engineer Captain First Rank Relobrov, a professorial locking man with pince nez, born and raised in Tallinn, Estonia, and with all the inborn graciousness and hospitality of that mellow old city. His chief interest seems to be! hydrography. He speaks some English. Rear Admiral Dmitriev, a real gentleman of iihe old school, ex Imperial Navy, is stationed here, he has travelled over most of the world. He has taught navigation to practically every present day Soviet naval officer, and is 67 years old. He fought in the Russo-Jap War.
Principal subjects in order of their importance are:
navigation, seamanship, ordnance, communications, and engineering.
Classroom work consists largely of lectures and explanation by
instructors (all naval officers). The^e is very little questioning of or recitation by students, who iusily take copious notes
during these periods. It is believed that blackboards are little
used by students and are mostly for demonstration and explanation
by instructors. Examinations are held semiannually and wholly determine the marks and standing, of the students. Those students not
quite passing may be given a re-exam, turned back into the next
lower class, or sent to ranks of the navy. Various subjects have
different weights in computing the final multiple. Examinations
are not especially long. Honor students, consisting of about ten
percent of the class, have their photographs posted on the bulletin board in the recreation room^untili they are displaced in class
standing by others. After graduation and two years in the fleet,
the top students at the Naval School are generally those selected
for post-graduate and specialist training, if their military capabilities have turned out ti> be commenstirate with their scholastic
ability. Practical work, in practically all subjects carries much
weight.
The schedule in summer is:
0400 Reveille; 0445 Morning tea; 0530-0900 Four 40-minute recitation periods in classroom;
1000 Breakfast; 1030-1300 Three periods, usually practical work; 1300-1500 Independent study in the library or such classroom as lihe individual desires. The instructor is present in each such available classroom to advise and
answer questions of individuals; 1500 Dinner; 1530-1600 Enforced rst in banks; 1600-2000 Recreation on the ground or study, as the individual desires; occasionally there are seamanship drills; 2000 -2200 Recreation on grounds or study, as the individual desires; 2200 Lights out.
Liberty is granted on Sunday for the junior class and on Saturday
afternoon and Sunday for other classes. Leave in time of peace was
one month annually", but since the outbreak of the war, it has been
completely cut out.
Practice cruises are made on board combatant ships of all types. While on board ship, students of the first three classes exercise no authority over Red Navy men. Those of the senior class have nominal authority in certain cases, such as in command of ship's boats, but generally exercise authority only among groups of students on board. The usual period of sea duty (cruise) is: 1st year U months, 2nd year U months, 3rd year 5 months, 4-th year 6 months.
Interior discipline is directly in the hands of naval officer in command of each company of students. Under him,are the usual company, platoon and squad petty officers chosen from the ranks of that course, and who assist him in military functions and in maintaining discipline. Students of different classes are not mixed at drill or in the messhall. Petty officers of each clase are furnished from that class and exercise authority only over members of that class, except when on watch, when they may exercise such authority over any student as the fulfilment of their duty demands. Student petty officers are usually chosen for a period of a full year, on the basis of military and scholastic qualities. They may be removed for disciplinary reasons or for poor performance of duty, but this occasion rarely occurs• Punishments are based on the fact that the act was committed and not the degree of the act itself. The same punishment is given for being one minute over liberty as for one hour or one day. Minor offenses are punished by lowering the military aptitude mark; more serious offenses are punished by confinement.
Barracks house units of each class in large bunk rooms and accommodate about 100 students. Iron beds are very close together. Hanging space and small lockers are in separate rooms. Arms, including rifles, light and heavy machine guns, tommy guns, all with ready ammunition, are kept in ready racks in the bunk rooms. Each student has his own heavy, dull edged sword of plain appearance. Toilet and bath facilities appear inadequate and have characteristic gamey odor of such places in the USSR, but they are superficially, at any rate, quite clean. Messing takes place 'in a large bright screened hall accommodating the entire student body. Tables seating about twenty are presided over by student petty officers of the same class as those seated at the table. There are white table cloths and backless benches. Students march in, stand at attention alongside the tables, and seat themselves on command of the duty officer. The galley is large, airy and well-screened with much the same appearance on small scale as the U. S. Naval Academy galley. The menu is based on weights of food per day in each category, as is the practice in the Red Navy. Calory count per diem is added up and appears to be the item of chief interest on the weekly menu; it averages close to 2,980 calories total per day; Alcoholic drinks are forbidden to students at any time, and drunkenness is punished by confinement offrom three to ten days, with repeated offenses beinging transfer to the ranks of the Red Navy.
Uniforms are those of the Red Navy, with the exception of the cap ribbon and shoulder marks. Ex-sailors who have served at the front wear a cap instead of a flat hat. The usual summer uniform is black trousers, black shoes, white jumper, and white flat hat. Shoulder straps are black with a two inch fouled anchor in gilt. Petty officers have the usual Red Navy petty officer marks, on the shoulder straps, in addition to the above mentioned anchor. The hair of students is close cropped. They have no beards or moustaches.
The appearance of the students, in general, is good. They are on the average smaller in stature than American midshipmen, as is the average Russian considerably smaller than the average American.
Physically they appear well enough fed and show no exterior evidence of any deficiencies in diet,-such as is general among the civilian population of the country as a whole. Most of them are beautifully sunburned from seamanship drill with no jumpers on. Their military carriage and marching while enroute to the messhall is not up to the standard of the U. S. Naval Academy.
There are indications that individual discipline is of the Prussian type and considerably more strict and machinelike than American. This has been quite evident in observing relations between Red Navy officers, where in spite of "Comrade Captain" and so forth, the distinctions between ranks and the subservience of the junior is infinitely greater than in either the U.S., French, Italian, or British Navies.
For recreation, each company has a wplay room" something on the order of the Smoke Hall at the U.S. Naval Academy, with a piano, magazines and newspapers, and games. The walls are covered by slogans, wall newspapers (occasionally in English or French for the increase of interest in foreign languages), photographs, pictures of Stalin and Lenin, and a large portrait of Admiral Kuznetsov. The chief effort in the latter is usually concentrated on the grand effect of the full dress uniform. Very few of them actually resemble the Commissar of the Navy. There are no facilities for sports other than the cutters, which may* be used for sailing in spare time. Motion picture exhibitions and plays are given weekly.
III. Training of Ratings, in General.
In the Red Navy, as in the British, greater dependence is placed in "enlisted" men in the supervision and maintenance of special equipment. Red Navy petty officers are sent to shore schools for considerable periods to master below-decks specialties - in the case of radio, as long as two years. The officers,in general,apparently function more exclusively in the capacity of administrators than in the U. S.. Navy and bend most of their efforts to keeping the ship off the rocks, while the petty officers keep the engines and radio functioning.
IV, The Polyarnoe Anti-Submarine School.
This school was visited in May, 1942. Its instructional apparatus, which was under the command of Engineer Captain Aronov, was contained in four rooms on the ground floor of a large building as follows: room 1 was a large classroom in which a destroyer was installed. The installation had been well carried out in accordance with the drawings, the bridge hut, instrument cupboards and directing gear being clearly separated, so that classes under instruction could get a good idea of the general layout of the set. The dome was filled with water, and the set could be operated. Room 2 contained the mass procedure teacher. This installation was not, at that time, complete and the signal injector had not arrived; the apparatus was, however, in operation. Room 3 contained the anti-submarine attack teacher. This room was divided by a partition, and this apparatus was also in working order. Room 4 contained a trawler. This set was well mounted, together with a clear idea of the general layout, but work had not been completed by May, 1942.
Three classes of ratings and one of anti-submarine control officers were under training. The three ratings classes were seen under instruction and averaged about 12 men in each class. For the most part, the ratings seemed to be very young. It appeared that the best ratings of the first classes were, themselves, in charge of subsequent classes.
No officers were present at the attack teacher when it was visited, and the duty of the anti-submarine commanding officer was being performed by a rating.
In general, the installations were very well carried out, and instruction appeared to be well organized. Captain Aronov said that the ratings showed great interest in their training. He appeared to be a capable instructor and showed a good understanding of his sub ject.
It was understood that arrangements would shortly be made for Soviet ratings to gain sea experience in vessels of the First Minesweeping Flotilla, and that a Soviet submarine would be made available for training purposes.
The school was well organized, and appeared to be making good progress, although training was possibly handicapped by the lack of higher ratings for instructional purposes.
V. Fleet Training.
Little information is available on fleet training, but it does not appear to be extensive. During the latter part of 1941, there appeared to be little training going on in the Black Sea. All submarines were employed operationally, and did not exercise with surface craft, chiefly because anti-submarine measures were non-existent, nor did they practice attacks. A submarine commander stated at that time that it was not necessary to do any training then, since all submarines had completed their annual program before the war started. He did admit, however, that the question of attacks for commanding officers would require consideration. Newly built submarines, and those completing refits, got their training by going to easy and peaceful patrol positions.
H. Comparative Ranks
I. Naval Ranks in the Soviet Navy
RUSSIAN / TRANSLATION / U.S. EQUIVALENT
Admiral Flota / Admiral of the Fleet / Admiral of the Fleet
Admiral / Admiral / Admiral
Vitse Admiral / Vice Admiral / Vice Admiral
Kontr Admiral / Rear Admiral / Rear Admiral
Kapitan Pervovo Ranga / Captain of the First Rank / Senior Captain
Kapitan Vtorovo Ranga / Captain Second rank / Captain
Kapitan Tret'evo Ranga / Captain of the Third Rank / Commander
Kapitan-Leitenant / Captain Lieutenant / Lieutenant Commander
Starshi Leitenant / Senior Lieutenant / Lieutenant
Leitenant / Lieutenant / Lieutenant, Junior Grade
Mladshi Leitenant / Junior Lieutenant / Ensign
Michman / Warrant Officer / Warrant Officer
Kursant / Midshipman / Midshipman
Glavni Starshina / Chief Petty Officer / Chief Petty Officer
Starshina Pervoi Stat'i / Petty Officer First Class / Petty Officer First Class
Starshina Vtoroi Stat'i / Petty Officer Second Class / Petty Officer Second Class
Starshi Krasnoflotets / Senior Red Navy Man / Seaman First Class
Krasnoflotets / Red Navy Man / Seaman Second Class
II. Army Ranks in the Soviet Nary
RUSSIAN / TRANSLATION / U. S. EQUIVALENT
General Polkbvnik / Colonel General / Lieutenant General
General Leitenant / Lieutsnant General / Major General
General Maior / Major General / Brigadier General
Polkovnik / Colonel / Colonel
Podpolkovnik / Lieutenant Colonel / Lieutenant Colonel
Maior / Major / Major
Kapitan / Captaia / Captain
Starshi Leitenant / Senior Lieutenant / Senior 1st Lieutenant
Leitenant / Lieutenant / 1st Lieutenant
Mladshi Leitenant / Junior Lieutenant / 2nd Lieutenant
It is probable that non commissioned ranks and enlisted men carry the same titles in other branches of the Soviet Navy as they do in the line and naval engineering corps.
I. UNIFORM AND INSIGNIA
On February 15, 194-3, gold and. silver shoulder marks were relnstituted in the Russian Navy by edict of the Praesidium of the Supreme Council of the U.S.S.R., following a similar edict made for the Army a month earlier; it made insignia of rank conform with those worn prior to the Russian Revolution.
Stripes which had previously been worn by Soviet naval personnel and which were very similar to those worn by the U. S. Navy, were abolished, except that they continued to be worn on service dress blue uniforms of officers of the line and naval engineering in addition to the new shoulder marks. These stripes are identical to those worn in the U. S. Navy with the following exceptions:
(a) The stripes and stars are placed farther up the arm than
in the U. S. Navy.
(b) The narrow stripe for captain lieutenant (lieutenant commander) is placed between the second normal stripe and the star.
(c) The 5-pointed star is so placed that two of its points and
not one are pointed toward the stripes.
(d) Broad stripes, worn by captains first rank (senior captains)
and flag officers, are narrower than those worn by U. S. officers,
being only 1.26 inches in width.
Shoulder marks as adopted by the Soviet Navy are either gold or silver in color, to denote the service to which the wearer belongs. A system of stars and stripes on them denotes rank. The color of the stripes and of the piping further denotes the branch of service.
Services of the Soviet Navy are divided into major and minor branches; the shoulder marks worn by officers belonging to a major, branch are wider than to those belonging to a minor branch. Major branches consist of the line, naval engineering, coast defense, coast defense engineering, aviation, aviation engineering, supply, and medical corps officers with special military medical education. Minor branches are the medical corps (for officers without special military medical education) veterinarians, and the legal and administrative corps.
Gold embroidered shoulder marks are used by officers of the line, naval engineering, coast defense, and naval aviation; those of all other branches of the service wear silver. Piping and stripes are black for officers of the line, naval engineering, and coast defense engineering —they are red for members of the coast defense, veterinarians, legal, and administrative officers—they are light blue for naval aviation and aviation engineering—they are crimson for officers belonging to the supply corps. Shoulder marks of medical officers have green stripes and red piping. Shoulder marks are 5.5 to 6.3 inches long and 2.56 inches wide for major branches, and 1.77 inches wide for minor branches.
The gold or silver braid for flag officers is of a special herringbone design; there are no stripes on these shoulder marks. Stars are superimposed in a straight line on the shoulder marks to denote rank (1 star for a Rear Admiral, 2 stars for a Vice Admiral, 3 stars for an Admiral, U stars for an Admiral of the Fleet). Stars for flag officers
of the line and of the naval engineering corps, are gold with tufts of black rays protruding from underneath; a red pentagon, upon which is inscribed a black anchor, is superimposed on the center of the star. Stars on the shoulder boards of all'other flag officers are plain silver or gold. The metal buttons on the shoulder boards correspond in color to that of the braid. For flag officers belonging to one of the major branches, they bear a State seal (hammer and sickle) superimposed on two crossed anchors. Those for flag officers belonging to minor branches are the same as those for all other officers of the Soviet Navy—they bear only an anchor.
Shoulder marks of senior officers (captains of tlie first, second, and third ranks) have two stripes; those of junior officers (captain lieutenant to and including junior lieutenant) have one stripe. These stripes run lengthwise. The stars for senior officers are 4/5 of an inch between their points, while those for junior officers are only 1/2 of an inch. The metal buttons correspond in color to that of the braid, and bear an anchor.
Anchors, stripes, and buttons on the shoulder boards of warrant officers, midshipmen, and ratings are gold for the line and naval engineering corps, and silver for all other branches. They are df two sizess the larger size, which is the same as those for commissioned officers, is worn on great-coats, peacoats, and single-breasted naval jackets; the smaller ones, which are 2 inches long and 2.36 inches wide, are worn on flannel shirts and jumpers. Shoulder marks of warrant officers, of midshipmen, and of ratings are black in color. Warrant officers have a broad stripe running lengthwise. Midshipmen have a metal anchor on their shoulder boards. If a midshipman has served in the Soviet Navy prior to his being accepted by the academy, his shoulder marks bear his rating as well as the anchor. Chief petty officers have one wide gold stripe running widthwise, petty officers first class have three narrow stripes running widthwise^ petty officers second class have two stripes, seamen filrst class have one stripe, and seamen second class have no stripes. In addition to the stripe, yellow letters indicating the fleet to which the wearer's ship or unit belongs are stencilled on the larger shoulder, marks as well;- they are stencilled on the small shoulder boards of seamen second class only.
FLAG OFFICERS:
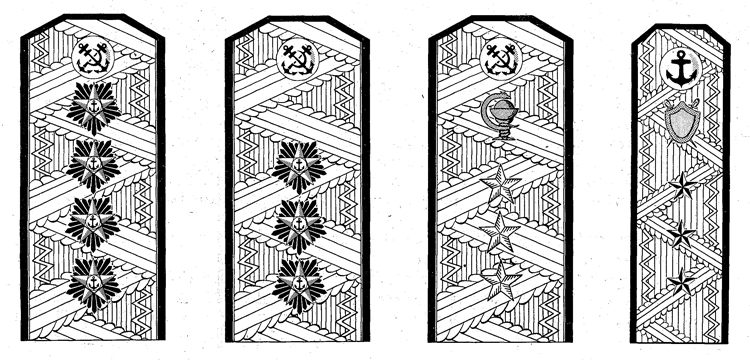
ADMIRAL OF THE FLEET (LINE)
ADMIRAL (LINE)
COL.GENERAL MEDICAL CORPS (WITH SPECIAL MILITARY MEDICAL EDUCATION)
COL.GENERAL LEGAL CORPS
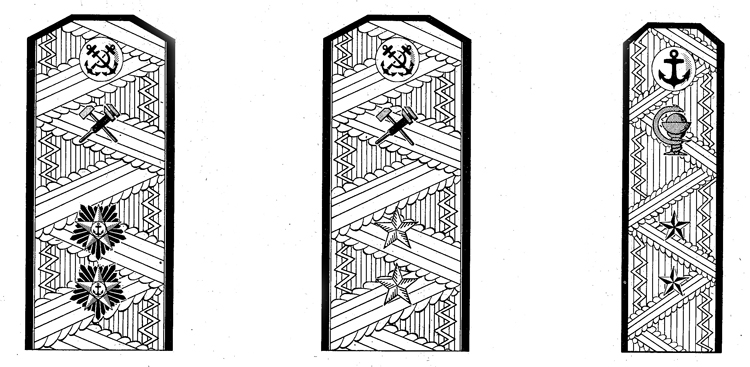
ENGINEER VICE-ADMIRAL
ENGINEER LT. GENERAL
LT. GENERAL
VETERINARY
CORPS .
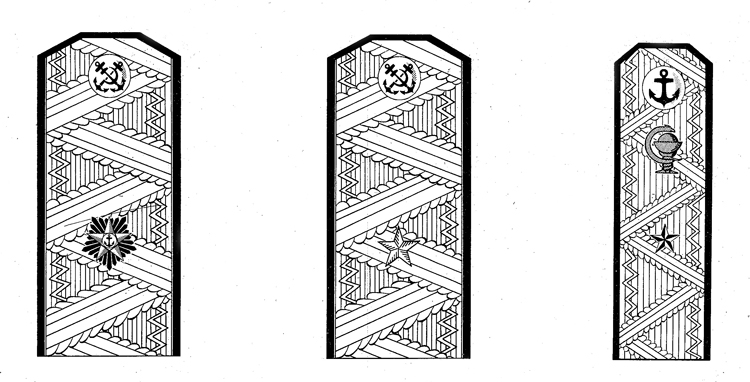
REAR ADMIRAL , (LINE)
MAJOR GENERAL COAST DEFENSE
MAJOR GENERAL
MEDICAL CORPS
(WITHOUT SPECIAL
MILITARY MEDICAL
EDUCATION)
SENIOR AND JUNIOR OFFICERS:
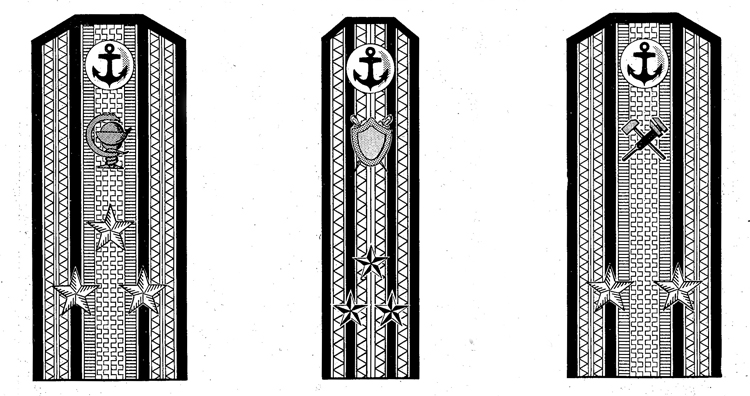
COLONEL
MEDICAL CORPS
(WITH SPECIAL
MILITARY MEDICAL
EDUCATION)
COLONEL LEGAL CORPS
ENGINEER CAPTAIN 2ND RANK
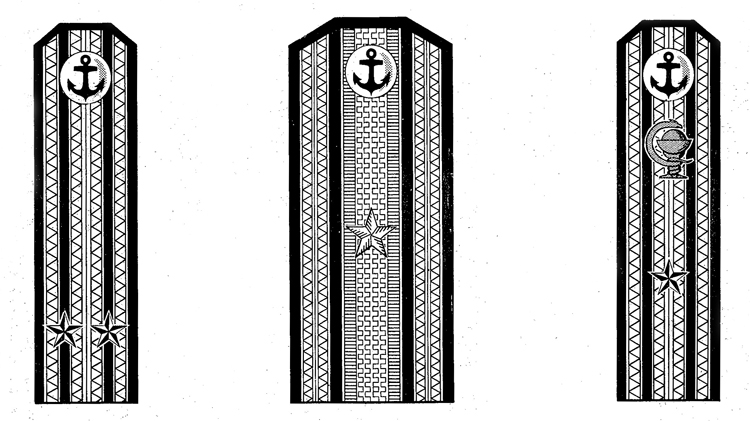
LT. COLONEL
ADMINISTRATION
CORPS
CAPTAIN
3RD RANK
(LINE)
MAJOR
MEDICAL CORPS
(WITHOUT SPECIAL
MILITARY MEDICAL
EDUCATION)
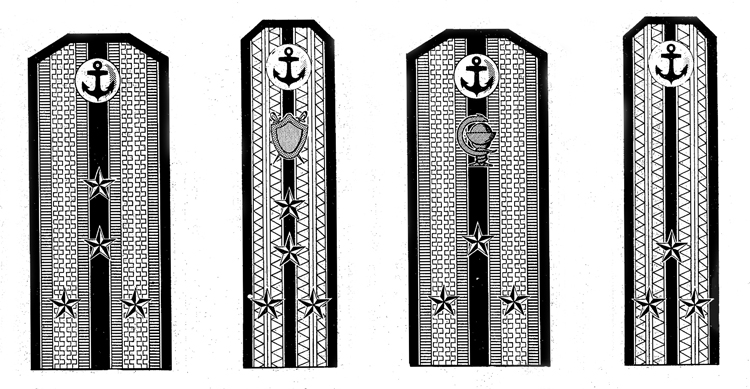
CAPTAIN
LIEUTENANT
(LINE)
CAPTAIN LEGAL CORPS
SENIOR LIEUT.
MEDICAL CORPS
(WITH SPECIAL
MILITARY MEDICAL
EDUCATION)
SENIOR LIEUT.
ADMINISTRATION
CORPS
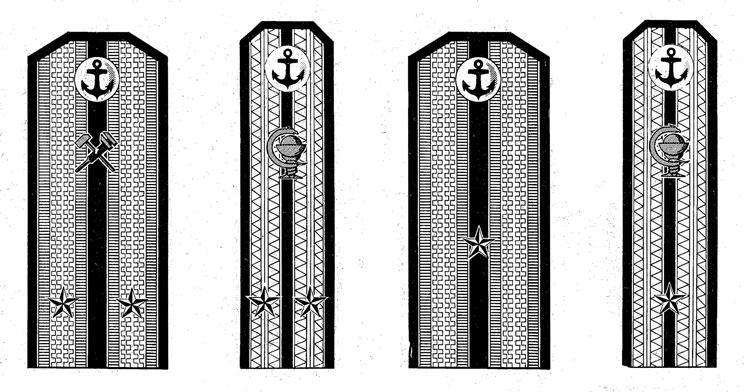
ENGINEER LIEUTENANT
LIEUTFNANT
VETERINARY
CORPS
JUNIOR
LIEUTENANT
SUPPLY CORPS
JUNIOR LIEUT. MEDICAL CORPS (WITHOUT SPECIAL MILITARY MEDICAL EDUCATION)
WARRANT OFFICERS, MIDSHIPMEN AND RATINGS
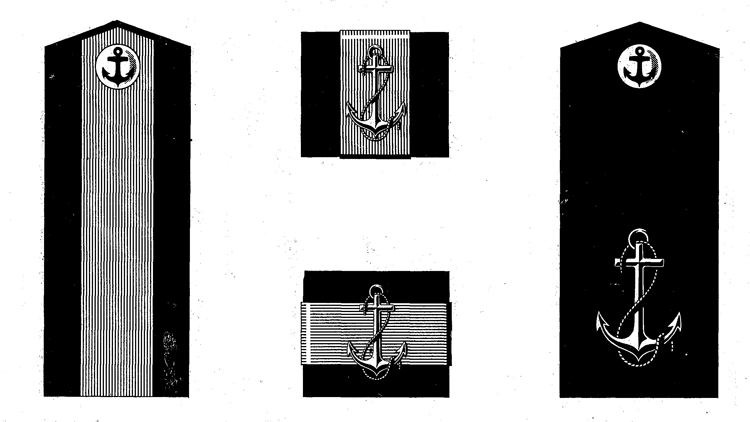
WARRANT OFFICER
MIDSHIPMAN
FORMER WARRANT OFFICER
MIDSHIPMAN FORMER
CHIEF PETTY OFFICER
MIDSHIPMAN
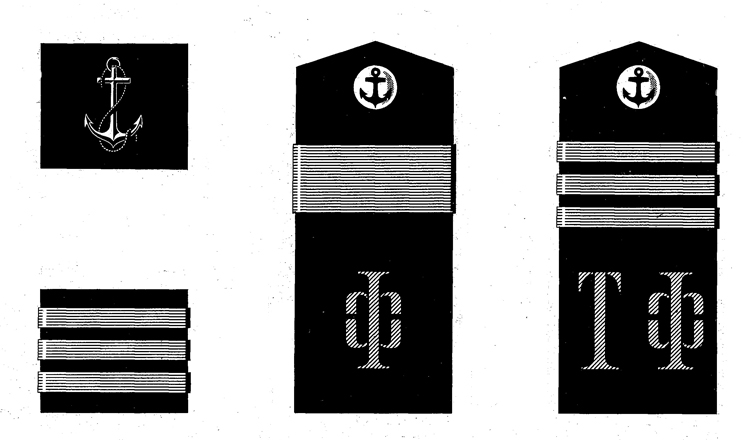
MIDSHIPMAN
PETTY OFFICER 1ST CLASS
CHIEF PETTY
OFFICER
(ATTACHED TO
NO SPECIFIC
FLEET)
PETTY OFFICER
1ST CLASS
(ATTACHED TO
FAR EASTERN
FLEET)
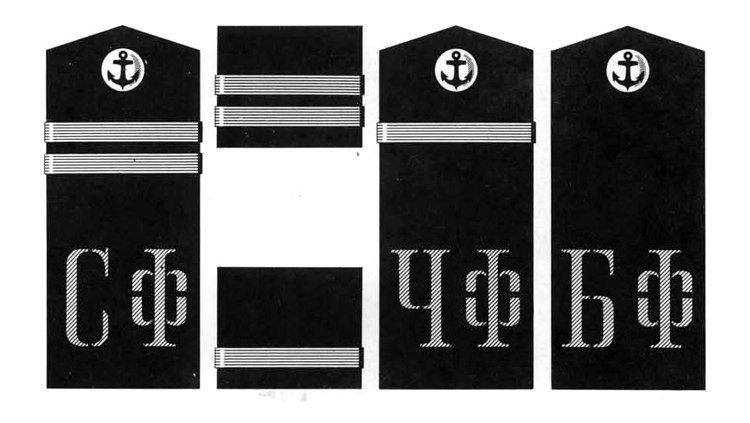

PETTY OFFICER
2ND CLASS (ATTACHED TO NORTHERN FLEET)
PETTY OFFICER
2ND CLASS
SEAMAN FIRST CLASS
SEAMAN FIRST CLASS (ATTACHED TO BLACK SEA)
SEAMAN 2ND CLASS (ATTACHED TO BALTIC FLEET)

REAR ADMIRAL DUNCAN, U.S.N., U. S. NAVAL ATTACHE, MOSCOW, DECORATING A PETTY OFFICER, FIRST CLASS, WITH THE DISTINGUISHED SERVICE MEDAL
J. High Ranking Naval Officers
I. The Commissariat.
(a) Admiral H. G. Kuznetsov was appointed People's Commissar of the Navy and Chief of Naval Operations on May Day, 1939, at the early age of 37. He is an exceptionally able and ruthless administrator, and enjoys the reputation of being a most efficient organizer; in March, 1939, he was made a full member of the Central Executive Committee of the Communist Party. He was born in 1902,. and started life as an errand boy. In 1917, he served as a volunteer in the North Dvina River Flotilla. He was graduated from the Naval Academy in 1926, and was appointed to the cruiser CHERVONNAYA UKRAINA (since sunk) in the Black Sea. He served for four years as executive officer, and two years as commanding officer of Black Sea cruisers. For 17 months, prior to his appointment as commissar, he was Comman-der-in-Chief of the Pacific Fleet, with the rank of Rear Admiral. He speaks excellent Franch, and it is quite obvioua that he does not come of peasant stock.
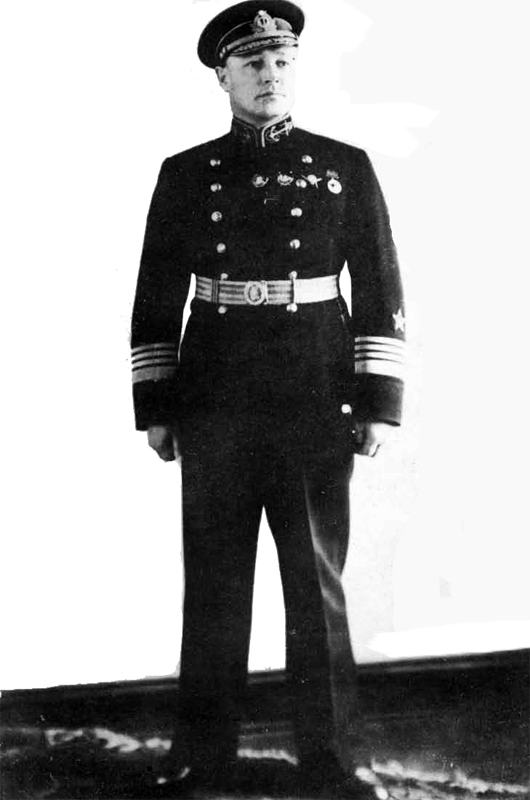

Admiral H. G. Kuznetsov, Peoples Commissar of the Navy
(b) Admiral L. M. Galler is People's Vice Commissar of the Navy. Be is the son of an engineer officer in the Imperial Navy. He waa commissioned in th« Imperial Navy in 1905, and by 1917 was a commander and executive officer of a Baltic Fleet Battleship. He joined the Bolsheviks during the revolution and helped seize the Kronstadt Naval Base. Nearly all of his active service has been spent in the Baltic Sea, where he commanded various ships and was Chief of Staff of the Fleet prior to 1935. He has also served as Chief of th» Naval Staff. At the tim« of the purge (1937) he was already a full admiral, and was practically the only flag officer who survived this purge. He is a good typ» Tsarist officer and very highly thought of in his own service.

Admiral L. It. Galler, Vice Commissar of the Navy.
(e) Admiral I. S. Isakov is the Chief of the Naval Staff. He was born in 1898, and graduated from the Imperial Naval Academy at St. Petersburg. He is a good type Tsarist officer, although only a young lieutenant in 1917. During the Civil War, he served in the Northern Fleet and Volga River and Caspian Sea flotillas. He has never been closely associated with the Communist Party. He has spent most of his active duty in the Baltic Sea; in 1937, he was Chief of Staff of the Baltic Fleet. Prior to that time, he taught at the Soviet Naval Military Academy. In 1939, he was elected a deputy of the Supreme Council of tha D.S.S.R., and during the same year, he headed an unofficial naval mission to the U.S. for the purpose of arranging for ship construction in this country. He was appointed to his present position in 1941. For the past year, ha has been absent from his post, presumably being on active duty with the fleet.

Admiral I. S. Isakov, Chief of the Naval Staff.
(d) Vice Admiral V. I. Levchenko is a People's Vice Commissar of the Navy; he is 46 years old.
(e) Rear Admiral S. P. Ignatier is
a People's Vice Commissar of the Navy; he is a former "politico".
(f) Rear Admiral N. K. Smlrnov is a People's Vice Commissar of the Navy; he is a former "politico".
(g) Lieutenant General S. F. Zhavoronkov is Chief of Naval Aviation.
(h) Lieutenant General S. I. Vorobyav is head of the Supply Department.
(i) Lieutenant General I. S. Mushnov is head of Armaments and Munitions.
II. Baltic Fleet
(a) Admiral V. F. Tributs, Commander-in-Chief since May, 1939, was born in 1900, and originally served in the Imperial Navy as a sick bay steward, and after that as a private in the Red Army. He entered the Naval Academy in 1923 and was commissioned in 1926. He graduated from the Naval War College in 1932. He has been Executive Officer of the second line battleship MARAT, and after that Chief of Staff of the Baltic Fleet. He is a member of the Central Auditing Committee of the Bolshevik Itrty. He was promoted to the rank of admiral in June, 1943.
III. Black Sea Fleet
(a) Vice Admiral V. A. Vladimirski was appointed Commander-in-Chief in June, 194-3; he is 40 years old. He appears to be very energetic and outspoken, an able officer and well liked by his officers and men. Prior to his appointment as Commander-in-Chief I he was in command of a destroyer flotilla in the Black Sea.
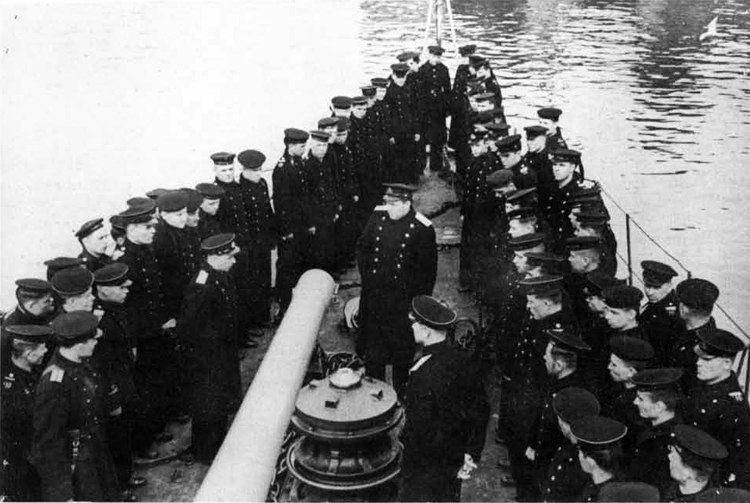

Vice Admiral Vladimirski, Commander-in-Chief of the Black Sea Fleet, inspecting the DD SOOBRAZATELNI.
(b) Vice Admiral N. E. Basisty is Commander, Cruisers,
Black Sea Fleet. He is rather older than Vice Admiral Vladimirski.
(c) Lieutenant-General Kumanin is Commander of Coast Defense of the Caucasus coast from Sukhum to Batura.
IV . Pacific Fleet
(a) Admiral I. S_. Yumashev. Commander-in-Chief, was born in 1895, the son of a railway employee. He served as a Petty Officer in the Imperial Navy. In 1918, he became a member of the Communist Party and in 1941, he was appointed a candidate member of the Central Executive Conmittee of the Bolshevik Party. He has commanded a cruiser squadron and has been Chief of Staff and Commander-in-Chief of the Black Sea Fleet. Although he possesses limited intelligence, he is extremely tough and a hard character. He was promoted to the rank of admiral in June, 1943.
(b) Rear.Admiral V. A. Alafuijov was appointed Chief of Staff in March, 194-3; be is about 45 years of age. Prior to this appointment, he was Assistant Chief of the Naval Staff at Moscow. He is considered to be keen, alert, and forceful, and one of the most capable of all Soviet Flag Officers.
V. Northern Fleet
(a) Vice. Admiral A. G. Golovko was appointed Commander-in-Chief In July, 1940 at the age of 32. He has a strong character, is keen, alert, aggressive, courteous, and willing to give assistance. He is the son of a veterinary surgeon. He has been in command of the Caspian Sea and Amur River Flotillas; during the Spanish Civil War he was Soviet Assistant Naval Attache at Madrid. He is a good administrator, but has had limited sea-going experience because of his youth.

Vice Admiral A. G. Golovko, Co Commander-in-Chief, Northern Fleet, with Rear Admiral Duncan, U.S.N., U.S. Naval Attache.
(b) Rear Admiral S. G. Kucherov was appointed Commander of the Tfhite Sea Flotilla in March, 1943. Prior to this appointment, he was Chief of Staff, Northern Fleet, and in 1942, he was Chief of Staff to Admiral Kuznetsoff.
VI. Caspian Sea Flotilla
(a) Rear Admiral F. S. Sedelnikov has been Commander of this flotilla since before 1940.
Vll. Amur River Flotilla
(a) Vice admiral F. S. Oktyabrski was appointed Commander of the Flotilla in June, 1943, a position which he held several years ago. His naval career was started as a stoker; later he became a mechanic. He was sent to the Naval Military Academy in 1925. Later he commanded a flotilla of Motor Torpedo boats in the Pacific. He is a member of the Central Auditing Committee of the Communist Party, and is said to be very popular within Party circles. In 1938, he was appointed Commander-in-Chief of the Black Sea Fleet, which position he held until June, 1943. His recent transfer is not readily understandable.
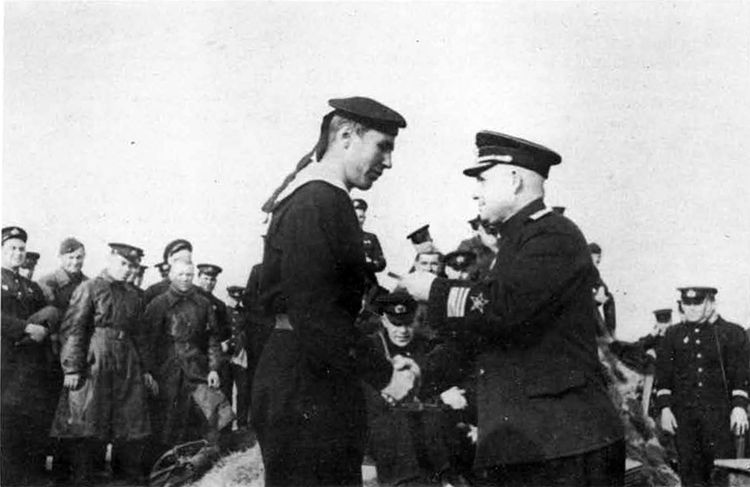

Vice Admiral Oktyabrskl, Commander-in-Chief of the Amur River Flotilla, while still Commander-in-Chief Black Sea Fleet.
CHAPTER IV. TACTICS AND OPERATIONS
A. In General
The tactical naval policy of the U.S.S.R. is dictated by the desire to employ its fleet defensively and not offensively, completely disregarding the fundamental principle for which all navies are built - to gain or dispute command of the sea. For that reason, the Russians allowed their Baltic Fleet, which at the outbreak of the war consisted roughtly of two battleships, three cruisers, twenty-six destroyers, ten torpedo boats, eighty motor torpedo boats, and one hundred submarines, to be completely bottled up within the narrow confines of Kronstadt and Leningrad by the Germans employing air power, light surface craft, and minefields.
B. Soviet Baltic Fleet
The Russian Baltic Fleet driven back into the narrow confines of Kronstadt and Leningrad is able to exert little if any pressure in the Baltic Sea proper. Apart from being icebound during the winter months, surface vessels of the Russian Fleet are only able to break out of the Gulf of Finland at considerable and probably unjustifiable risk. The German Air Force assisted by small surface craft, D/F and radiolocation stations, together with the aid of extensive minefields, completely dominates the Gulf of Finland. The Russians are even denied the opportunity, through lack of bases, of affording air cover to their submarines which might possibly attempt to run the gauntlet during the summer months. Furthermore, this German stranglehold is strengthened by the German shore batteries near Peterhof. These interfere with Soviet minesweeping efforts in the approaches to Leningrad and Kronstadt, an essential preliminary to any attempt on the part of Soviet submarines to break out into the Baltic, A grave disadvantage for the Russians is the climatic conditions which, in the summer months, allow aerial observation to be carried out practically continuously. Soviet submarines, operating in the Baltic in 1942, did little damage but the mere threat to Axis shipping of enemy submarines in the Baltic must have dislocated Axis shipping to some extent. If the U.S.S .R. were able to overcome the enemy hold on the Gulf of Finland, she would have an adequate submarine force available for service. It is estimated that the Baltic Fleet has about 36 submarines consisting of 9 large, 19 medium and 8 small craft; about 20-25 of these are ready for sea. There should be no trouble in regard to the manning position, but there may be an insufficiency of torpedoes and a lack of oil fuel and spare parts owing to the siege conditions in Leningrad.
Although there is no conclusive evidence available, it is more than probable that the greater part of the personnel of the surface ships of the Baltic Fleet are employed in other branches of the Navy Commissariat, such as Coast Defense, including anti-aircraft and in Marine brigades. Of these surface craft, it is believed that the battleship PETROPAVLOVSK lies half sunk in Kronstadt Harbor and that her sister ship the GANGUT is probably berthed alongside in the Neva River with adequate camouflage. Her armament is reported to be efficient. The two modern 8,000 ton cruisers KIROV and MAXIM GORKI now have their armament complete, although these ships had both,at one time,been extensively damaged. The original destroyer flotillas, made up of approximately 36 modern boats, have been reduced down by casualties to about onerthird of their original strength. The complements of these vessels may well have been retained on board, as these craft are exceptionally useful for bombardment of German shore positions along the southern coast of the Gulf of Finland in the ORANIENBAUM and PETERHOF sectors.
It must be a source of considerable satisfaction to the Germans that, due to a variety of causes, they are able to contain the whole Baltic Fleet by means of air power, light surface craft, and the modern devices of radio and radio-direction finders.
C. Black Sea Fleet
Although the Soviet Black Sea Fleet has been driven back to unsuitable and ill-equipped bases at Batum and Poti, it is nevertheless exercising some of the advantages of sea power. These two Georgian harbors contain not only the greater part of the Soviet Fleet but also all the remaining Black Sea Russian merchantmen and tankers. It is fortunate indeed that the German threat to the Cauqasus has been removed since this considerable amount of shipping is very much congested and insufficiently dispersed against any determined large scale bombing attack. The Soviet C-in-C must also be relieved to know that the Axis have no heavy naval forces in Black Sea waters since the repair facilities at these bases would be quite unable to cope with any large scale damage after a heavy Fleet action. In this connection?it is understood that at Batum there are no docking facilities of any description ana rather meagre limited repair shops. Poti, the manganese port some 30 miles to the northward, is better off in this respect, since it possesses two floating docks capable of taking any modern destroyer and some efficient workshops, but it seems unlikely that either of these docks can accommodate a cruiser. The modern 8,000 ton cruiser M0L0T0V has been lying disabled at this base with her stern completely blown off since September, 1942, and,so far, no repairs have been effected. On the other hand, a complete new bow has been fitted to a destroyer casualty which does prove that major repair work can be carried out on smaller craft. The Fleet is further handicapped by having no permanent ammunition stowage, victualling and supply yards. Russians, when pressed, are exceedingly capable im-provisers, and it seems as if the Fleet is now sufficiently supplied with ammunition and torpedoes. There should be no lack of submarine spare parts, since, as an emergency measure, it would be feasible to assemble spares from nine Caspian Fleet submarines. With the threat to Baku removed, t&ere is no longer any function for these boats to perform. Between these two bases, the following naval vessels are berthed:
Two modern cruisers (one, M0L0T0V - damaged); two old cruisers; one old dreadnought battleship; one Flotilla Leader; six/seven modern destroyers (two damaged), two/three old destroyers and about 40 submarines of various classes, including large 750 ton boats, medium 550 ton class and some 12/13 baby 200 tonners.
In addition to this Fleet, there are also two modern cruiser hulls (KUIBYSHEV and FRUNZE), which were successfully towed away from the MARTI yard at NIKOLAEV prior to the German occupation of this important Black Sea naval building yard on the River BUG. There is also the hull of an uncompleted Flotilla Leader ERIVAN lying in BATUM. The battleship SEVASTOPOL has performed little if any useful sea service during the war, but is probably effective as a powerful A/A battery for harbor defence. The services of the Black Sea Fleet, throughout the war, have followed the usual Russian tradition of restricted operations/confined in the main?to close support of the Red Army ashore. Its main units have unfortunately never been used for any major sea operation, and there is no doubt that great opportunities were lost in the early months of the war of attacking Axis seaborne supplies along the Rumanian and Bulgarian coasts. On the other hand, the older cruisers and small craft have performed most able
and gallant service in covering the landings in January, 1942, :wMeh. led to the re-occupation of the Crimean towns of KERCH and FEODOSIA. The cruiser KRAZNY-KAVKAS, together with destroyers, was instrumental in bringing supplies both of men and material to the beleagured fortress of SEVASTOPOL in the face of attack from German aircraft in great strength. The Fleet also suffered, from bombing before it was forced to retire eastward to the temporary base of TUAPSE. Its casualties are not accurately known, but approximately comprise one cruiser, two flotilla leaders, five modem destroyers, four old destroyers, three heavily armed gunboats, and an unknown number of submarines. In addition to the main bases at EATUM and POTt, there is also a submarine base at OCHEMCHIRI some way further north. At one time, the port of SUKHUM was used as the headquarters of the Naval Commander-in-Chief, but since January, 1943, it has been located at MAKOPSE, some 15 miles southeast of TUAPSE.
Roughly from January until June, 1943, the Black Sea Fleet was occupied with safeguarding the shipment of military reinforcements and supplies from Batura, Poti, and Sukhum to the ports of Tuapse and Gelendzhik, from which points attacks on Novorossisk were made. Since the re-occupation of Novorossisk by the Russians, it has been occupied chiefly in aiding land forces, including one or two amphibious landings. Air, submarine and surface forces are all being used of fensively against Axis shipping in the Black Sea, upon which the Germans in the CRIMEA and, to a lesser extent, in South Russia, entirely depend. In general, it can be said that although the C-in-C realizes the importance of striking at Axis shipping, his efforts on the whole have met with little success, and German convoys continue on their work without incurring any really substantial losses. But the Germans are being forced to provide better and more frequent surface escorts and close air cover. Constant minesweeping is also essential, in view of the mining efforts which the Russians are making. The Russian air forces are also carrying out high level bombing of the Axis convoys and on the assembly ports of SEVASTOPOL, YALTA, FEODOSIA and KERCH.
Since the re-occupation of the entire eastern coast of the Black Sea and most of the Sea of Azov coast, the Black Sea Fleet has been able to utilize more advanced bases in its attacks on Axis shipping. The degree to which these bases have been re-equipped is not known; however, during the Soviet advance along the northern coast of the Sea of Azov, the units which the Russians were able to assemble were very active} several amphibious landings took place. For example, the small port of Yalta, southwest of Mariupol, was captured in this manner.
D. Far Eastern Fleet and Amur River Flotilla
Because of the fact that the U.S.S.R. is still neutral in the Pacific, activity of the Far Eastern Fleet and of the Amur River Flotilla is limited to peacetime operationsj these consist, chiefly of patroling the coast from the Korean frontier to Bering Strait, as well as along the Northern Frontier of Manchukuo on the Amur River. Because the Japanese have been seizing occasional Soviet merchant ships which carry Lend-Lease supplies from the U.S. West Coast to Vladivostok and neighboring ports, Soviet destroyers have recently been convoying these ships through the First Kurile Strait.
A few units of the Far Eastern Fleet have been transferred to the Northern Fleet, since the beginning of the war; units so transferred consist of at least one 3000 ton destroyer leader, twd destroyers, and 7 or 8 submarines.
E. Northern Fleet
Formerly the most active fleet by far, the Soviet Northern Fleet is,at the present time, engaging in little#operational activity. The main function of this fleet was that of protecting Allied convoys coming to and leaving from Murmansk and Archangel* For the past several months, there have been no convoys routed to these northern ports with the resulting inactivity of this fleet. The Northern Fleet has also aided land forces in two dramatic but useless commando type landing attempts behind Axis lines.
Chapter V. STRENGTH AND DISPOSITION OF THE SOVIET NAVY
A. Baltic Fleet
2 overage Battleships (23000) tons): GANGUT - probably ready for sea. PETR0PAVL0V5K - lying half sunk in Kronstadt Harbor.
2 heavy Cruisers (8000 tons): KIROV - ready for sea if repairs have been made. MAXIM GORKI - probably ready for sea.
1-2 Destroyer Leaders (3000 tons): LENINGRAD - ready for sea. MINSK - reported as undergoing repairs; may have been sunk.
8 Destroyers (1,65O tons): DROZD - ready for sea. GROZIASHCHI - ready for sea. SILNY - ready ibr sea. SLAVNY - ready for sea. STOROZHEVOI - ready for sea. 3 others (names unknown) - probably undergoing repairs.
36 Submarines (only about 20-25 of these are ready for sea): 9 large units (900-1300 tons); 19 medium units (700 tons); 8 small units (200-300 tons)
1 Cruiser Minelayer: MARTI - ready for sea.
2 Destroyer Minelayers: RISTNA - ready for sea. URAL - probably ready for sea.
7-10 Minesweeping - patrol vessels.
50 Motor Minesweepers, trawlers, etc.(approximate)
6-9 Auxiliary Gunboats.
35 other Auxiliary vessels, (approximate)
B. Black Sea
1 overage Battleship, (23,000 tons): SEVASTOPOL
*2 modern heavy Cruisers (8,000 tons): M0L0T0V - stern blown off - awaiting repairs. VOROSHILOV
1 overage heavy Cruiser (7,000 tons): KRASNY KAVKAZ
1 overage light Cruiser (7.000 tons): KRASNI KRIM
*1 Destroyer Leader (3,000 tons): KHARKOV - Germans reported this unit sunk in October, 1943.
*7 modern Destroyers (1,650 tons): BODRY, BOIKY, BEZPOSHCHADNY, SVOBODNI, SMISHLENNI, SOOBRAZATELNI, SOVEHSHENNI
2 overage Destroyers (1,300 tons): Names unknown
2 Torpedo boats (800 tons): SHKVAL, SHTORM
41 Submarines (33 of which are ready for sea; others refitting). Six of the following have been sunk:
6 large "L" Class units (1,300 tons): L-4 L-23 L-5 L-24 L-6 L-25
4 large "D" Class units (1,000 tons): D-l D-5 D-4 D-6
4 medium "S" Class units (750 tons): S-32 S-34 S-33 S-35
14 medium "Schch" Class units (660 tons): Schch-201 Schch-208 3chch-202 Schch-209 Schch-203 Schch-210 Schch-204 3chch-212 Schch-205 Schch-213 Schch-206 Schch-214
Schch-207 Schch-215
13 small ("M" Class units (200 tons): M-31 M-51 M-32 M-52 M-33 M-54 M-34 M-55 M-35 M-56 3 others
6 average "G" Class units (650 tons): Names unknown
30 Motor Torpedo Boats (approximate)
1 overage Gunboat:
KRASNAIA ABKHAZIA or KRASNY ADZHARISTAN
6 Minesweeping Patrol Vessels (600 tons): FUGAS, KAPSUL, PAKAVAU, TCHSKA, 2 others
12 overage Minesweepers
7 Minesweeping trawlers
45 Motor Cutters (approximate)
*The hulls of the incomplete cruisers FRUNZE and KUIBYSHEV are at Poti. No work has been done on them since 1941.
The hull of an incompleted unit either the DL ERIVAN or DD OZORNI is at Poti although work is progressing on her, she has not,as yet been completed.
C. Far Eastern Fleet
1 heavy Cruiser (8,000 tons): KALININ
3 Destroyer Leaders (3,000 tons): TASHKENT, TBILISSI, TOMSK
8 modern Destroyers (1,650 tons): RASTOROPNI, RAZYASHCHI, REDKI, REKORDNI, RESHITELNI, RETIVI, REZVII, RIYANI
3 overage Destroyers (1,300 tons): STALIN, VOIKOV, YAKOB SVERDLOV
6 Torpedo Boats (800 tons): BURUN, GROM, METEL, MOLNIYA, VYUGA, ZARNITSA
57 Submarines
11 large "L" Class units (1,300 tons):
L-7, L-13, L-8, L-14, L-9, L-17, L-10, L-18, L-11, L-19, L-12
37 medium "S" Class unit (750 tons): S-137
37 medium "Schch" Class units (660 tons): Schch-101 Schch-110 Schch-119 Schch-128 Schch-102 Schch-111 Schch-120 Schch-129 Schch-103 Schch-112 Schch-121 Schch-130 Schch-104 Schch-113 Schch-122 Schch-131 Schch-105 Schch-lU Schch-123 Schch-132 Schch-106 Schch-115 Schch-124 Schch-133 Schch-107 Schch-115 Schch-125 Schch-»134 Schch-108 Schch-117 Schch-126 Schch-135 Schch-109 Schch-118 Schch-127 3chch-136
8 small "M" Class units (200 tons): M-1,
M-30,
6 others-not identified
6 Patrol Vessels (600 tons): PODSEKATEL, PROVODNIK, STRELA. TROS, 2 others
12 Patrol Vessels (400 tons)
61 Motor Torpedo Boats
2 Net Layers
1 Seaplane Tender: PARTIZAN
40 Minesweepers
99 Coastal Motorboats
D. Northern Fleet
1 Destroyer Leader (3,000 tons): BAKU
A modern Destroyers (1,650 tons): GREMYASHCHI, GROMKI, GROZNI, RAZUMNI
3 overage Destroyers (1,300 tons): KARL LISBKNECHT, KUIBYSHEV, URITSKI
3 Torpedo Boats (800 tons): GROZA, SMERCH, URAGAN
20 Submarines
3 large "K" Class units (1,500 tons): K-1, K-3, K-21
4 large "L" Class units (1.300 tons): L-15, L-21, L-20, L-22
5 medium "S" Class units (750 tons): S-54, S-101, S-55, S-102, S-56
4 medium "Schch" Class units (660 tons): Schch-402, Schch-404, Schch-403, Schch-422
A small "M" Class units (200 tons): M-121, M-172, M-171, M-174
5 Motor Torpedo Boats: Two of these are former U.S. boats.
2 Patrol Vessels (600 tons): RUBIN, SAPFIR.
3 Minelayers: MURMAN,
PROSOUZ,
YUSHAR
*30 Patrol Boats:
includes trawlers, drifters, and subchasers.
*10 U.S. 185 foot AM's and 12 U.S. 110 foot SC's are at the present time enroute to this fleet, under Lend-Lease
E. Caspian Sea Flotilla
5 overage Gunboats
3 MARKIN Class boats (Ex-Torpedo Boats, 740 tons): ALVATER, BAKINSKI RABOCHI , MARKIN
2 LENIN Class boats (640 tons): KRASNI AZERBAIDZHAN, LENIN
9 Submarines: 6 medium "S" Glass boats; 3 small "M" Class boats.
30 Motor Torpedo Boats (approximate)
2 Minelayers (approximate)
7 Minesweeping Trawlers (approximate)
Various auxiliary craft
F. Amur River Flotilla
7 Monitors
18 Gunboats
10 Minesweepers
32 Armored Motor Boats
G. Lake Ladoga Flotilla
1 Gunboat: KONSTRUKTOR (former torpedo boat reconstructed)
5 Auxiliary Gunboats
8 Motor Torpedo Boats
20 Motor Minesweepers
other small craft converted to patrol and minesweeping cutters.
H. Lake Onega Flotilla
5-6 Patrol Vessels (some of which are armored)
8 Armored Tugboats
other small craft
CHAPTER VI. ORDNANCE
A. Guns
I. In General.
Little information is available on modern Soviet naval gun construction; it probably consists in part of a 7.1" 52 to 55 caliber gun, a 5.1" 55 caliber gun, a 4-" 53 caliber dual purpose gun, a 3" 55 caliber dual purpose gun, and several anti-aircraft guns of small caliber, as well as some variations to the above mentioned guns. Added to these, are guns which were built prior to and during the first World War by the Imperial Navy. These included a 16" gun (?), a 14" 52 caliber gun, a 12" 52 caliber gun, a 5.1" 55 caliber gun, a 4«7" 50 caliber gun, a 3.9" 60 caliber gun, a 3M 50 caliber gun, and a 3" 30 caliber anti-aircraft gun. The general principle governing rifling, in guns constructed during the last war, was that the depth of grooves should be 1/2 a lini (1.27 mm.), the width 3.5 lini (8.9 mm.), and breadth of land 1.5 lini (3.81 mm.), independent of the caliber of the gun; this principle may still be in existence today.
II, Tsarist 16" gun.
Although probably none of these guns were ever completed, they were to form the main battery armament of future battleships and battle cruisers; they were to be of similar construction and material as the 14" 52 caliber gun, but were to have a length of not over 4-5 calibers. The number of lands and grooves would probably have been 96.
The weight of the gun was to be 104 l/2 tons, the weight
of the shell 2,520 lbs., and the muzzle velocity (calculated) 2,800
ft, per second.
III. Tsarist 14" 52 caliber gun.
Twelve of these guns were to form the main-batteries of the battle cruisers of the Borodino Class, which had been launched prior to the Russian Revolution but were never commissioned. These guns had a length of powder chamber from the rear end of the tube to the base of the shell when in place of 112"„ The diameter of the powder chamber was 15.96". This gun was very similar to the 12" 52 caliber gun, but was constructed of chrome nickel steel, instead of Martens steel, with an elastic limit of 4550 atmospheres. The weight of the guns was 80 »4 tons. The rifle consisted of 84 lands and grooves, angle 6°, uniform twist, one turn in 30 calibers, A Vickers breach mechanism and gas ejector were used. It is not 'known if any of these guns are still in existence; if they are, they must be used as coastal batteries, as the U.S.S.R. has employed no gun larger than 12" on her naval units.
IV. Tsarist 12" 52 caliber gun.
Twelve of these guns mounted in 4 centerline turrets still form the main battery armament of the overage battleships GANGUT, PETR0PAVL0VSK, and SEVASTOPOL, although it has been reported that the guns in #2 and #3 turrets of the SEVASTOPOL have been replaced by guns "of a higher caliber". They are built of Martens steel and weigh 50.6 tons. The weight of the shell is 810 lbs.; they have a muzzle velocity of 3-150 ft. per second. The length of the powder chamber from the rear end of the tube to Us base of the shell'when in place is 96". The diameter of the po?/der chamber is 13*68". Rifling consists of 80 lands and grooves of uniform twist, angle 6°, one turn in 30 calibers.
Russian Naval 12" 52 caliber Gun Scale 1:40
V, Modern 7.1". 52-55 caliber gun
forms the main battery armament on all Soviet heavy cruisers; it is probably the largest gun yet constructed under the Soviet regime. No information ia available on this gun.
VI. Modern 5.1" (130 mm.) 50 caliber gun
is called by the Russians the B-13-2s. It is used as main battery armament on all Soviet Destroyer Leaders and destroyers of recent construction. This gun, which fires at an elevation of from 5° to 45°, is placed in a gun shield. It is fired by means of a hydraulic trigper mechanism, which is operated by pedals and by means of percussion and electric fuses. The elevating gear is arranged in quadrants. It has one control lever on the right side. The transversing gear turns 360°, and has two control levers. It is a breech loader of Vickers type; the shells are fed pneumatically, and the charge is fed by hand. It has one right and one left sight. Its barrel is of a 19.3?- -odel. The tube and casing consist of a single riece; there is no recess in front of the casing. The rifling has 40 grooves; they are of constant steepness and run from the left upwards to the right. The length of the rifling is 25 calibers. The breech mechanism is steel, a forging of rectangular shape.
View of Modern Soviet 5.1" Gun from the right side.
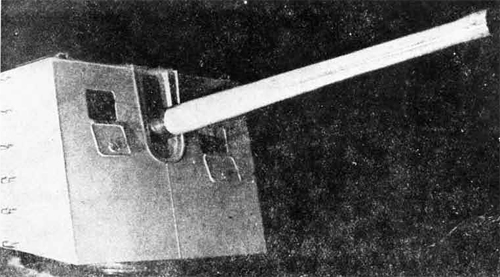
Modern Soviet 5.1" Gun - general view.
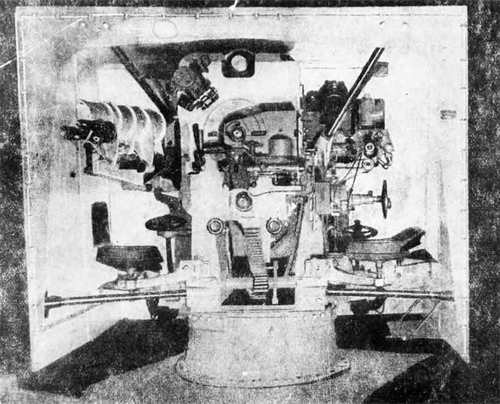
View of the Modern Soviet 5.1" Gun from the breech end.
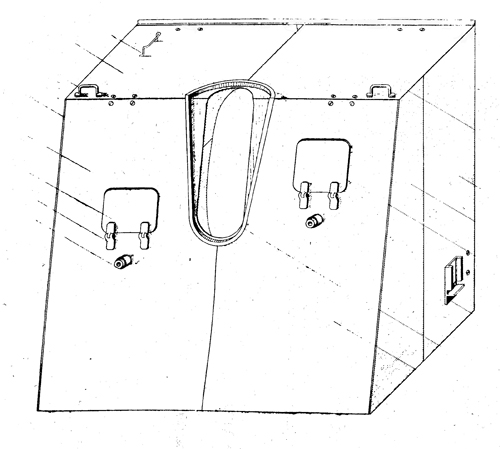
Armored shield of the Modem Soviet 5.1" Gun.

Barrel of the Modern Soviet 5.1" Gun.
VII. Tsarist 5.1" (130 mm.) 55 caliber breech loading rifle.
This gun probably forms the main battery armament for the overage light cruiser, KRASNY KRIM, and possibly is to be found on other older units^ of the Soviet Navy; it is a built-up gun of Martens steel. It consists of the tube in one length, two reinforcing bands, the rear one being of uniform thickness and extending from the breech to about the middle of the length of the tube, and the front one, tapering slowly to a muzzle, without a tulip. Outside is the jacket, extending to about 20" forward of the joint between reinforcing bands tapering over the chase.
Rifling consists of 30 lands and grooves of uniform twist, at an angle of 6°, one turn in 30 calibers. The depth of the groove is 1 millimeter, the width 9.14 millimeters, and the breadth of land 4«4-7 millimeters. It has a Vickers breech mechanism^ and a Vickers system of air-blast for clearing the bore.

Tsarist 5.1" 55 caliber Gun. Scale 1:20
a = Tube
b1b2 = Reinforcing cylinder in two parts
c = Jacket
d = Breech piece
e = Recoil band
f = Strengthening ring
g = Breech ring
VIII. Modern 4" (102 mm.) 53 caliber, dual purpose gun
is used as pain battery armament on the larger submarines and probably on some surface craft. It is of light, mono block construction, and has a maximum elevation of about 75°, but is used, against, aircraft as Well; as against surface units. The breech is of a sliding KLock type and the lands are very sharp and high, curving to the right, as in other Soviet naval guns. The sight is a waterproof combination receiver and gunsight telescope5 it is left installed when the submarine dives. The watertight gunsight housing includes a sight setting mechanism which can be.set either locally or by remote control. The train and elevation of the gun is done by hand wheels; there is practically no lost motion in the gearing. This gun trains and elevates extremely easily and fast, and has good balance. Fixed ammunition is used for this gun, weighing 16 kilograms, with the case being very short and squat, but quite large in diameter. A nose fuse is fitted to the projectile, but it is covered with a metal cap. The slide of the gun is chrome plated, the rest of the gun being made of steel.
IX. The Modern 3" (76*2 mm.) 55 caliber, dual purpose universal naval gun
is known as Mark 34-K by the Russians. This gun, the principles of which were designed in 1935, was modernized in 1939• It is placed in an armored shield. The barrel has a very heavy breech mechanism, and its center of gravity is shifted to the breech face. This makes it possible for the gun to attain a high angle of elevation, while maintaining the normal elevation of the trunnions for firing at low elevation^ the breech block is wedge-shaped. This gun is operated by two gunners by means of two foot pedals or the manual trigger; it is provided with a universal optical sight of the "MO" type, which consists of two similar mechanical optical sights, one on the right of the gun, and the other on the left. The one on the right is used for aiming at a horizontal target, while the one on the left is used for aiming at a vertical target. The wind gauge and sight are set by turning the flywheels of the mechanized gear. There is a barrel securing device for unloading the gun while underway; it is placed on the front of the armored shield.
General specifications are as follows:
Length of the barrel, 4223 millimeters.
Length of the rifled portion, 3379 millimeters.
Number of grooves, 28.
Width of the rifling, 5.25 millimeters.
Depth of the rifling, .75 millimeters.
Length of the cartridge load, 862 millimeters.
Height of the axis of the trunnions, 1504 millimeters.
Extent of horizontal firing, 360©.
Extent of vertical firing, -5°-+85°.
Speed of vertical aiming for one turn of the flywheel, 4°»
Speed of horizontal aiming for one turn of the flywheel,6°.
Muzzle velocity, 820 meters per second.
Horizontal range, 14,200 meters.
Vertical range, 9,300 meters.
Rate of fire per minute, 15 to 18 rounds.
Weight of the shell, 6.5 kilograms.
Weight of the charge, 1.88 kilograms.
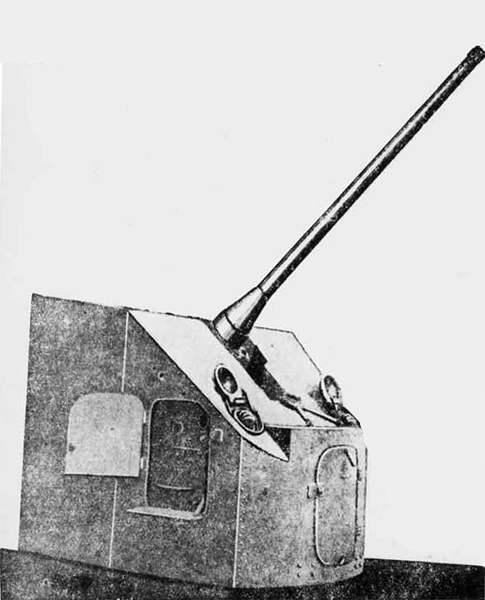
General view of Modern Russian 3" Dual Purpose Gun.
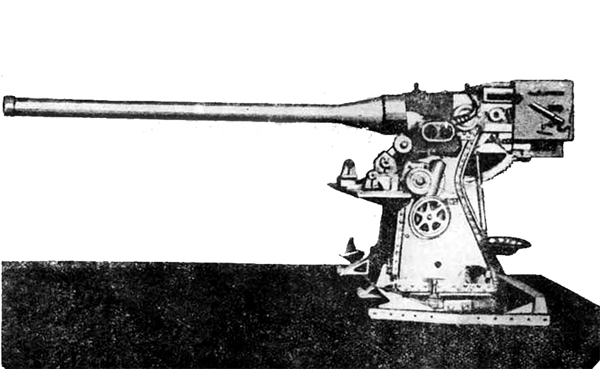
General View of Modern Russian 3" Dual Purpose Gun.
Armored shield of* i odfirn Rus3ian 3" Dual Purrose Gun.
X. 1.8" (45 mm.) 46 caliber, dual purpose universal naval gun
is used on Soviet submarines as well as on merchant vessels; it possibly forms the main armament on the small "M" Class submarines (200 tons) and secondary on larger boats, such as the "S" Class (750 tons). This gui- was modernized in 1938; changes made to it at that time in- ,. eluded the addition of semi-automatic devices, the rcanner of securing the gun to the deck, alteration of the azimuth circle, etc. Its primary use is that of a short-range anti-aircraft gun, but it can also be used against horizontal targets. The gun carriage is a trunnion mount with a Bofors-type cradle. The absorbing gear is hydraulic; the recuperator has springs. This gun is operated by one man only, although its sights can be operated by a second. The control levers have both horizontal and vertical aiming, and are on the left side of the gun. Indirect aiming is possible only within the field of vision betv/een the limit of movement of the intersections, or 19° to the right or left.
It is equipped with a Soviet ShB-1 Classified sight, having a field of vision of 38°. The breech block is wedge-shaped and vertical; it opens below and is semi-automatic.
This gun, when mounted on submarines, is hermetically plugged by means of a cork, which will keep the barrel dry down to ir:0 meters of water.
Three types of amiTiur.ition can be used in this gun; an antiaircraft percussion <;ren,ode with sensitive fuse, an srnor-pierc:i ng explosive effect shell, and an ordinary armor-jiercing shell.
General Specifications are as follows;
Diameter of the cartridge chamber, 50.2 mm. and 53.2 mm.
Length of the entire barrel, 2072.5 mm.
Length of the chamber as far as the rifling, 325 mm.
Number of grooves, 16.
Design of breech block, wedge-shaped.
Rate of firing, about 30 rounds a minute.
Type of carriage, Trunnion.
Height of line of fire, 1,215 mm.
Horizontal firing, 360°.
Maxijnum angle of elevation, 85°.
Maximum angle of depression, 10°.
Angle of elevation of the gun for one turn of the control
lever of the elevating mechanism, 4-°. Height of the axis of thg trunnions, 1,200 mm. Maximum horizontal range, 9.500 meters. Maximum vertical range, about 6,000 meters. Weight of the entire mount, 5,006 kilograms.

View of the right side of a Modern 1.8" Dual Purpose Gun.
General view of the mount of a Modern 1.8" Dual Purpose Gun.
View of the left side of
a Modern 1.8" Dual Purpose Gun.
XI. The Modern 12.7 mm. 79 caliber, dual purpose Machine gun
is called "DK (DEGTYAREV)" by the Russians. It is claijned that because of its long caliber, when this gun is fired at a target 200 meters distant at an angle of 90°, 50$ of the bullets will penetrate 20 mm. armor and 100% will penetrate 16 mm. armor. It is a gas operated weapon; its cartridge belt is made of semi-rigid metal and contains 50 bullets. The barrel of the DK is a massive tube having no special cooling device; it is cooled by means of ribbing on the barrel itself. The rifled section of the barrel contains eight grooves. To reduce its recoil force, this gun is equipped with a positive muzzle brake, which reduces this force by !£.%. The DK is placed on a naval pedestal mount. It is equipped with both universal and classified sightsj the classified sight is used when aiming at aircraft only.
General specifications of the DK gun are as follows:
Angle of elevation, 82°.
Maximum rate of fire, 240 rounds per minute.
Maximum safe rate of fire, 86 rounds per minute.
Muzzle velocity, 850-870 meters a second.
Aiming range of horizontal sight, 3,700 meters.
Aiming range of anti-aircraft sight, 2,400 meters.
Length of the machine gun, 1593.5 nun.
Length of barrel, 1,003 mm
Length of rifled part of barrel. 890 mm
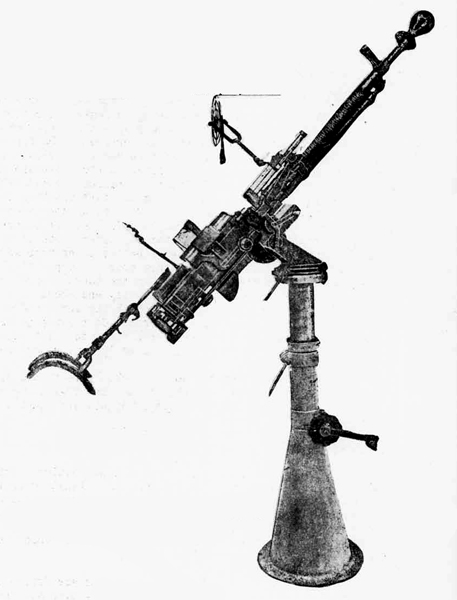
View of the Modern Soviet 12.7 mm Dual Purpose Machine Gun.
B . Torpedo-Tubes.
I. In General. As far as is known, the Soviet Navy uses two sizes of torpedo tubes, an 18" and a 21". 18" torpedo tubes are to be found on battleships, torpedo boats, the smaller motor torpedo boats and 200-ton submarines; the 21" torpedo tubes have been placed on cruisers, destroyers, the larger motor torpedo boats, and large and medium-sized submarines. No information is available on the construction of the 18" tube, but it may be presumed that they are somewhat similar to the 21".
II. 21" torpedo tubes appear to be made of steel with one riveted seam;. The inside finish is rough and painted. There are four milled steel bearing surfaces fitted longitudinally 90° apart to accommodate the torpedo, raised about 1/4. of an inch from the tube surface. The exact diameter of the tube bet?»een bearing surfaces is 533 millimeters (about 20.9 inches); the length of the tube is 24»6 ft. The raised bearing surfaces of the tube provide ample room for the necessary air escape upon loading. There is no guide slot fitted, this being accomplished by two fins, fitted on opposite sides of the torpedo, taking up on the raised portion of the bearing surfaces to prevent carting. It is believed to be usual for no gyro angle setting mechanism to be fitted or to have any mechanism for correcting the course of a torpedo outside the tube. The inner door must be open to do so. Torpedo ejection is accomplished by air (300 lbs.)> the firing being either electric or manual. There is a bubble swallower, installed about one third of the way down the tube from the inner door. The release finger for starting the driving mechanism is locked on dead top center, and is released immediately upon the motion of the torpedo. The firing latch is placed well forward of the torpedo; the Russians claim that this gives them more certain action and that fewer dummy torpedoes are fired, thereby. A stop bolt similar to that found on U.S. tubes is fitted which raises automatically*upon firing. A starting lever trip is used to start the torpedo, also similar to that used in the U.S. The torpedo chamber pressure,upon torpedo discharge,is 25 atmospheres, or 370 lbs. per square inch. No lock is provided between the inner and outer doors of the tube, although a warning target sign shows when the outer door is open. No tail nut can be fitted to the inner door. A depth fitting mechanism is fitted for setting depths in the tube. Poppet valves are also fitted which operate automatically and about 6" pipes are led to the bilges from these valves. Both the inner and outer doors of the tube are opened by hand. The outer door can also be opened hydraulically by means of a lever above the tube. The inner door is of the bayonet type, similar to that used in U.S. submarines.
On triple mount torpedo tubes which are fitted on most Soviet cruisers, there are handwheels for the off-setting of the outer two tubes for spread. Telescopic sights are mounted on top of the triple tubes.
C. Torpedoes
21" torpedoes are of all steel construction. They have a diameter of 533 mm. (about 20.9 inches) and a length overall of 7,197 mm. (about 23.6 feet); this extra length appears to be in the air flask section. They have a total weight, fully equipped, of 3,538.7 pounds and a weight without air and water of 2,650.1 pounds; the differential between these two weight is aft. These torpedoes have a positive buoyancy of 259.4 pounds.
It is believed that Soviet torpedoes are driven either by steam or by electricity. The most satisfactory type are those steam
driven by a mechanism of piston-drive construction, similar to that of an ordinary steam engine. The differential on these torpedoes turns the two propeller shafts, but in different directions. Although some sources state that these torpedoes are capable of making 55-60 knots, it is thought that their top speed is actually only about 35-40 knots. They have a range at top speed of 4,000 yards, and a range of 12,000 yards at minimum speed.
Soviet 21" torpedoes are discharged from their tubes usually by 4 atmospheres of pressure, but up to nine atmospheres are available; there is a volume of air of 20-25 atmospheres. These torpedoes have two screws; one is a square blade, with a very rugged appearance, and the other has a lip extension. The first propeller gives the impression, when looking at it directly along the axis, that there would be no free space between the following edge of one blade and the leading edge of the next blade, at the point of greatest width* The drive is of Whitehead type, and is said to be very dependable. The depth rudders are about 1/4. of an inch thick and occupy about four times the area of the steering rudders. Two weights, totalling about 263 pounds, are installed in the aft reservoir and hydrostatic compartments.
The horizontal and vertical planes on the torpedo are fixed to a tail assembly enclosing and protecting the propeller and extending beyond them. It is believed that the sides, on to which the elevator is attached, are also guides which travel down th* tube track together with another set of guides which are at about the mid-section of the torpedo sides. These tail skids are about 14." long and about 7/8 of an inch wide. The vertical rods,to which the rudder is attached,carry the lever mechanism from the body of the torpedo to work the rudder and elevator.
The warhead on 21" torpedoes is 5 or 6 feet long; it weighs 880 pounds and contains 660 pounds of explosives. Two exploders are fitted to the warhead on the top c/1, one behind the other, in case the first one should fail* These exploders are about 6 inches long and five inches in diameter, with screw threads fitted for a booster* The arming device is a small three-blade propeller fitted to the exploder, itself. It is reported that the exploder is fired by contact only; some experiments have been made on magnetic heads in the U.S .S it., but they were not found to be successful. These torpedoes have the overall appearance of careful manufacture.
It is said that the Russians have no wakeless torpedoes as standard equipment but that they have some experimental models and that their laboratories are experimenting with battery operated electrical torpedoes as well, but that up to late 1942, they had been able to produce torpedoes of this type only inferior in range and speed to the gas engine type.
D. Mines
I. In General. Soviet mines are of the magnetic, accoustic and contact type and are reported to be the same as the German in principle; various types are planted by surface craft, submarines, and aircraft.
II. Mark M. 08/39
Planted by: Surface vessel.
Weight of charge: 115 kgs.
Length of anchor cable: 110 meters.
Limiting depth in which 110 meters,
may be planted:
Limiting depth at which mine may ride below surface: 4 meters
Method of activation: Galvanic and contact.
Total weight: 592 kgs.
Length: 1,240 mm.
Width: 915 mm.
Height: 1,123 mm.
III. Mark M. 26
Planted by: Surface vessel.
Weight of charge: 240 kgs.
Length of anchor cable: 132 meters.
Limiting depth in which may be planted: 132 meters,
Limiting depth at which mine may ride below surface: 6.1 meters,
Method of activation: Contact.
Total weight: 890 kgs.
Length: 1,615 mm.
Width: 895 mm.
Height: 990 mm.
MARK M. 26
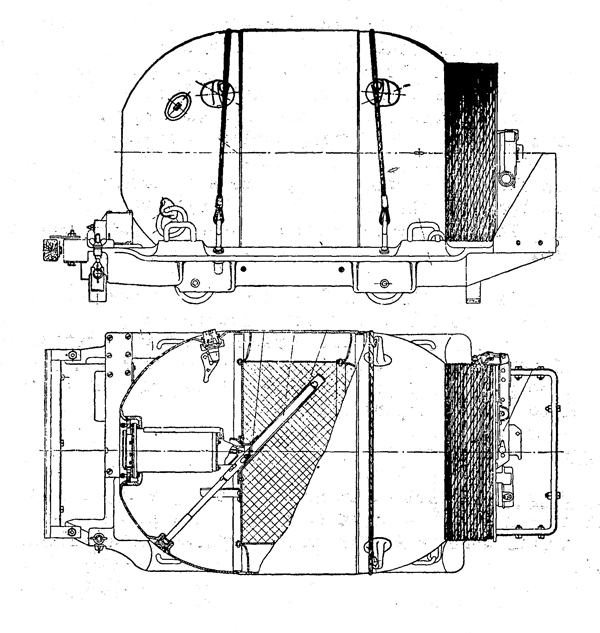
1. General view, mine on its anchor.
2. View in cross section
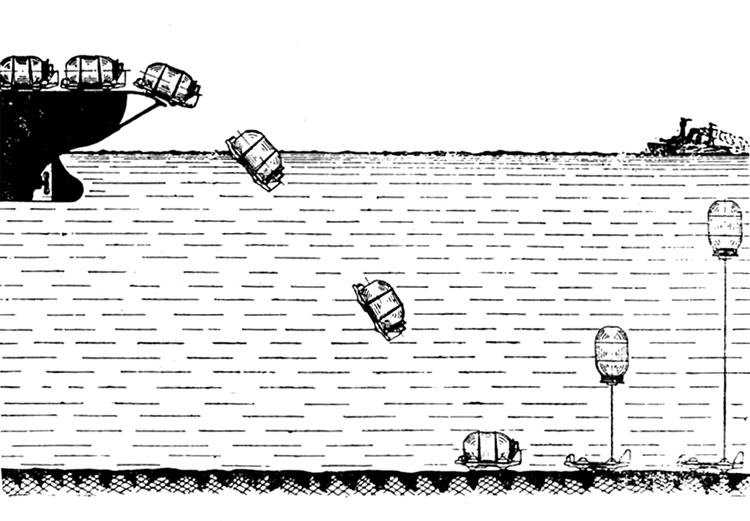
Steps in Planting Mark M. 26.
IV. Mark M. KB
Planted byi Surface vessel.
Weight of charge: 230 kgs.
Length of anchor cable: 263 meters.
Limiting depth in which may be planted: 263 meters.
Limiting depth at which mine may ride below surface: 9.0 meters.
Method of activation: Galvanic, contact.
Total weight: 1,065 kgs.
Length: 2,162 mm.
Width: 927 mm.
Height: 1,190 mm.
MARK M. KB
General view.
General view.
General view.
MARK M.KB
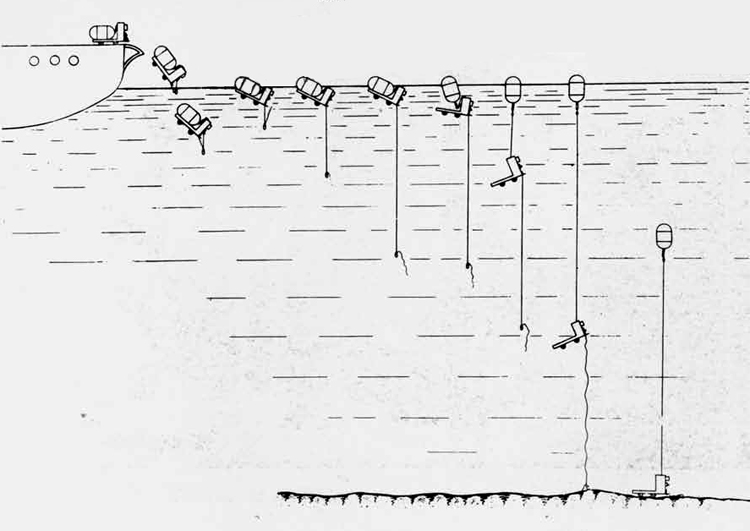
Steps in Planting.
V. Mark M. AG
Planted by: Surface vessel.
Weight of charge: 230 kgs.
Length of anchor cable: 395 meters.
Limiting depth in which 395 meters - plus
may tie planted: amount of submergence.
Limiting depth at which mine may ride below surface: 91 meters.
Method of activation: Antenna and antenna
galvanic.
Total weight! 1,120 kgs.
Length: 2,162 mm.
Widths 927 mn.
Height: 1,205 mm.
MARK M. AG
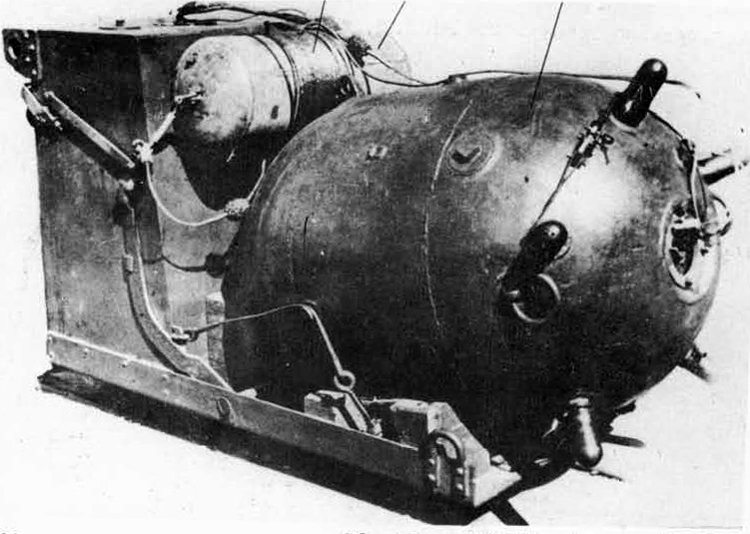
General view - mine ready for Planting with 2 antennae (lower and upper)
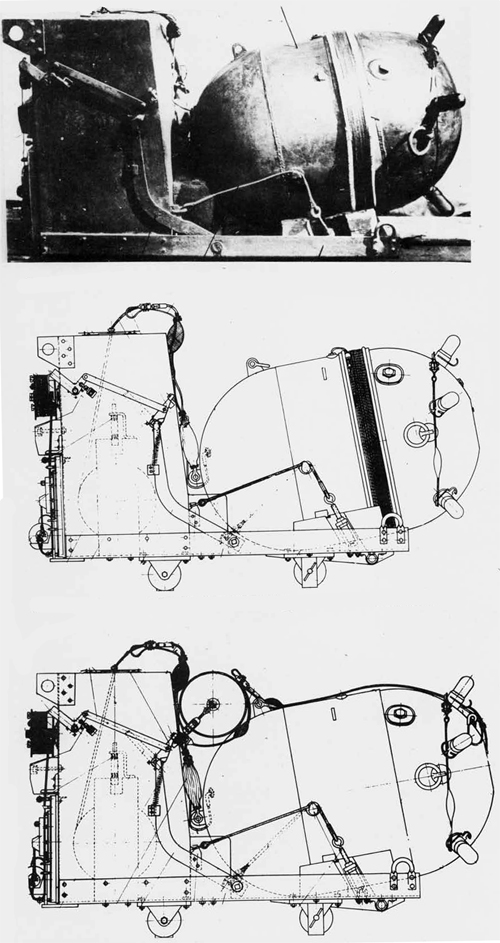
General view mine ready for Planting, with Jower antenna.
General view mine ready for Planting, with one lower antenna.
General view mine ready for Planting, with 2 antennae (lower, and upper).
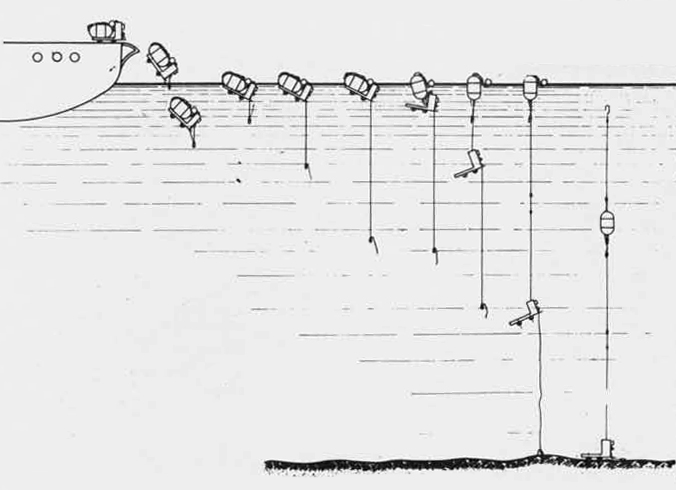
Steps in planting mine AG with 2 antennae (lower and upper).
VI. Mark AMG
Planted by: Aircraft.
Weight of charge: 250 kgs.
Length of anchor cable: 150 meters.
Limiting depth in which may be planted: 100 meters,
Limiting depth at which mine may ride below surface: from 3 to 9 meters,
Method of activation: Galvanic, contact.
Total weight: 1,050 kgs.
Length: 3,600 mm.
Diameter: 950 mm.

Loading a Mark M. AMG (?) mine - Naval Air Force of the Northern Fleet.
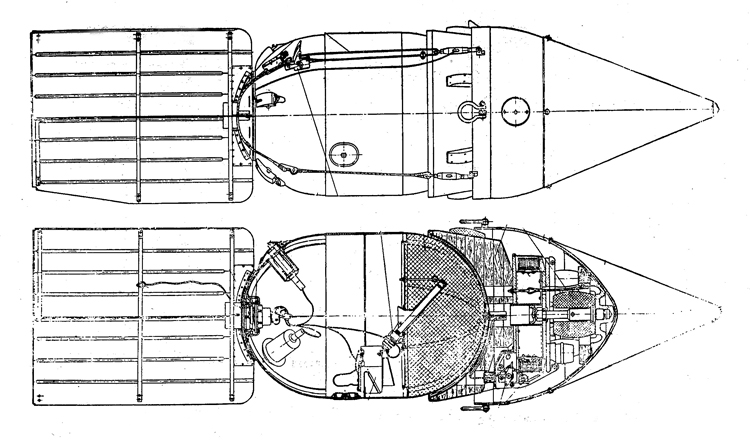
2 Sectional views.
Steps in Planting,
VII, Name unknown:
Planted by: Submarine.
Means of ejection: Mine tubes.
Method of activation: Contact.
Total weight of mine and anchor: 600 kgs.(1,322.7 lbs.) .
Weight of mine: 400 kgs. (881.8 lbs.).
Weight of anchor: 200 kgs. (440.9 lbs.).
Total length of mine and anchor: 2,000 mm. (78.74 inches)
Length of mine: 1,700mm. (66.929 ")
Length of anchor: 300 mm. (18.811 inches).
Diameter: 900 mm. (35*43 inches).
Length of anchor cable: 140 meters (459 ft.).
Several types of Soviet submarines are fitted for mine-laying. For example, the "L" Class has two mine tubes aft, below the two deck torpedo tubes. Each tube can be loaded with ten mines of this type, or 14 mines of shorter length. Mines are loaded in the tubes by submerging the nose of the submarine and lifting the aft end until the tubes are clear of the water; this is done at specially constructed mine loading docks. It has been reported that certain Soviet submarines can lay cylindrical influence mines both magnetic and accoustic, as well as moored contact mines.
Mines are usually planted from "L" Class submarines at periscope depth, but they can be laid at any depth. The tubes are first flooded and then the doors are opened by means of an electric motor. Planting is accomplished by means of an electrically operated mechanism which pulls the aft mine from the tube and pushes the remaining mines aft. The mine is launched anchor first, while the submarine is travelling at slow speed.
The anchor of this type of mine has a plummet for adjusting the depth of the mine below the surface of the water. This plummet is released when the mine is ejected from the mine tube. The mine and anchor sink together until the plummet hits bottom and releases the mine from the anchor. The mine then rises to a depth below the surface equal to the length of the plummet cord.
VIII. Mark M. FLT
Planted by: Submarines.
Means of ejection: Mine tubes.
Weight of charge: 230 kgs.
Length of anchor cable: 130 meters.
Limiting depth in which may be planted: 130 meters.
Limiting depth at which mine may ride below surface: 9.0 meters.
Method of activation: Contact.
Total weight: 820 kgs.
Length: 1,770 mm.
Width: 860 mm.
Height: 795 mm.

General view of mine on its anchor.
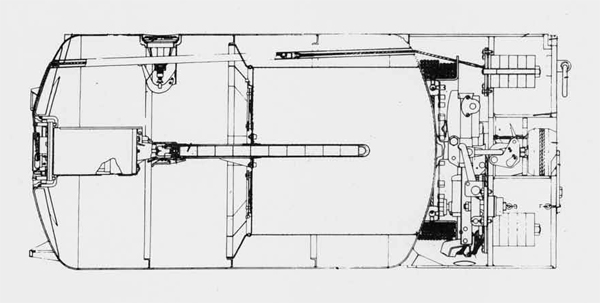
Sectional view of mine with anchor.
Steps in Planting.
IX. Mark M. PLT-3
Planted by: Submarines
Means of ejection: Torpeclo tubes.
Weight of charge: 100 kgs,
Length of anchor cable: 150 meters.
Limiting depth in which may be planted: 130 meters,
Limiting depth at which mine may ride below surface: 9 meters,
Method of activation: Galvanic, Contact
Total weight: 500 kgs.
Length: 2,355 mm.
Diameter: 533 mm.
MARK M/PLT-3
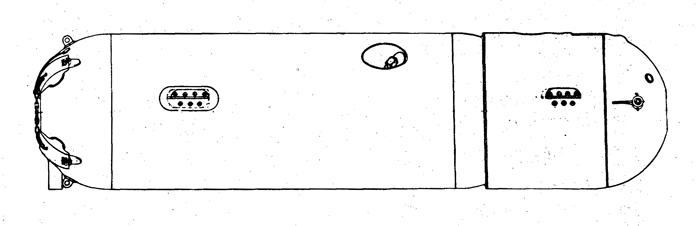
General view.
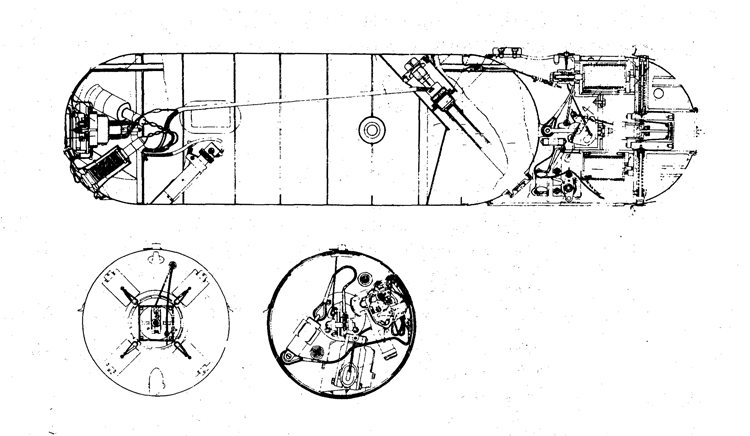
Sectional view of mine with anchor.
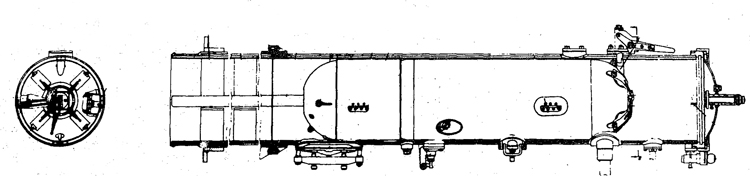
View of mine within a Torpedo Tube,
Steps in Planting.
X. Mark MlRAB
Planted by: Surface, river,
Weight of charge: 64 kgs.
Length of anchor cable: On bottom.
Limiting depth in which maybe planted: Calculated 5 meters from the bottom.
Limiting depth at which . mine may ride below surface;: Calculated 5 meters £rom the bottom
Method of activation: Noncontact, induction.
Total weight: 280 kgs.
Length: 1,030 mm.
Width: 688 mm.
Height: 700 mm.

General view.
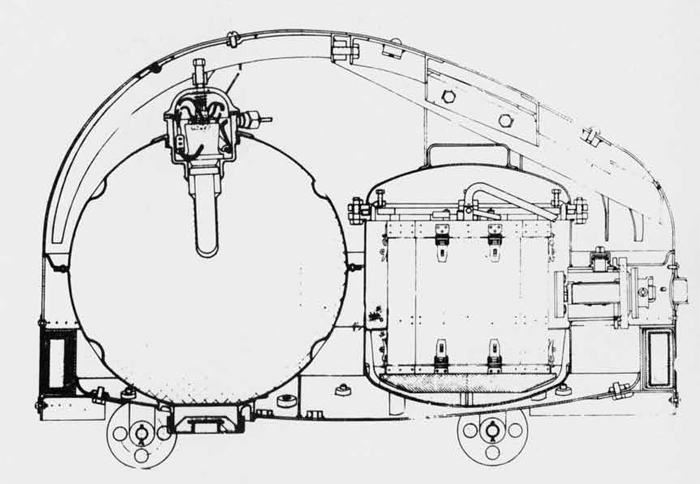
Sectional view.
XI. Mark Mine Protector MZ-26.
Planted by: Surface vessel.
Weight of charge: Explosive in
1 kg. charges.
Length of anchor cable: 110 meters.
Limiting depth in which may be planted: 110 meters
Limiting depth at which mine may ride below surface; 18 meters.
Method of activation: Pressure of sweep wire.
Total weight: 413 kga.
Length: 1,240 mm
Width: 720 mm.
Height: 1,270 mm.
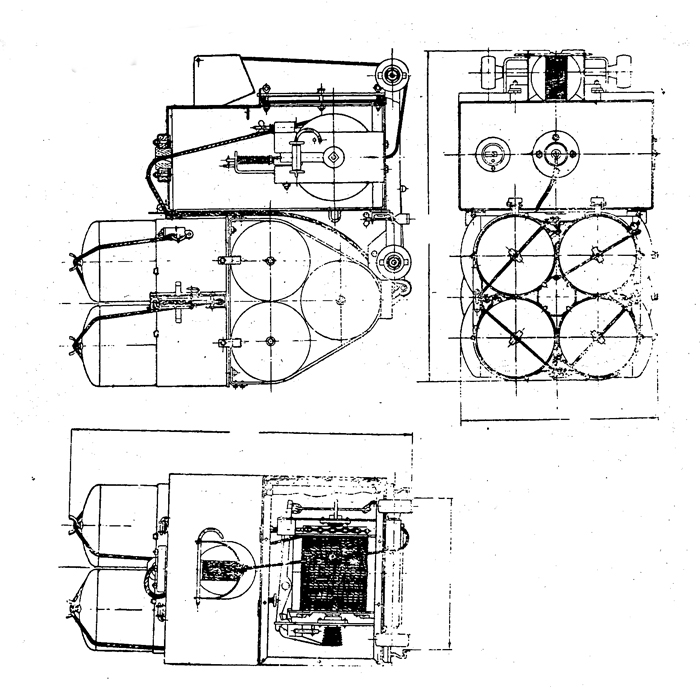
General view.
Steps in Planting.
CHAPTER VII. GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS AND DESCRIPTION OF NAVAL UNITS
A. BATTLESHIPS
1. OVERAGE BATTLESHIP SEVASTOPOL (Ex PARIZKKAIA KOIttKUKA. ISx. SEVASTOPOL)
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Date laid down: 1909,
Date commissioned: 1915.
Normal displacement:. 23,000 tons.
Length 0,A.:, 594 feet.
Beam: 87 feet.
Maximum -draft: 27 feet.
Type of machinery: Parson's Turbines.
Horsepower: 42,000.
Number of Propellors: 4«
Type of boilers: Yarrow.
Number of Boilers: 25.
Full speed: IB knots.
.Cruising speed: 16 knots with a cruising radius of 4,000 miles.
Aircraft normally carried: 2.
Launching device: 1 catapult.
Fire Control: director control.
Number of searchlights: 6.
ARMOR
Belt 8 3/4 inches amidships; 5" and 2" at ends; 3" to 4" internal belt.
Turrets: 12" - 10"; 8" barbettes.
Decks: 3".
FC towers: 10" forward.
The armor belt is about 15 feet wide, five feet of it being below the water line, of uniform thickness; there is a second 3" or 4" internal belt from 11 feet inboard above the protective deck extending between it and the barbettes. The space between the main and internal belts is divided up into water tight compartments.
ARMAMENT
12 12" 52 caliber- guns in triple turrets with a maximum elevation of 25°, a muzzle velocity of 2644 feet per second,'and a maximum range of 30,000 yards.
10 4.7" 50 caliber guns in .casemates with a muzzle velocity of 2624 feet .per1 .second.
6 4.1" anti-aircraft guns.
3 3.9" anti-aircraft guns.
4 3" anti-aircraft guns.
The port plates above each gun are in the form of a hinged flap, allowing each i2" gun to elevate to 25°maximum.
Arcs of fire: end triple 12" turrets is 310°; central turrets, 130° on each beam; the after 4.7" gun, 90°; the other 4.7" guns, 85°,
Main battery guns in number 2 and number 3 turrets have been replaced by guns of a "higher caliber", reports indicate.
Number of torpedo tubes: 4 18" submerged.
GENERAL
It is not believed that the modernization of this unit included
an increased compartmentation of the Bull'as in th©' case of the other two units of this class. There is no evidence of external blisters having been fitted. The first stack was trunked aft, and a tripod foremast with a FC top, and catapult have been fitted. Otherwise, the reconstruction does not appear to have been as extensive as on her sister ships.
This unit is reported to be most unhealthy, unsanitary and badly ventilated.
The Sevastopol proceeded from the Baltic Sea to the Black Sea in 1930 in company with the overage light cruiser Profintern. Her general condition at that time,was reported to be unfit and the official explanation of her remaining in the Black Sea was that she could not face the return voyage.
DISTINGUISHING FEATURES
The main deck level center-line disposition of the four large triple turrets is unique among existing capital ships, readily distinguishable from the air.
At long range on the surface, this vessel bears a faint resemblance to the Japanese battleahip3 of the FUSO Class.
OBB SEVASTOPOL

Three main battery triple turrets
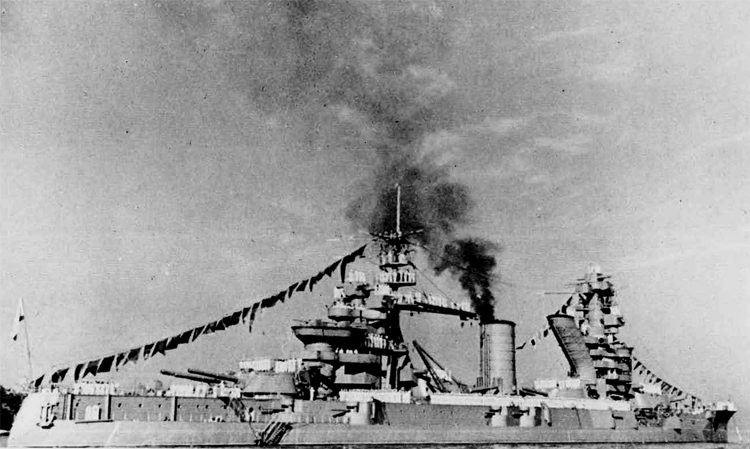
OBB SEVASTOPOL
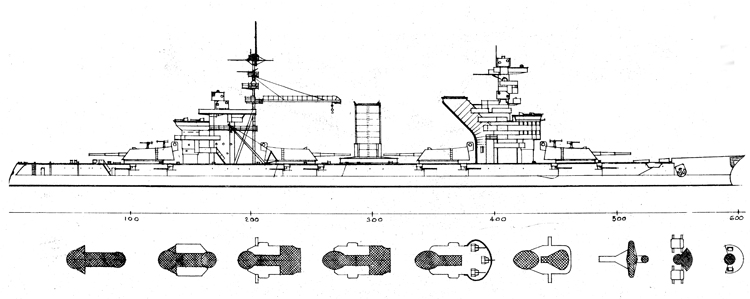
OBB SEVASTOPOL
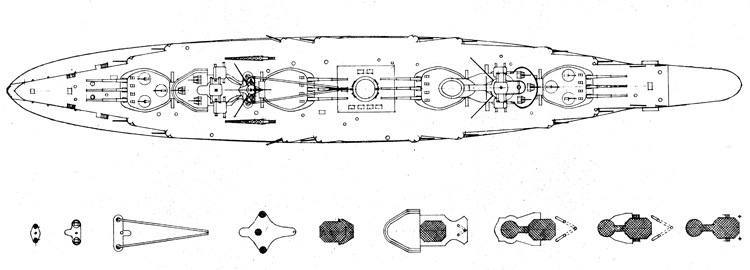
OBB SEVASTOPOL

Stern view, showing main and anti-aircraft batteries
OBB SEVASTOPOL
Main Battery Turret.
II. OVERAGE BATTLES!; IPS SEVASTOPOL CUSS (FETROPAVLOVSKj Ex MARAT, Ex PETROPAVLOVSK) (GANGUT, Ex OKTYABRSKAYA REVOLUTSIA. Ex GANGUT)
GENERAL.SPECIFICATIONS
Date laid down: 1909.
Date commissioned: January, 1914
Standard displacement: 23,000 tons.
Normal displacement, full load: 26,000 tons.
Length, O.A.: 619 feet.
Beam: 87 feet.
Mean draft: 27 1/2 feet.
Type of machinery: Parson's Turbines.
Horsepower: 50,000.
Number of propellors: 4
Type of boilers: Yarrow.
Number of boilers: 25.
Full speed: 23 knots with maximum radius, 990 miles.
Cruising speed: 16 knots with a cruising radius of 4>000 miles.
Aircraft normally carried: 1 on the Petropavlovsk; 2 on the Gangut.
Launching Device: 1 catapult.
Fire Control: director control.
Searchlights: 6.
ARMOR
Belt: 8 3/4" amidships; 5" to 2" ends; 4" to 3" internal belt.
Turrets 12" to 10"; 8-inch barbettes.
Decks: 3".
FG-towers: 10" forward.
Underwater protection: Additional conpartmentation of the underwater
bull upon refitting.
The belt is about 15 feet wide, 5 feet,of it below the water, of uniform thickness. There is a secondary 3" to 4" internal belt some 11 feet inboard above the protective deck, expending between- the end barbettes.
The space between the main belt and internal belt is divided up into watertight compartments. The watertight integrity has been considerably increased by the construction of a large number of watertight bulkheads, both longitudinal and athwartships, a double bottom and special torpedo bulkheads. No external anti-torpedo bulges appear to have been fitted.
ARMAMENT
12 12" 52 caliber guns with a maximum elevation of 30° to 40°, and a muzzle velocity of 3000 feet per second.
10 4.7" 50 caliber guns in casemates with a nuzzle velocity of 2600 feet per second.
,6 4»1" anti-aircraft guns.
3 3.9" anti-aircraft guns.
3 3" anti-aircraft guns with a nuzzle velocity of 2700 feet per second.
The port plates above each gun are in the form of hinged flaps, allowing each 12" gun to elevate up to 30° to 40°
maximum, arcs of fire: end triple 12" turrets-310°, central tur-rets-130° on each beam; after group of 4 4-7" guns, 90°; the other 4.7" guns, 850,
Number of Torpedo tubes:4 1$'carried below the waoerline.
GENERAL
These two units, together with the Sevastopol were laid dovm at the same time and were sister ships. The main differences between the Petropavlovsk and the Gangut were made during their refitting; the former was refilted during 1928-1931 and the latter during 1930-1933.
On the Petropavlovsk, the superstructure was developed to include a new foremast and bridge structure and added work above the after conning tower; on the Gangut, it was further developed to include fore and after fire control towers and bridge.
On the Petropavlovsk, the first funi:el was trunked aft, to help clear the bridge of fuel gasses; the forward stack of the Gangut was also trunked aft to clear the forward bridge structure of boiler gasses and a pair of heavy boat and plane handling cranes were added to the after superstructure.
As first completed, these units w=re most unhealthy and unsanitary and badly ventilated; these conditions largely remain today.
Since the outbreak of the Kusso-German war in June, 19-41, these two ships ha^-e be-n subjected to almost constant bombing by the enemy; it is probable that the Petrnpavlovsk which has been lying, in Kron3tadt harbor 3ince 1941» is, to all intents and purposes, sunk, and although it is claimed that her 12" batteries can still be used as shore installations, she has, to all intents and purposes, been sunk. The Gangut has also been extensively damaged by the most recent reports on her; in January, 194-3, it v/es stated that she was under repair in Leningrad Harbor.
OBB PETROPAVLOVSK

Aerial view.

Foremast
OBB PETROPAVLOVSK
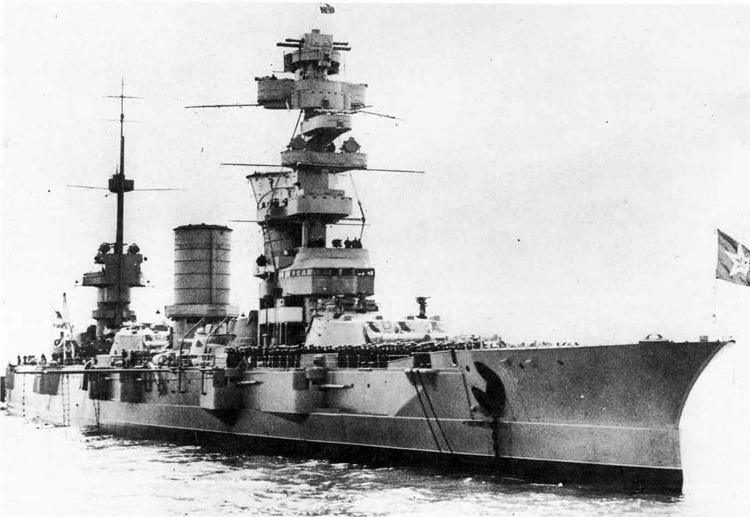

General view
Three main battery triple turrets.
OBB GANGUT
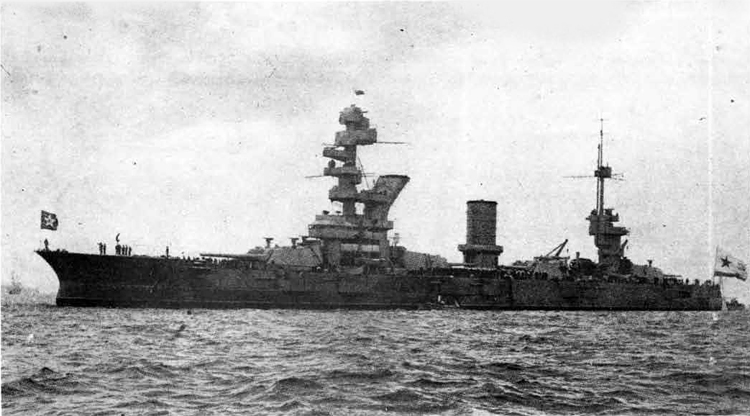
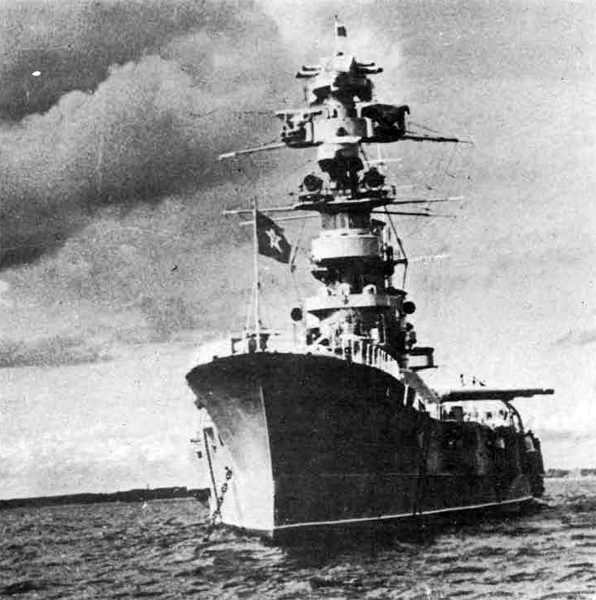


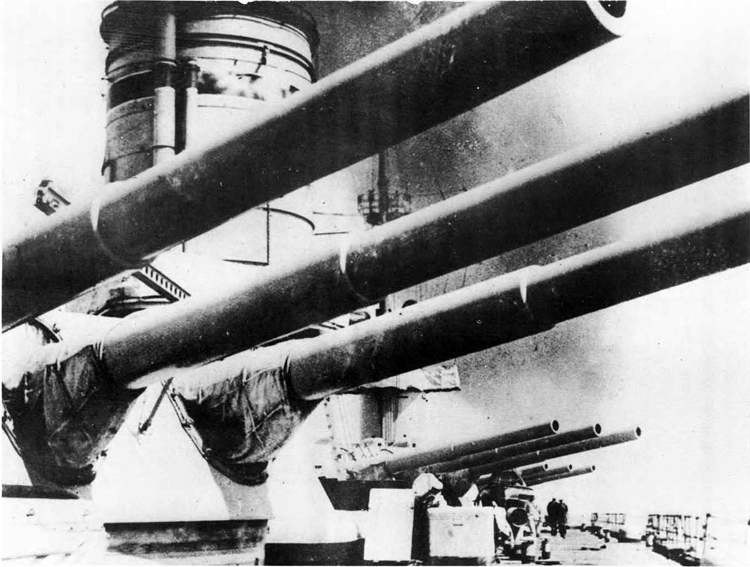
Three main battery triple turrets.
B. CRUISERS
I. HEAVY CRUISERS (Kirov Class)
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Dates laid down: 1935-1938.
Dates completed; 1937-1942.
Standard displacement: 8,000 tons.
Length: W.L. 613'6".
Beam: 57'11" .
Normal draft: 17'11"
Engines: Geared turbines.
Horsepower: 120,000.
Number of propellers: 2, three bladed.
Number of boilers: 6.
Number of fire rooms: " 2.
Maximum speed: 34 knots (designed).
Number of aircraft normally carried: 3.
Launching device: 1 catapult.
Fire control: director control.
Number of searchlights: 5, 36w in diameter. 3 forward 2 aft.
ARMOR
Turret: face about 2 3/4-"; top and sides about 1-3/4". Conning tower: 5 l/2"j four pieces of armor, formed by keys with entrance door aft.
Side: about 2 3/4n; belt about 10 feet wide, from forward side of number 1 turret to afterside of number 3 turret, riveted over shipfs skin.
Main deck: about 1/2" over engine room and boiler room areasj apparently ordinary plate,
ARMAMENT
9 7.1" 50 caliber in triple turrets, maximum range 40,000 yards. Weight of shell, 198 lbs. 6 4W anti-aircraft guns. 4 1.46n anti-aircraft guns. 9 Bofors type automatic guns. 2 Semi-automatic guns.
2 depth charge racks, one on each side of the fantail, hold an estimated total of 20 charges. They are simply inclined slots in the deck, several inches deep at the forward and about 2 feet deep at the after or dropping end, where they are rounded off. The fantail is cut square across and has a slight overhang.
The main batteries are in three triple turrets, two forward and one aft. Each turret is set in a single slide, making individual elevation of guns impossible, but plugging opening in front of turret (face plate), regardless of the angle of elevation. There is only one port opening for all three guns. The muzzles of the guns have a one inch collar screwed on the projecting end of the liner, the collar bearing against the end face of the outside tube. This is apparently to prevent the liner from backing up in the tube and to prevent closure of the plug. The entrance to the main turrets is in the back side. There are no bulkheads between the guns; the turret interior is bright and rough and uncluttered. At zero angle of elevation, gun breeches are about on a level with the deck in the after end of the turret. There is a power loading with loading gear following the guns to permit loading at any angle of elevation.
These units are fitted for minelaying; they normally carry 100 mines.
There are two depth charge rails.
The 6 4" anti-aircraft guns .are in single mountings, 3 to a side. As there is no place under cover'connected to the mine tracks, mine storage must be entirely on the tracks on deck.
There are 3 stereoscopic rangefinders in the Spotting Top, as well
as one to each High Altitude Director; each is 6 meters long.
There is a rangefinder 1 l/2 meters long to each group of 3 Bofors
guns.
6 21" torpedo tubes in triple mounts, placed between the stacks.
GENERAL
There is an after submarine lookout position built around the main
mast.
There is no actual lookout position for aircraft, but plenty of lookouts are spread around with glasses; they have no arcs from which to read off bearings and angles of sight, however. The catapult is underway between the break in the forecastle and the after deckhouse and stack.
There are no hangars for the aircraft. All three planes are very susceptible to damage from bomb fragments. One is placed on the catapult and one on each side of the forward funnel on platforms just before the catapult.
While in port, aircraft is usually not kept on board. There are no wooden decks on these units, but there is a great deal of nonrfire-propfed wood below decks and in tlie cabins. These'units are all riveted with the exception of very few plates on the deckhouse and on.the forecastle which are butt welded. Little light,metal is used in their construction with the exception of cabin doors and on some interior ladders.
They have a very roomy coni'iiELg tower,, with a number of 8 inch by 2 inch eye slits around the walls; the inside diameter of the conning tower is about 14- feet.
The officers1 country is amidships, from just abaft number 2 barbette to the break in the forecastle. The wardroom is first, extending across the ..shop and about 40 feet long. The frames for inside panelling are about 1 1/2 feet inboard from the skin of the ship. Offi- . cers! staterooms are outboard on both sides from the wardroom aft to the break in the forecastle; they are small, some single and some double. The captain's suite is on the boat deck, in a slight abaft position of the conning tower and surrounds the forward half of number one stack.
The space between the inner and outer shell of the stacks is about 10 inches, The metal of the; outer shell is exceptionally thin sheet. These cruisers are lightly built, but well laid out.
DISTINGUISHING FEATURES
2 widely separated broad raking stacks with sloping stack caps. The tower is set at the forward end of the bridge. The upright light tripod masts flank theCstacks; the main mast is heavier. The hull breaks abaft the first stack; it -has''%_ transom stern, and a
relatively long quarterdeck.
The main battery guns are mounted close together.
A French-type multiple rangefinder masthead director is mounted on
the Italian design tower.
Anti-aircraft rangefinders resemble the Kupola type rangefinder seen in large German warsnips with the exception that they have flat roofs.
The hull plating appears to follow French practices. The KIROV class heavy cruiser shows a resemblance to:
Improved Gordi (Soviet destroyer)
Emile Bertin (French light cruiser)
Le Fantasque class (French destroyer)
Narvik class (German deatroyer)
CA VOROSHILOV OR M0L0TOV - Anti-Aircraft Fire.
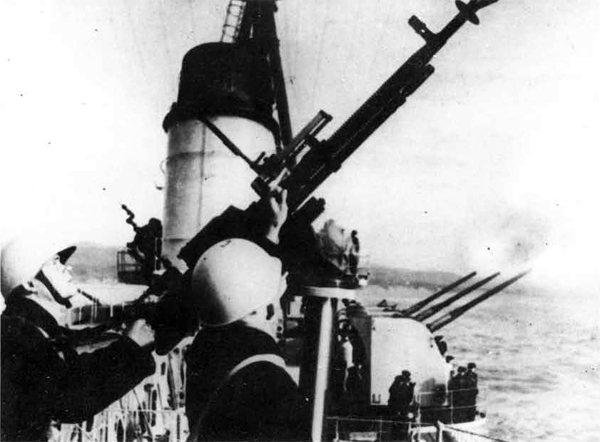

HEAVY CRUISERS (KIROV CLASS)
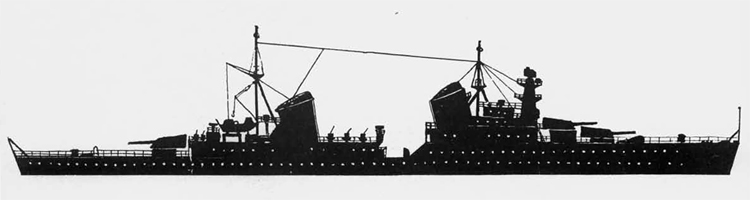
CA KALININ

Closeup of tower on CA. M0L0T0V
HEAVY CRUISERS (KIROV CLASS)
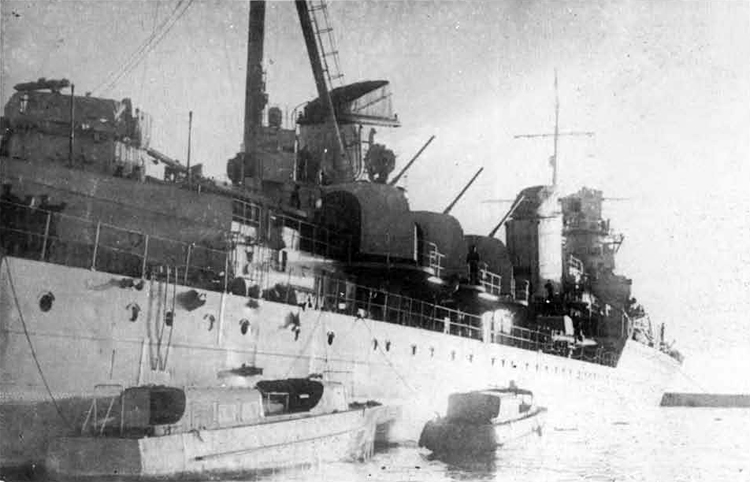
Starboard view of CA MOLOTOV

Closeup of Main Battery AFT. of CA. KIROV
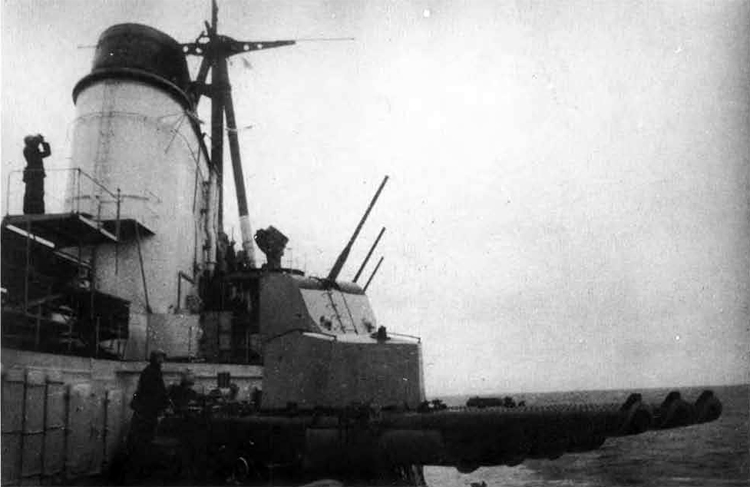

Starboard torpedo tubes of CA. VOROSHILOV or MOLOTOV

Closeup of British Vickers Machine Gun on CA. MOL0T0V
II. OCA KRASNY KAVKAZ
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Date laid, down: 1914
Date commissioned: 1930.
Standard displacement; 8,000 tons.
Length, O.A.: 545 feet.
Beam: 52 feet.
Draft: 19 feet.
Type of machinery: Parson's Turbines.
Horsepower: 60,000.
Number of propellors: 4
'Type-of boilers: Yarrow.
Number of Boilers:- 13.
Full speed: 21 knots.
Cruising speed: 14 knots with a cruising radius of 3,700 miles.
Number of aircraft: 1 seaplane.
Launching Device: 1 catapult.
Number of searchlights: 5.
Fire Control: director control.
ARMOR
Waterline belt: 3"to 2".
Deck: 1".
Turret: 3".
Conning tower: 3".
The conning tower and gunhou.ses appear to have very light armor plating.
No waterline belt is visible, though the hull appears to be built of
thicker plating than'usually used in units of her type and dimensions.
ARMAMENT
4 7.1" 50 caliber guns with a maximum range of 40,000 yards, set in single
turrets.
4 3.5" anti-aircraft.guns (twins).
2 Vickers'anti-aircraft guns.
8 anti-aircraft machine guns.
12 21n torpedo tubes in triple turrets.
Fitted for minelaying normally carrying 200 mines.
Number of depth charge throwers: 4
Some doubt exists as to the effectiveness of the numerically'v/eak battery of this unit;.4 pieces seem hardly sufficient for modern sight control methods.
This unit was originally designed to mount a battery of 5^1<f guns. ^ She mounts an unusually heavy torpedo armament for a heavy cruiser.
GENERAL
The construction of this vessel was field up for many years; she was originally to have been a light cruiser of the same design as the . KRA3NY KRBI and the CHERVOMAIA UKRAJMA (since sunk).
As completed, her design was completely altered; her main battery of 4 7.1U guns places her in the category of heavy cruisers.
In 1934> she presented a considerable fire hazard because of so much wooden construction on board, such as: main deck planking, officers' country (all cabins are made of wood), sleeping accommodations for the crew which are of extremely wide-fixed bench construction all along the interior sides and in which are housed-boards, which pull out as do boards above top drawers of office desks. Both the benches and housed boards are of duckboard effect.
Men sleep athwartships.
The main radio room is on the main deck wrier the bridge; there are 3 smaller additional rooms extending to below ivaterline on the 3 decks and directly below the main radio shack.
DISTINGUISHING FEATURES
The upright thick stacks and multiple leg masks with masthead range finders.
The vertical outline of her mainmast is unique, as are the single gun turrets.
She resembles the iC-uSWY KRUi at angles off the bowj otherwise, she has a very distinctive profile.

Port View.
OCA KRASNY KAVKAZ


Starboard view.
Ill. OCL KRASNY KRIM (Ex PR0FINTERN)
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Date laid down: 1913.
Date commissioned: January, 1925.
Standard displacement: 7,200 tons.
Normal displacement: 7,600 tons.
Length O.A.: 522 feet.
Beam: 54 feet.
Pvieah draft: 21 feet.
Type of machinery: Parson1s or Brown-Curtis Turbines.
Horsepower: 55,000.
Number of propellors: 4
Type of boilers: Yarrow.
Number of Boilers: 13.
Number of aircraft normally carried: 2 seaplanes.
Launching Device: Crane.
Fire Control: director control.
Number of searchlights: 7.
ARMOR
Waterline belt: 2".
Deck: 1 In.
Gun protection: 3"
Conning tower: 3"
This unit has been described as having-3ir armor for the full length under
the main and lower decks, but from inspection it appears that there is no
special side armor; apparently, the hull is built of thicker plating than
usually obtains in vessels of this type and dimensions.
ARMAMENT
11 5.1" 55 caliber guns in single mounts.
4 4.1" anti-aircraft guns in twin mounts.
7 3.5" anti-aircraft guns.
2 Vickers anti-aircraft guns.
6 anti-aircraft machine guns.
6 I8" torpedo tubes in triple turrets.
Fitted for minelaying, normally carrying 60 mines.
This unit may have been rearmed with 7.1" guns and new anti-aircraft
guns, but there is no confirmation of this fact.
GENERAL
This unit proceeded to the Black Sea in 1930 in company with the OBB SEVASTOPOL, staying for repairs at Brest and Naples, where it was reported that her condition'was very unsatisfactory and that only minor repairs would be undertaken.
Her present condition is-unknown, but she was refitted in 1937.
DISTINGUISHING FEATURES
She resembles the OCA KRASNY KAVKAZ; otherwise she has a very distinctive profile.
OCL KRASNY KRIM (Ex PROFINTERN)


OCL KRASNI KRIM (Ex PROFINTERN)
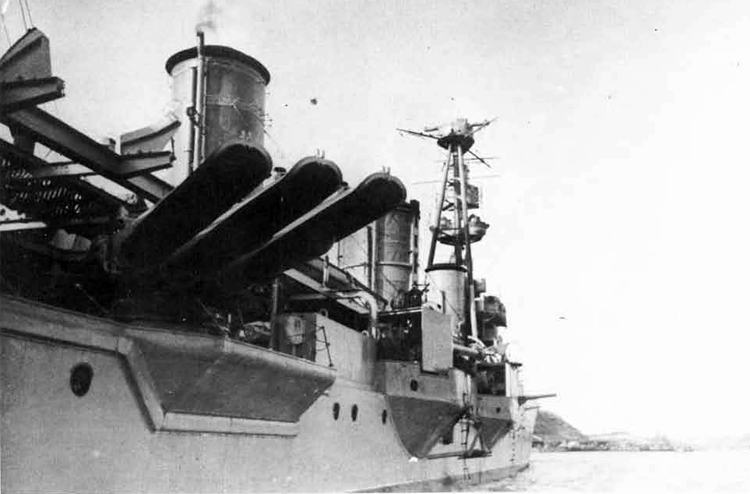
View of a torpedo tube mount.
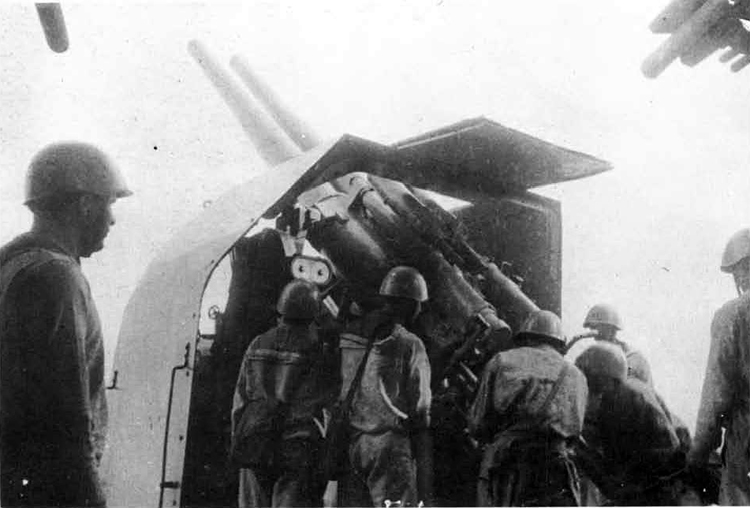

View of twin 4.1" anti-aircraft gun mount.
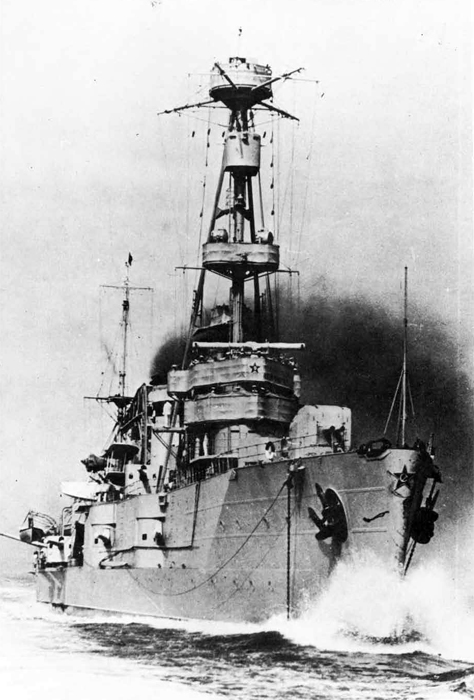
View of foremast of GHERVOMAYA UKRAINA, (KRASNY KRIM class, since sunk)
C. DESTROYERS
I. DESTROYER LEADERS (LENINGRAD CLASS)
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Dates laid down: 1932-1939.
Dates completed: 1935-1942.
Standard displacement: 2,900 tons.
Length: W.L. 4001 3".
Beam: 38' 5".
Normal draft: 10' 10".
Type of machinery: Geared Turbines.
Horsepower: 6.2,000 (designed).
Type of Boilers: Water tube boilers, 3-drum type.
Pull speed: 38 knots (designed).
Fire control: director control.
ARMOR
There are weather shields attached to the guns. No side or deck armor has been reported.
ARMAMENT
5 5.1" 50 caliber guns in single shields.
2 .3" anti-aircraft guns.
2 1.46" anti-aircraft guns.
1 anti-aircraft multiple barrel machine gun.
6 21" torpedo tubes in triple mounts.
Fitted for minelaying, normally carrying 100 mines. 4 depth charge tracks, fitted with racks.
, iB 5.1" gun could have been mounted to greater advantage on the after deck house, just forward of ;jU gun.
There are super-firing single-shield mounts forward and aft with a fifth main battery gun mounted betv-.^n the bridge and forward stack. The center line triple torpedo tube mounts flank the after stack.
GENERAL
Compartmentation is believed to follow the modern practice for vessels of this type.
This class represents the first attempt of the U.S.8.R. in construction of larger warships.
They are reported to be poor seaboats—veiy top-heavy and wet forward.
DISTINGUISHING FEATURES
The design of this class reflects French influence; they resemble French contretorpilleurs of recent design.
2 separate tall raking stacks without stack caps; the first stack is broader and the second stack is slightly more raked.
There is a tall bridge and upright pole foremast stepped at the after edge of the bridge; an upright light tripod mainmast is set just forward of the after stack.
The spacing and shape of the stacks and of the bridge gives this class a very distinctive appearance.
DESTROYER LEADERS (LENINGRAD GLASS)

DL MOSKVA (since believed to have been sunk)
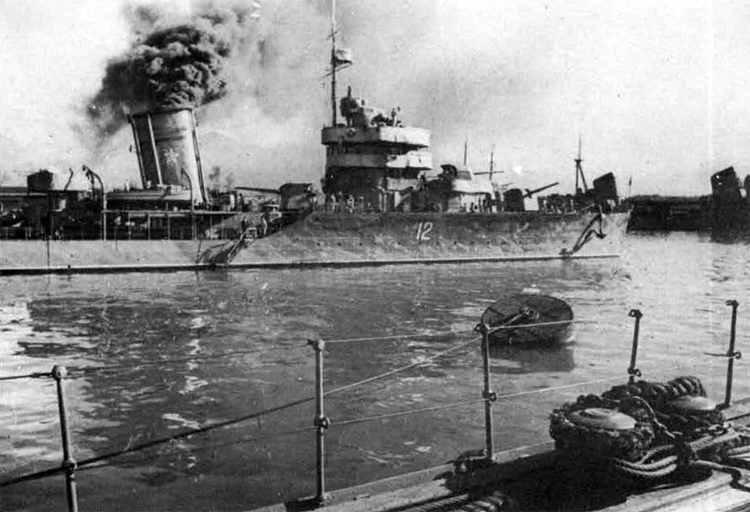

DI KHARKOV
DESTROYERS LEADERS (LENINGRAD CLASS)
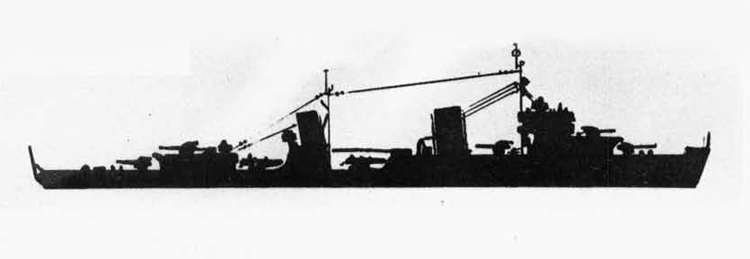
Silhouette of DL "TBILISSI".
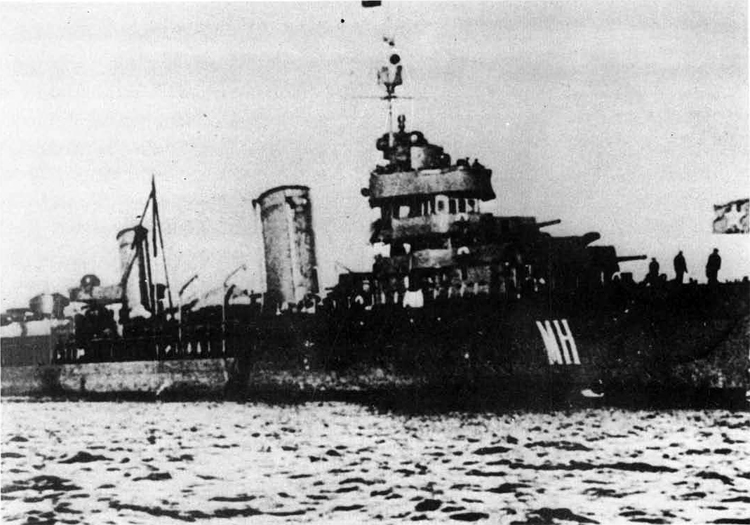

DL MINSK (since sunk)
II. DESTROYERS (IMPROVED GORDY CLASS)
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Dates completed: 1939-1941.
Standard displacement: about 1,800 tons.
Length O.A.: about 375 ftet.
Beam: about 35 feot.
Mean draft: about 12 feet.
Speed: 37 knots.
ARMAMENT
4. 5.1" guns in single shields.
2 3" anti-aircraft guns.
2 1.4.6" anti-aircraft yuns.
6 21" torpedo tubes, set in two triple mounts on the main deck.
Fitted for minelaying.
Super-firing gun positions are forward and aft.
GENERAL
Little infornation is available on this type.
They are indicative of the latest trend-in Soviet destroyer construction.
These units are of Italian design.
DISTINGUISHING FELATURES
Two separate raking, squat, flat-sided stacks with sloping stack caps.
A ranking pole mast is stepped just forward of each stack.
Super-firing gun positions are forward and aft.
There is a long bridge with a prominent director placed nenr the foremast.
Prominent deck houses are abaft the forward stack and forwai"d of the
after stack.
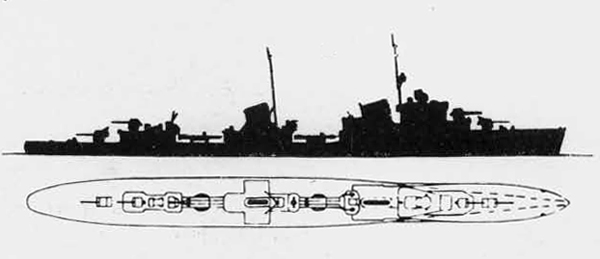
Silhouette of DD of the improved GORDY Class.

DD of the improved GORDY Class in the Black Sea.
III. DESTROYERS (MODIFICATION OF THE IMPROVED GORDY CLASS)
GENERAL
A modification of the Improved Gordi Class destroyer has been built; little or no information is available on this type.
It has been reported that only one unit of this class has been built; her location is not known.
DISTINGUISHING FEATURES
This type has only one shield gun mounted on the forecastle. The first stack is thinner than the second.
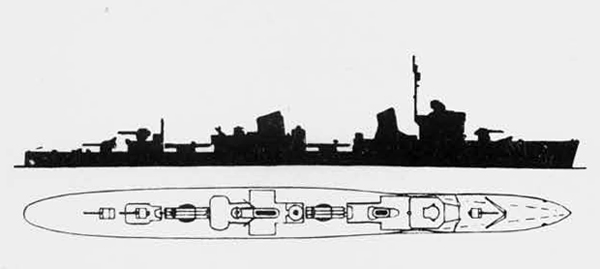
Silhouette of the modification of the DD of the improved GORDY Glass.

Modification of a DD of the improved GORDY Class.
IV. DESTROYERS (GORDY CLASS)
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Dates laid down: 1937-1940.
Dates completed: 1938-1941.
Standard displacement: 1600 tons.
Length: O.A. 375', W.L. 364'.
Beam: 33' 6".
Normal draft: 9'7".
Type of machinery: Geared Turbines
Horserpower: 4.6,000 (designed) .
Type of boilers: 3-cirum tnie.
Number of boiler roons: 3
iJumber of firo rooms: 2.
Full speed: 37 knots.
ARMAMENT
4- 5.1" 52 caliber guns with a maximum elevation of 4-5 and a maximum
range of 26,000 yards.
2 3" anti-aircraft guns with a maximum elevation of 85° and a maximum
range of 4.500 yards.
2 1.46" anti-aircraft guns.
2 Bofors type guns.
6 21" Torpedo tubes, in two triple mounts.
These units are equipped for minelaying, usually carrying 100 mines.
Depth charges are fir^d only froir. a trap; there are no throwers. The
charges are set to "safe" until the actual subnarine report is received.
A super-firing shield runs forward and aft.
On the units observed, the armament was very well kept.
GENERAL
Air lookout is of a very high standard. Everybody on deck acts as a
lookout.
Using all the boilers, the maximum speed is 37 knots; using two, it is
about 28 knots.
One unit of this class I'q said to lave re-ached 40.2 knots on trials.
These vessels are very maneuverable anil-although the hulls are lightly
built, they stand up well to their own gunfire.
There is no splinter protection anywhere.
There are no rcidio direction finders.
These vessels are said to be much better seaboats than the LENINGRAD
class destroyer leaders; they are of Odero-Terni-Orlando (Italian)
design.
DISTINGUISHING FEATURES
A single broad raking stuck with a sloping stack cap, placed close abaft
the bridge.
2 raking pole masts.
There is a proi.inent director on the bridge.
There is a wide transom stern.
These u,iits are similar in appearance to: "0" to "T" classes (British destroyers); T-l class (German torpedo boat); Grecale class (Italian destroyer). They bear a resemblance to the Li. S. destroyer escort series.

A Gordy Class DD underway in the Black dea.
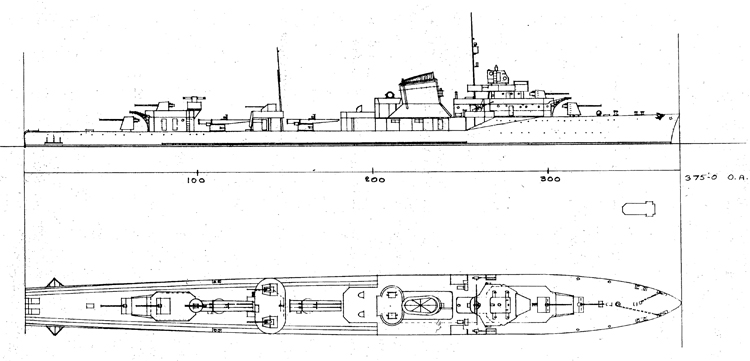
GORDY CLASS
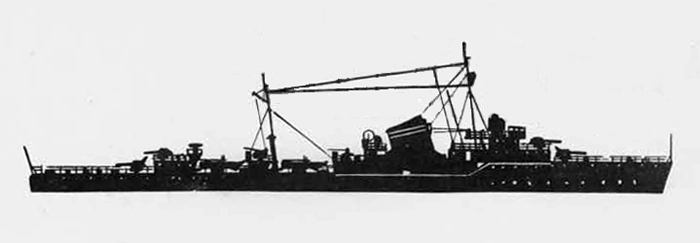
Silhouette of DD RIYANY.
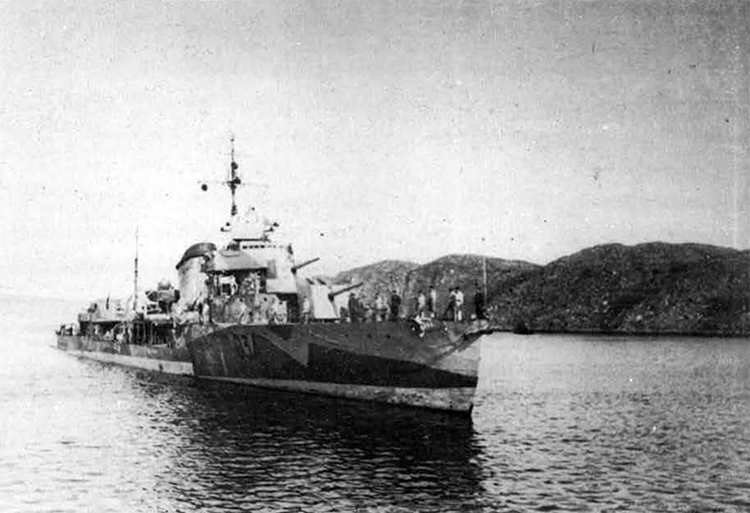

A DD of the Gordy Class, attached to the Northern Fleet.

DD STREMITELNY
DESTROYERS (GORDY CLASS)
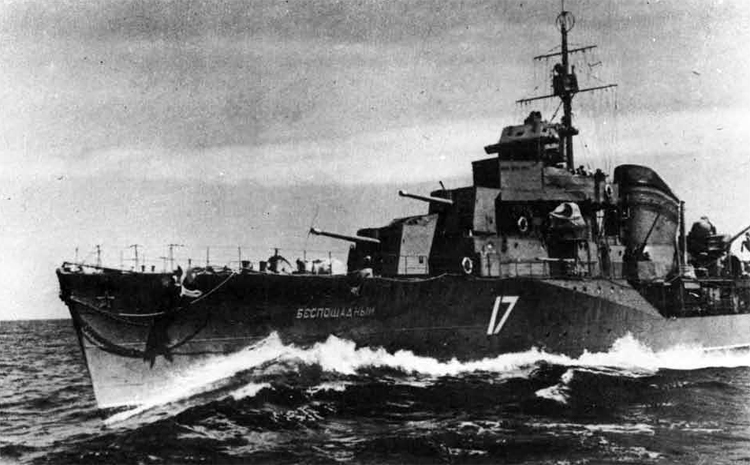

DD BESPOSHCHADNY

Forward gun mounts on the DD SOOBRAZITELNY
DESTROYERS (GORDY CLASS)

Streaming a paravane aboard the DD BOIKI
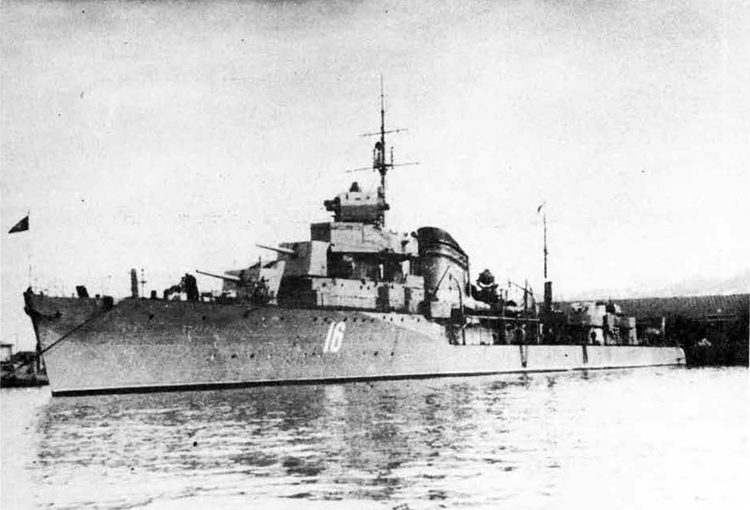

DD BOIKI
V. OVERAGE DESTROYERS (PETRQVSKI GLASS)
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Date laid down: 1916.
Dates commissioneds 1917-1928.
Normal displacement: 1,300 tons.
Length O.A.: 303 feet.
Beam: 30 feet.
Mean draft: 10 feet.
Type of machinery: Parson's Turbines.
Designed horsepower: 29,000.
Number of propellors: 2.
Type of boilers: Thornycroft.
Number of boilers: 5
Pull speed: 28 knots with a maximum radius of 720 miles.
Cruising speed: 22 knots with cruising radius of 3,100 miles.
Number of searchlights: 2.
ARMAMENT
4 3.9" guns.
2 7 pounder high altitude guns.
1 1.46" anti-aircraft gun.
4 machine guns.
12 18" torpedo tubes, set in four triple cent€:rline mounts, one between
the first stack and foremast and one behind each stack.
Fitted for minelaying. '
Number of mines usually carried: 50.
One open mount gun is placed on the short forecastle; two are placed on
the quarterdeck; and the fourth is placed on the afterdeck house in a
super-firing position.
GENERAL
Although this class represents the most powerful class of destroyer built under the imperial regime, their present efficiency is doubtful.
None of these units have even approached the designed speed of 33 knots under the Soviet flag.
The "Felix Dzherzhinski"was sunk during the Russian Revolution, but was raised in 1925 and refitted in 1928-29.
DISTINGUISHING FEATURES
Three evenly spaced low raking stacks, with slanting tops.
Two raking pole masts.
Deck house between second and third stacks extends outboard flush with
ship's sides.
Triple torpedo tube centerline mounts flank the first stack.
These units have a very distinctive profile; they are very similar to
the URITSKI Class.
OVERAGE DESTROYERS (PETROVSKI CLASS)
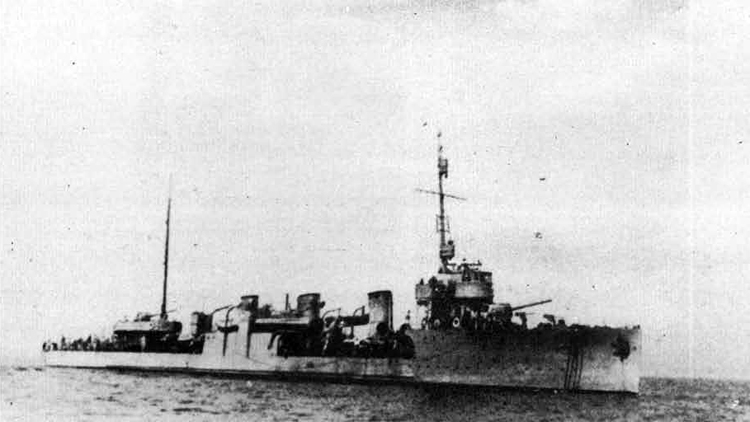
ODD of the PETROVSKI Class.
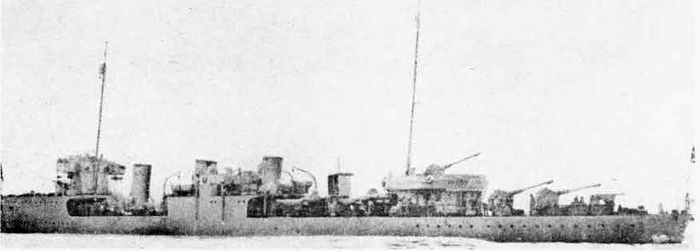
ODD SHAUMYAN
OVERAGE DESTROYERS (PETROVSKI CLASS)
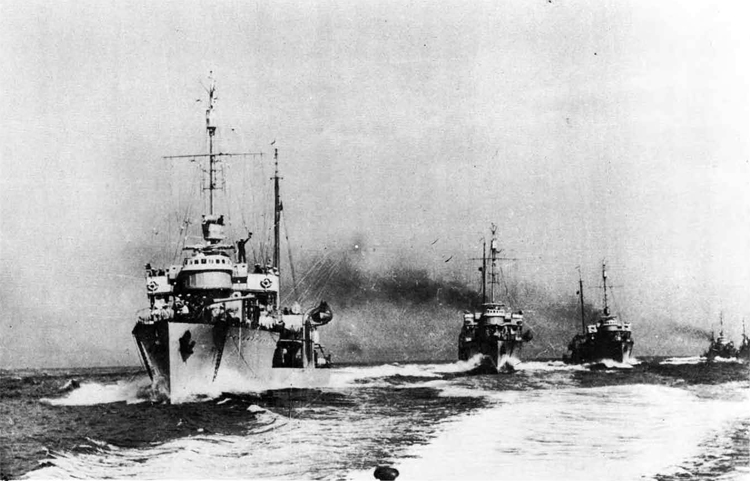

ODDs of the PETROVSKI Class underway.
VI. OVERAGE DESTROYERS (URITSKI CLASS)
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Date laid down: 1913. Dates co; Dieted: 1915-1917. Normal displacements 1,280 tons. .. Length O.A.: 321 feet. ' Beam: 31 feet. Maximum draft: 10 feet. Type of machinery: AEG/Vulcan Turbines. Horsepower: 30,000 (designed).
Number of propellors: 2
Type of boilers: Thornycroft.
Number of boilers: 4. Pull speed: 28 knots.
Cruising speed: 15 knots with a cruising radius of 700 miles. Economic speed: 10 knots with a radius of 2,800 miles. Number of aircraft normally carried: 1 seaplane. Number of searchlights: 2.
ARMAMENT
4 3.9" guns with a maximum range of 16,000 yards.
2 3" 23 caliber high-altitude guns.
2 machine guns.
9 18" torpedo tubes, set in three triple centerline mounts, one behind
each stack.
Fitted for rninelaying.
Number of mines normallHy carried: 50-80.
One open gunmount is placed on the short forecastle and three aft.
Battery control is apparently local.
Torpedo control is elemental, similar to that on old U. S. Iowa's.
These units are equipped with electric heating apparatus for torpedoes,
to prevent their freezing in the water.
GENERAL
These units were designed in Germany, built in Leningrad.
The STALIN has been reconstructed and differs from the rest of this
class in appearance.
In August, 1943, the U. S. Naval Attache, Moscow, visited one of these
units which was attached to the Northern Fleet; he found her to be in
good condition and clean, especially as regards to essentials such as
care in painting around moving parts.
DISTINGUISHING FEATURES
The spacing of the 3 stacks and the superstructure give this class a
distinctive appearance.
The stacks are spaced unevenly and are low' raking with slanting tops.
There are two raking pole masts.
The deck house between the second and third stacks extends outboard
flush with ship's sides.
These units differ chiefly from the PETROVSKI Class in that they lack a
torpedo tube mount between the first stack and foremast and lack a
super-firing gun aft.
OVERAGE DESTROYERS (URITSKI CLASS)
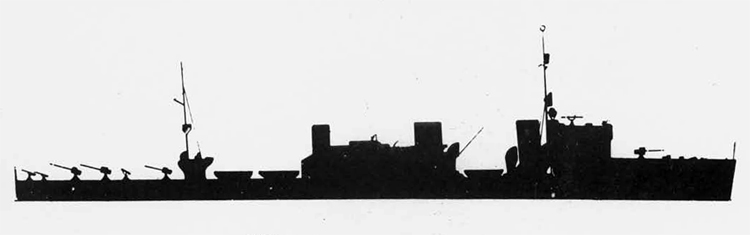
Silhouette of ODD STALIN.
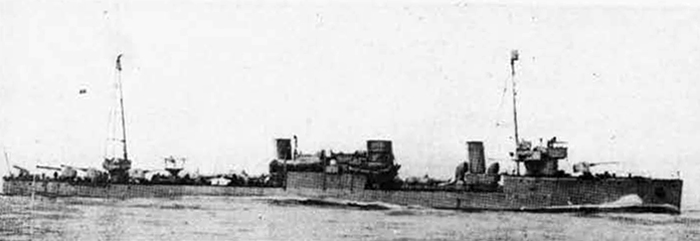
ODD Ex RYKOV
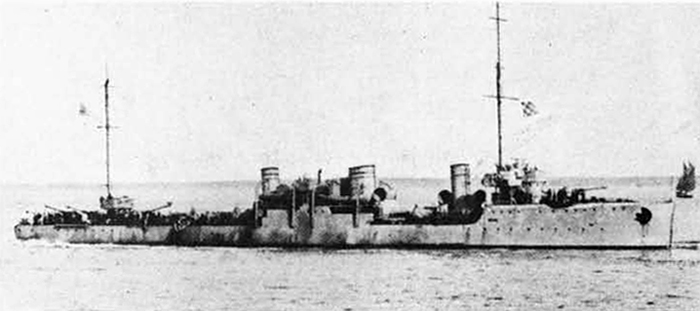
ODD ENGELS
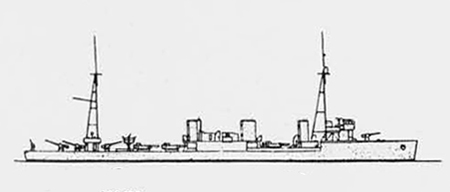
Silhouette of ODD KARL LIBKNECHT.
VII.OVERAGE DESTROYERS (YAKOV SVERDLOV)
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Date completed: 1915.
Standard displacement: 1,200 tons.
Normal displacement: 1,320 tons.
Length 0.A.: 336 feet.
Beam: 31 feet.
Maximum draft: 10 feet.
Type of machinery: Vulcan Turbines (AEG type)
Horsepower: 33,000 (designed).
Number of propellors: 3.
Type of boilers: Vulcan.
Number of boilers: 6.
Full speed: 28 knots.
Cruising speed: 21 knots with a cruising radius of 2,000 miles.
Number of searchlights: 2.
ARMAMENT
4 3.9" guns with a maximum range of 16,000 yards. 1 3".23. caliber high-altitude gun.
1 1.4-6" anti-aircraft gun.
2 machine guns.
Fitted for minelaying.
9 18" torpedo tubes, set in three triple centerline mounts. Number of mines normally carried: 80.
GENERAL
In 1915 on trials she made 35.7 knots.
She ms built for and served in the former Imperial Russian Navy as the NOVIK.
Her design and original propelling plant was furnished by the Vulcan Yard, Stettin, Germany. Funds for her construction were raised by popular subscription; she was known as the best destroyer of her day. She was rebuilt and rearmed in 1931. Recent alterations include enlarged bridge, tripod foremast, extended forecastle and alteration in the position of the after superstructure and the mainmast. She is reported as being employed on cruiser duties.
DISTINGUISHING FEATURES
She has 4 stacks.
There is an absence of the amidships deckhouse.
Except for the above differences, she is similar to the PETROVSKI
and URITSKI Classes.
OVERAGE DESTROYER {YAKOB SVERDLOV)
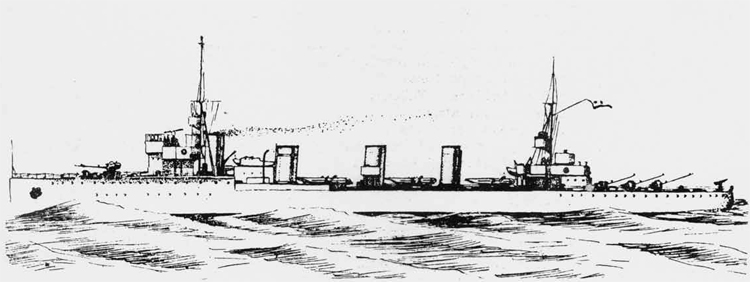
OVERAGE DESTROYS YAKOB SVERDLOV
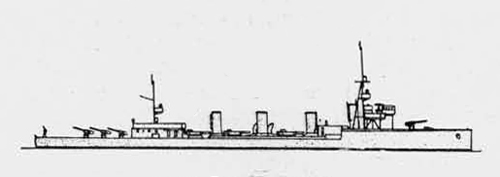
Silhouette of Overage Destroyer YAKOB SVERDLOV

Overage Destroyer YAKOB SVERDLOV
D. ESCORT VESSELS AND TORPEDO BOATS
I. ESCORT VESSELS (ALBATROSS CLASS)
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Length: About 275 feet.
Beam: About 25 feet.
Displacement, full load: About 800 tons.
Number of boilers: 2.
Steam pressure: About 25 atmospheres.
Type of engines: Turbines, main propulsion.
Speed: About 26 knots.
Machinery arrangement: Boiler-engineroom-boiler.
AMOR
Hull plating 4 mm. (unconfirmed).
ARMAMENT
No information available; at least one gun on forecastle.
GENERAL
Little information is available on this class. Two units are under construction at Komsomolsk, having been laid down there in 1940; one is 35% complete, the other about 50$ complete. They may be an improved design of the Shtorm Class torpedo boats (see next page). There is no light metal; or galvanizing.
These units are all riveted; there is no welding except on a few interior non-strength bulkheads.
Rubber and cotton covered electric cable is used inside, reportedly due to a lack of armored or lead covered cable.
DISTINGUISHING FEATURES
In appearance and eventual employment, this class is very similar
to new U.S. destroyer escorts.
They have a flush deck.
They have two strongly raked stacks with the deckhouse abaft number
2 stack.
II. TORPEDO BOATS (SHTORM CLASS)
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Dates completed: 1932-1939.
Normal displacement: 800 tons.
Length O.A.: 251 feet.
Beam: 24 feet.
Liaximum draft: 10 feet.
Type of machinery: Geared Turbines.
Horsepower: 13>2OO.
Number of propellers: 2.
Full speed: 25 knots (designed).
Minimum speed on trial: 21 knots.
ijumber of searchlights: 2.
ARMAMENT
2 4" 53 caliber guns.
3 3" 55 caliber high altitude guna with a maximum range of 27,000 yards.
These boats are excessively armed for their size; a U.S. iJaval officer
describes them as being "but floating turrets".
3 18" torpedo tubes, centerlined in a triple mount.
4 depth charge tracks.
GENERAL
They are reported as being poorly constructed and to roll heavily, owing to'excessive top hampers.
They represent the first attempt of the U.S.S.R. at surface craft construction.
DISTINGUISHING FEATURES
There are 2 separate low stacks; the forward stack is higher and placed
near the break in the forecastle deck.
There are 2 raking pole masts; the main mast is stepped on the small
deck house abaft the second stack.
These boats have a distinctive profile.

Torpedo Boat of the Shtorm Class.
TORPEDO BOATS (SKTOHM CLASS)
Silhouette of the TB VIYUGA.
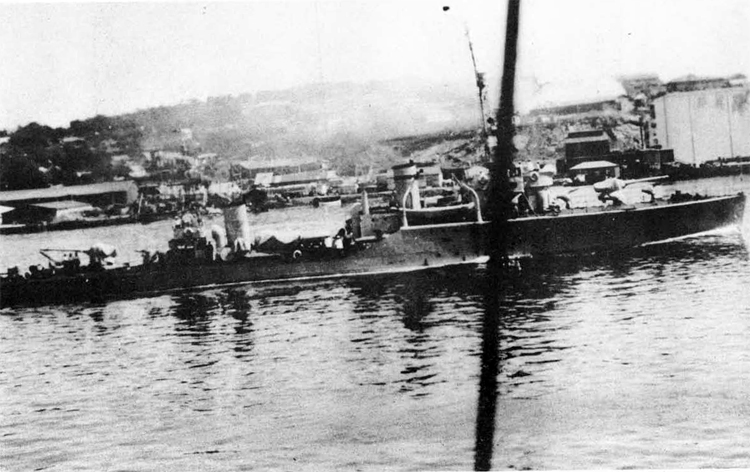

TB of the SHTORM Class in VLADIVOSTOK Harbor in 1938.
III. TORPEDO B0ATS (MATROS CLASS)
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Dates completed: 1938-1939.
Normal displacement: 570 tons.
Length O.A.s 236 feet.
Beam: 23' 6".
Maximum draft! S1.
Horsepower: 6,500,
Full speed: .25 knots (designed).
Cruising speed: 15,.knots with a cru-ising radius of 500 miles.
Economic speed: 10 knots with a radius of 1,980 miles.
ARMAMENT
2 A" guns.
1 1 pounder gun.
I machine guns.
1 13" Torpedo Tube.
Fitted for minelaying, normally carrying 25 mines.
GENERAL
These units are actually small torpedo boats, but are used variously as patrol, escort vessels, minelayers, and minesweepers0 There are believed to be several variations of this class.
DISTINGUISHING FEATURES
They have one low raking stack amidships and 2 raking pole masts (the rig varies in individual units). They have a short forecastle. A A long low main deck. An overhanging squared off stern.
They have a very distinctive profile, presenting a very low silhouette with a notable absence of top hamper.
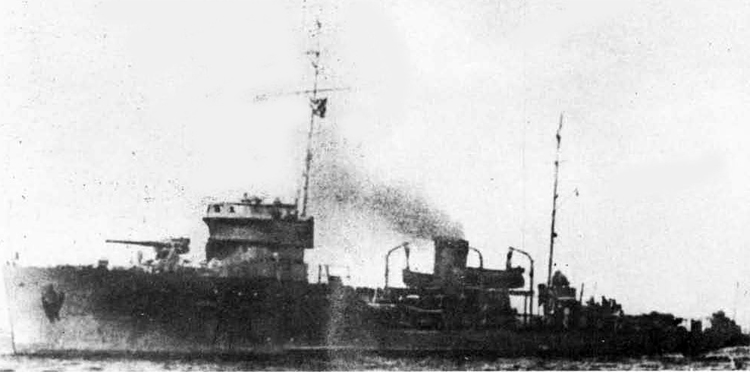
Patrol vessel of MATROS class
TORPEDO BOATS (MATROS CLASS)
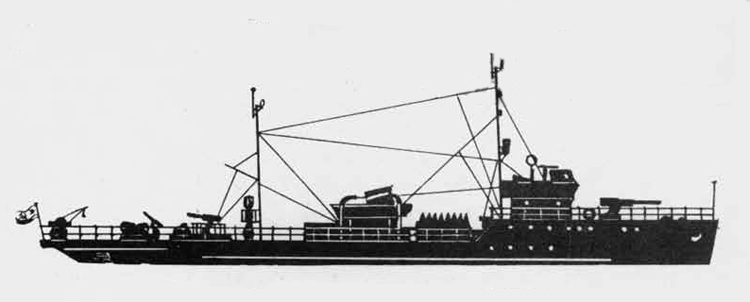
Silhouette of Patrol Vessel STRELA

Patrol Vessels, - PROVODNIK in the foreground and STRELA in the background.
IV. MOTOR TORPEDO BOAT
The bulk of the earlier models of Soviet motor torpedo boats appear to be a modification of since discarded Thornycroft designs. Torpedoes are launched through a trough in the stern. Their standard displacement ranges from 6 to 35 tons; they have a length overall of from 25 to 45 feet, and a beam of from 8 to 12 feet. They cany 1 to 3 13" torpedo tubes and 1 or 2 machine guns.
The U.S.S.R. is beginning to acquire a considerable number of U.S. motor torpedo boats under Lend-Lease; so far, they have received some Higgins and Vosper boats.
The general description of one of the more modern Soviet type PT's is as follows:
This class is a V-bottom Sharpy type. The propellers have open strut mountings. The length of the boat is 68 feet, beam 12 feet, draft 3 feet. Displacement is 33.6 tons, while the dead weight of hull and machinery is 30.8 tons. 3 engines are normally installed on this class. Their speed at 2,000 r.p.m. is about 45 miles an hour. A fourth motor is being supplied by the Packard Motor Company and other U.S. manufacturers under Lend-Lease.
MOTOR TORPEDO BOATS
G-5 Type (Pacific Fleet)


Anti-Aircraft Gun on a Motor Torpedo Boat.
E. SUBMARINES
Although the USSR has built 7-8 distinct classes of submarines, they are not easily distinguishable, h.s it has been a practice ±n Soviet submarine construction to vary these classes to such a degree that often one class, even upon close observation, can easily be mistaken for another, and, in fact, one may be almost identical to another.
I. SUBMARINES ("K". IMPROVED PRAVDA CLASS and "P". PRAVDA CLASS)
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Date commissioned: 1935-1941.
Standard surface displacement: 1,500 tons.
Normal submerged displacement: 1,600 tons.
Length, W.L.: 282 feet 2 inches.
Beam: 22 feet 2 inches.
Normal surface draft: 11 feet 11 inches.
Full surface speed: 18 knoLa.
Full submerged speed: 8.5 knots.
Cruising surface speed: 9 knots with a cruising radius of 7000miles.
Cruising submerged speed: 5 knots, t/ith a cruising radius of 125 miles.
Horsepower: 4,200 (designed).
ARMAMENT
2 4.1" guns with a maximum range of 18,000 yards.
2 1.46" anti-aircraft guns.
2 machine guns. (?)
8 or 10 21" torpedo tubes.
Fitted for minelaying.
Number of mines normally carried: 18.(?)
GENERAL
They are the largest submarines yet designed and constructed under the
Soviet regime.
From exterior appearances and design, they show Italian influence.
The chief difference between the K and P classes is in the shape of the
conning tower; there are possibly other variations in dimensions and
armament. The tonnage of the K class may be slightly higher than that
of the P class.
They are said to be quite a successful tvpe of boat, capable of rapid
diving.

"K" Class submarine.
SUBMARINES ("K", IMPROVED PRAVDA CLASS and "P", FKAVDA CLASS)

"P" Class submarine
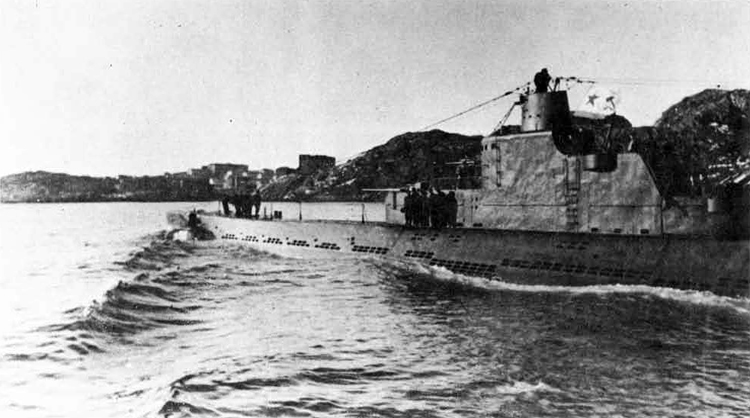

"K" Class submarine (?) attached to the Northern Fleet.
SUBMARINES "K" CLASS
Loading a torpedo on a K (?) Class submarine.
II. SUBMARINES ("L". LINEINAYA LODKA CLAS3)
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Dates commissioned: 1932-1941.
Normal surface displacement: 1,300 tons.
Normal submerged displacement: 1,500 tons.
Length O.A.: 266 feet.
Beam: 24 feet.
Normal surface draft: 13 feet 9 inches.
Type of engines: similar to liAN.
Number of engines: 2.
Type of motors: double armature.
Number of motors: 2.
Type of storage batteries: Triton.
Full surface speed: 15 knots.
Full submerged speed: 8 knots.
Cruising surface speed: 10 knots, with a cruising radius of about
5,500 miles.
Economic surface speed: 8.9 knots.
Economic submerged speed: 5 knots, with a cruising radius of about
110 miles.
Minimum tijne to submerge from normal cruising: 35-45 seconds.
They are of double hull construction.
ARMAMENT
1 4" 53 caliber gun, placed forward of conning tower.
1 50 caliber gun, placed on deck forward.
1 1.46" anti-aircraft gun placed on conning tower superstructure, aft.
8 21" torpedo tubes, six in the bow and two in the stern.
20 torpedoes are normally carried: the spares are stored forward.
Fitted for nn.nelaying, having two stern nine tubes; nine large mifles
or 14. small ones can be carried in each tube.
The U " gun is of light construction, with a sliding breach plug made
watertight by fit of plug; it trains 360° and is very smooth and rapid
in train and elevation.
GENERAL
The sanitary conditions are usually poor.
The general arrangement of this class forward to aft is as follows:
Torpedo tube room.
Torpedo storage and bunk room.
Wardroom and battery room.
Control room.
After battery and bunk room.
Engine room.
Motor room.
SUBMARINES "L" CLASS

"L" Class.
SUBMARINES »L« CLASS
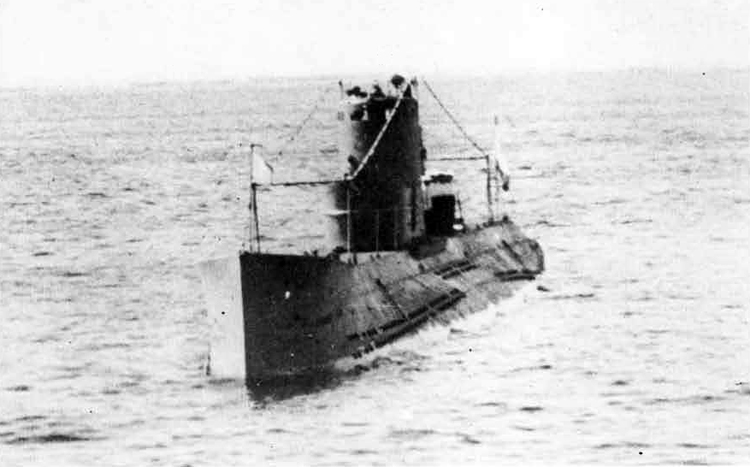
"L-II" Glass
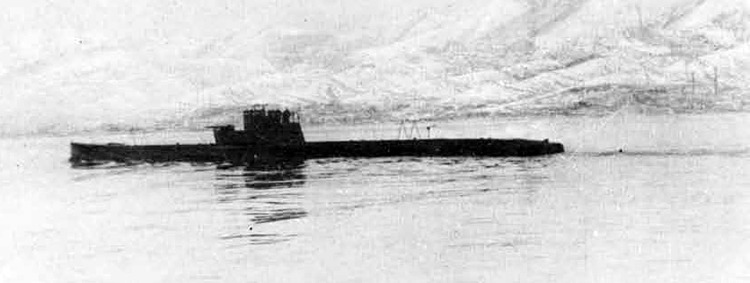
"L-II" Class.
SUBMARINES "L" Class
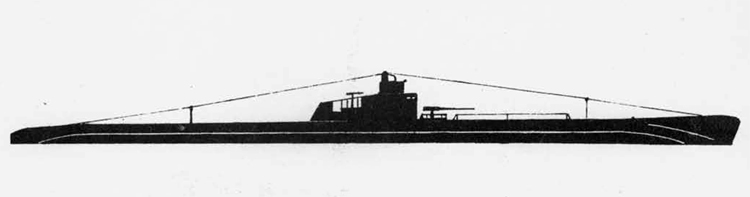
L-8" Class.
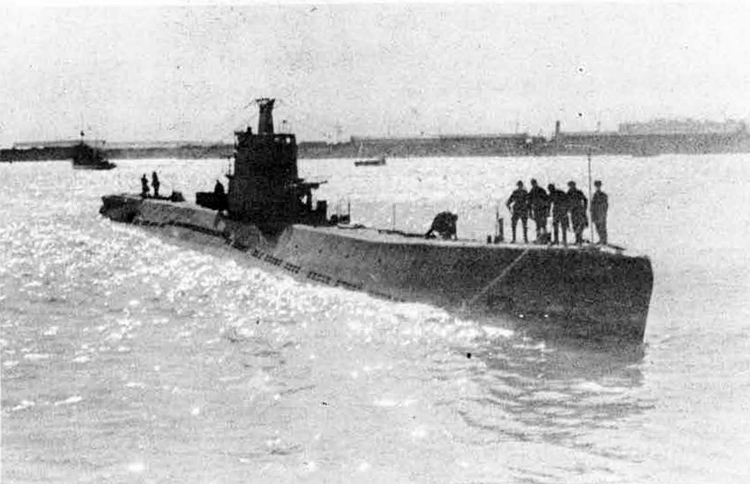

"L-XIII" Class.
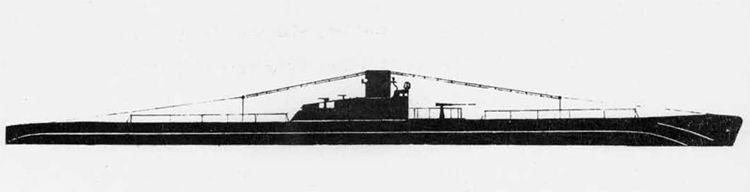
"L-14" Class.
SUBMARINES "L» CLASS
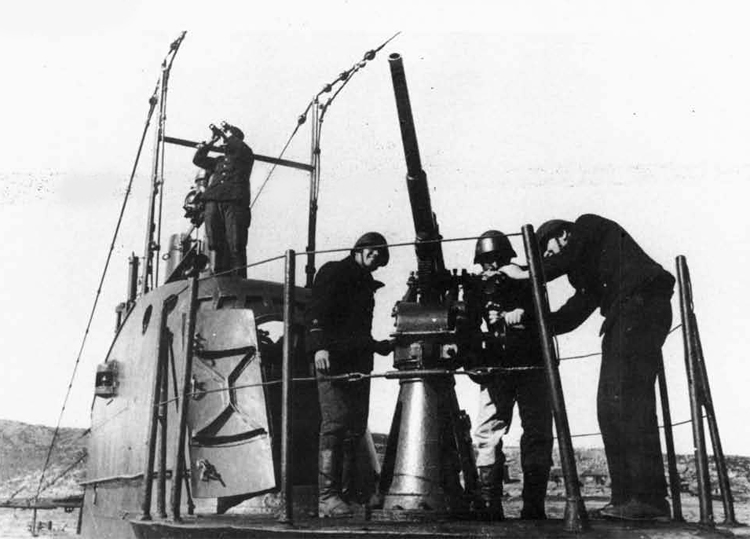
Conning tower of a "L" (?) Glass submarine.
III. SUBMARINES ("D". DEKABRIST CLASS)
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Dates commissioned: 1927-1934-
Normal surface displacement: 920 tons.
Normal submerged displacement: 1,150 tons.
Length O.A.: 241 feet 2 inches.
Beam: 24 feet.
Normal surface draft: 14 feet 1 inch.
Type of engines: Kolomna 6 cylinder, 4 stroke.
Horsepower; about 2,650.
Number of storage batteries: 4 with 56 cells each.
Full surface speed: 15 knots.
Full submerged speed: 8 knots.
Cruising surface speed: 12 knots.
liconomic surface speed; 8 knots (1 engine), with a cruising radiua of
about 5000 miles.
Economic submerged speed: 5 knots with a cruising radius of LID miles.
Number of periscopes: 2.
They are of double hull construction.
ARMAMENT
1 4" gun, placed ibrward of the conning tower on a level with the upper deck, but with a shield built around it.
1 1.46" anti-aircraft gun, placed on the after end of the bridge. 8 21" torpedo tubes, 6 in the bow and 2 in the stern.
10 torpedoes are normally carried there are no reloads for tho MM stern tubee. Torpedoes are usually fired In salvos of three.
GENERAL
Only a very small amount of fuel oil is carried, 30 tons under the batteries; about 100 tons additional can be carried in two external M.B. tanks.
These boats are under batteried; they have insufficient HP air compressor power. All in all, they are not a very popular type of boat.
SUBMARINES ("D", DEKABRIST CLASS)
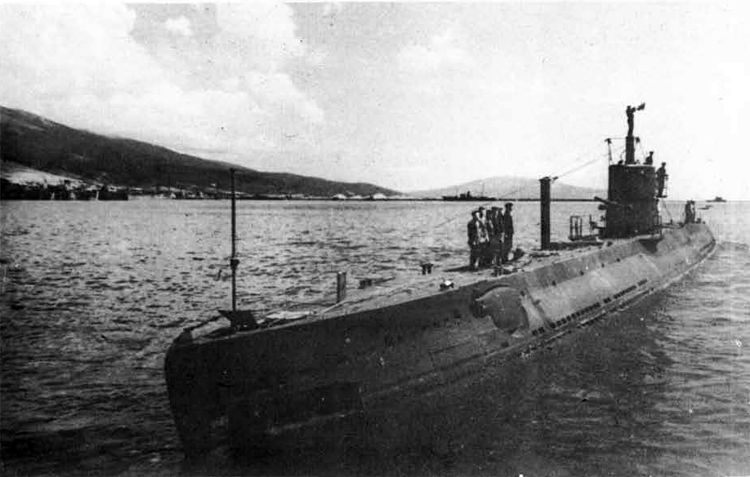


SUBMARINES ("D», DEKABRIST GLASS)
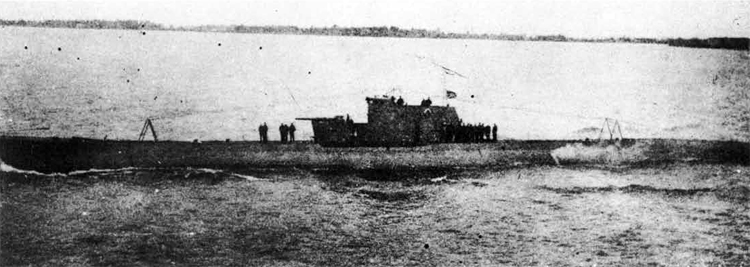
IV. SUBMARINES ("S" 5TALINET5 CLASS)
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Dates conpleted: 1940-1941
Normal surface displacement: 750 tons.
Normal submerged displacement: 1,000 tons.
Length, O.A.: 255', W.L.248'10".
Beam: 15' inside, 181 outside.
Normal surface draft: 12'6".
Normal submerged draft with periscope showing: 48'6".
Type of engines: Diesel Kolomna.
number of engines: 2.
Number of storage batteries: A3.
Full surface speed: 22 knots.
Full submerged speed: 9 knots, with a radius of 108 milts.
Cruising surface speed: 16 knots, with a cruising range of 16,000 miles.
Economic surface speed: 11 1/2 knots, with a radius of 9,000 miles.
Economic submerged speed: 3-4 knots.
Number of periscopes: 2 - the periscope is 36' above the deck when
extended. They are about 20" long, and have a diameter of 0".
Type of radio transmitters: Master Oscillator, Intermediate Amplifier,
and Power Amplifier type.
Engine speed:. 300-550 R.P.li.
Shortest time to submerge from normal cruising: 40-50 second.
The test depth is about 300 feet, although guage shows 480 feet.
No hydraulic systems are fitted.
ARMAMENT
1 4" 53 cal. gun forward of the conning tower on deck; it has a maximum elevation of 75°. 1 4-5 mm. High Altitude gun located on the cigarette deck.
6 21" torpedo tubes, 4 in the bow and 2 in the stern; a total of 6
spare torpedoes are noii/iflK^^pr ed aft and forward.
Torpedo tubes appear to be mads if ,steel, with one riveted seam;
the inside finish is rough and painted. ,
Torpedoes have a maximum speed of 36 knots.
These boats are not equipped to lay mines.
GENERAL
They have simple, easily understood operational characteristics— are fully capable of keeping the sea and fighting well. The ventilation below decks is very poor; there is no air conditioning. The general arrangement forward to aft is as follows:
Torpedo tube and bunk room. Galley.
Battery room and officers1 quarters. Engine Room.
Control Room. Motor Room.
Officers quarters and wardroom. Torpedo tube and bunk room.
DISTIHGU1SHIMG FEATURES
These boats are dark green in color.
The bridge and conning tower are very small, and the decks have
freedom from obstruction.
The overall silhouette is considered excellent.
SUBMARINES ("S" CLASS)
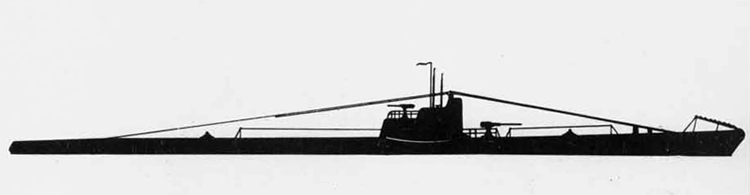
"S" Class.
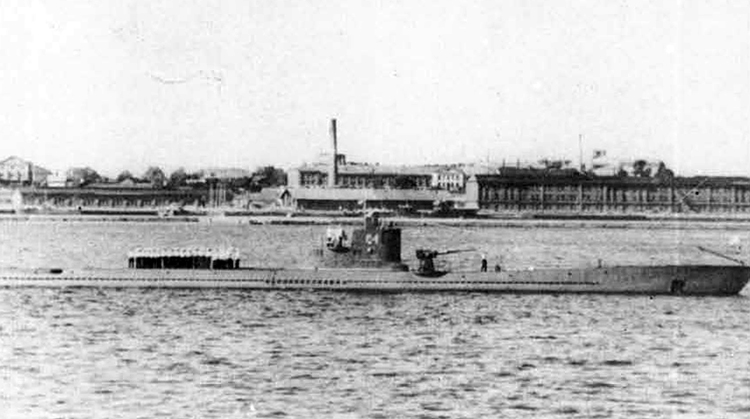
"S" Class.
SUBMARINES ("S" CLASS)

"S" Class (Stern View).
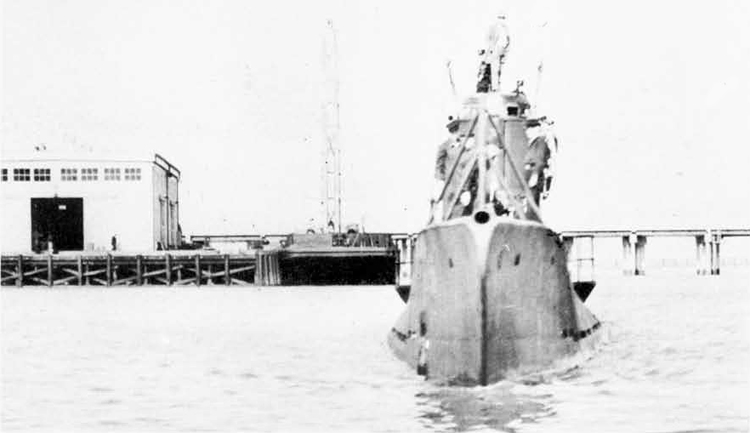

"S" Class (Bow View).
V. SUBMARHiES ("SCHCH" SCHCHUKA GLASS)
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Dates completed: 1934-1937.
Normal surface displacement: 660 tons.
Normal submerged displacement: 820 tons.
Length O.A.: 200 to 225'.
Normal surface draft: 12'10".
Type of enginesi Diesel, Kolomna.
Full surface speed: 14 knots.
Full submerged speed: 8 l/2 (designed).
Cruising surface speed: 10 knots with an approximate cruising radius
of 5,000 miles.
Economic surface speed: 8 knots with one engine.
Economic submerged speed: 5 knots with a cruising radius of 80 miles.
Minimum time to submerge from normal cruising: 55 seconds to 1 minute.
ARMAMENT
2 4.5 mm. guns, one raised forward of the conning tower, and the other
on casing abaft the conning tower.
6 21" torpedo tubes, 4 in the bow and 2 in the stern.
A total of 10 torpedoes are usually carded, including 4 spares.
Bow torpedoes can be only fired two at a time (#1 and HU, or #2 and #3)
GENERAL
These boats are generally popular—are easily handled even in rough seas, but are apt to be a little lively on the surface.
SUBMARINES "SGHCH" CLASS
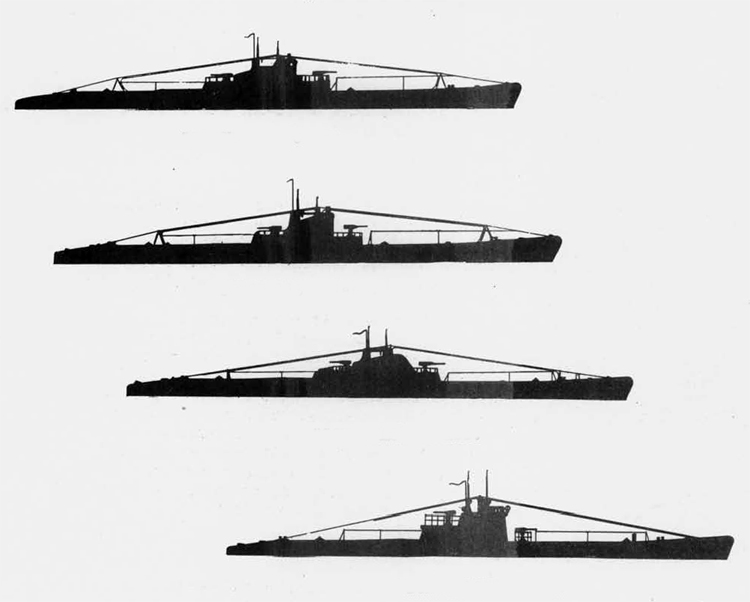
SCHCH-101" Class. "SCHCH-113" Class. "SCHCH-126" Class. "SCHCH-137" Class.

"SCHCH" Class.
VI. SUBMARINES ("M" MALUTKA CLASS)
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Dates completed: 1933-1940.
Normal surface displacement: 204 tons.
Normal submerged displacement: 256 tons.
Length O.A.: 144'4'', W.L. 142'9''
Beam: 10'10"
Engines-revolutions: 600 at 14 knots.
Motors-revolutions: 400 at 5 knots, 200 at 4 knots, 180 at 3 knots.
Full surface speed: 14 knots.
Full submerged speed: 7 knots.
Cruising surface speed: 10 1/2 knots with an approximate cruising
radius of 500 miles.
Economic submerged speed: 5 knots with a cruising radius of 40
miles.
Minimum time to submerge from normal cruising: 40 seconds to 1 minute.
Number of periscopes: 1.
Periscope: H.P. 6, L.P. 1 l/2; (earlier models may have had 4 and
2) frames are placed 1'8" apart.
ARMAMENT
1 1.46" gun.
2 18" Torpedo tubes; no spare torpedoes can be carried.
There is no torpedo hatch; torpedoes must be loaded and unloaded through bow caps with the submarine trimmed up.
GENERAL
In constructing these units, the U.S.S.R. has copied the Scandinavian countries and Germany in building up a force of small, tactically handy submarines for operations in restricted waters. These boats are equipped with good air purification systems and air conditioning, and the air is excellent, even after haying been submerged for 16 hours.
The battery has a capacity of 3,000 a.h. at 6 hours rate. There are 5 m.b. tanks, 3 trinning tanks, and 1 quick diving tank. There are 6 compartments; the motor room and after ends are one compartment.
Many various types of this class have been built (see photographs on the page following). One of the smallest types of this class has a surface displacement of only 160 tons, a full surface speed of 10 knots, and full submerged speed of 5 knots, with a maximum range submerged of one hour at 5 knots. These boats have only four compartments, a torpedo room, control room, engine room, and motor room, the batteries being under the control room deck.
DISTINGUISHING FEATURES
These boats present a rather odd and distinctive silhouette with a disproportionately large conning tower taking up about l/5th of the entire visible length of the hull.
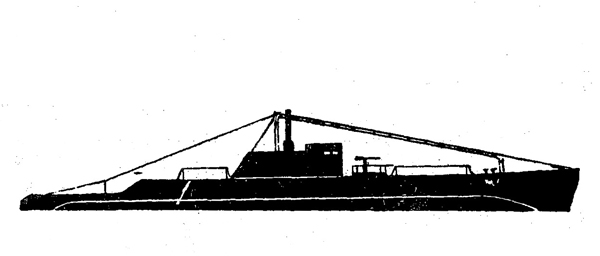
"M-I" Class.
SUBMARINES "M" CLASS.

"M-30" Class.

"M-VI" Glass.
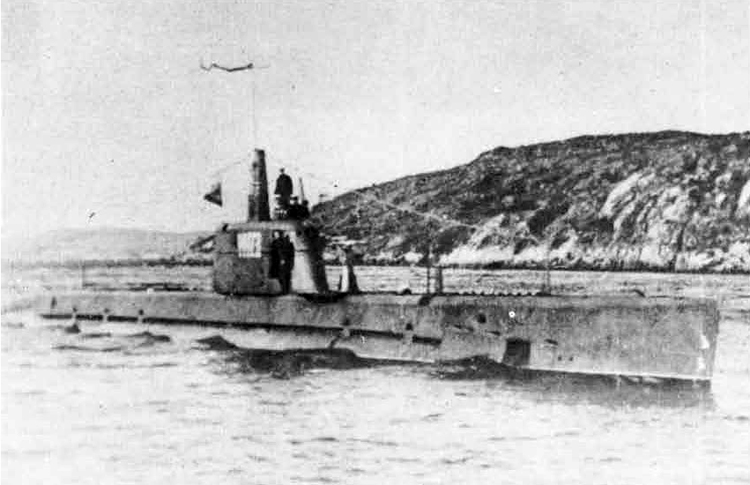
"M-XII" Class
SUBMARINES "M" CLASS
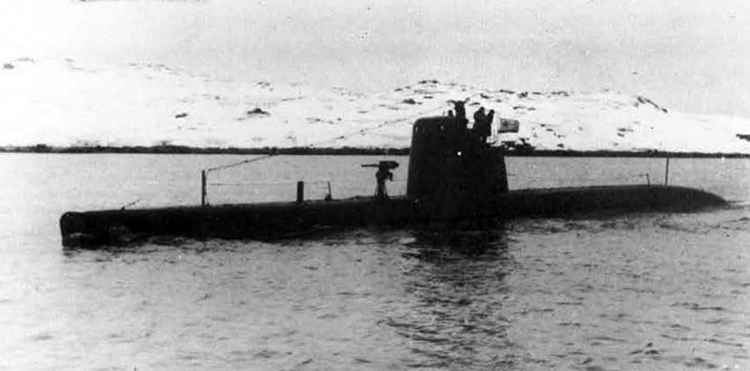
"M-XII BIS" Class.
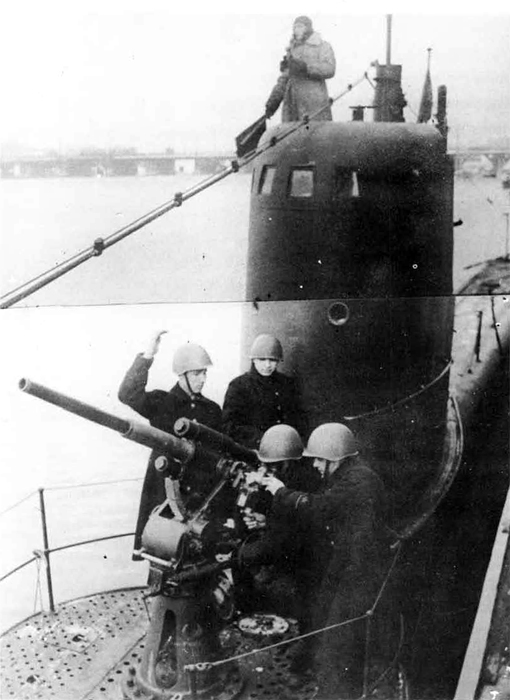

Closeup of Conning Tower and Forward Gun on a M-XII Bis (?)
Submarine in tie Baltic Sea.
VII. OVERAGE SUBMARINES ("B* BOLSHEVIK CLASS)
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Date commissioned: 1916-1917.
Standard surface displacement: 650 tons.
Normal submerged displacement: 780 tons.
Length O.A.: 223 feet.
Beam: 13 feet.
Normal surface draft: 15 feet.
Horsepower of engines: 2,600.
Horsepower of motors: 900.
Full surface speed: 16 knots.
Full submerged speed: 9 knots with a radius of 25 miles.
Economic surface speed: 6 knots with a radius of 3,000 miles.
Number of propellers: 2.
ARMAMENT
2 3" or 6 pounder guns.
1 one pounder anti-aircraft gun.
It has been reported that 1 1.46" anti-aircraft gun has been added
to all boats of this class.
Some boats mount only 1 3" gun.
4 18" torpedo tubes, all placed in the bow.
Fitted for minelaying, normally carrying B mines.
GENERAL
These units were known as the Bubnov Class in the Imperial Navy. At present, they are used primarily for training purposes, but are also employed operationally, when necessity dictates. Two of these boats were reconstructed in 1937; two others were paid off for scrapping in 1938; and still two more were lost by colliabn. Except for the 6 boats now in the Black Sea, it is not known how many are left.
Overage Submarine of the "B" Class
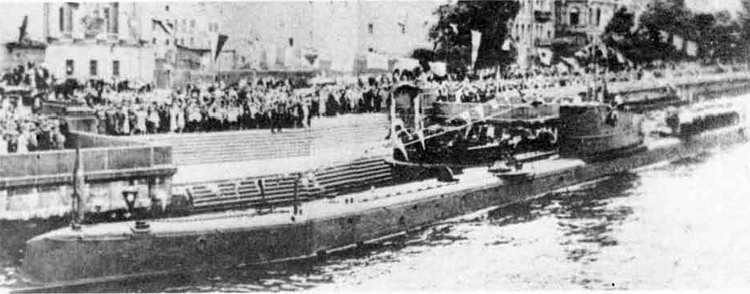
VIII. SUBMARINE RESCUE GEAR IN THE SOVIET NAVY
For rescuing crews of sunken submarines the USSR Navy uses individual rescuing apparati equipped with oxygen, designed to isolate the wearer, which are given to every member of the crew. A rubber suit is given to every man in addition %o the rescuing apparatus, which protects the body from the influence of low temperature of water and air.
The exit of the crew from a sunken submarine in such equipment takes place in the compartments where there are escape hatches.
In the compartments used for rescuing of the crew, there are small
buoys with buoyant ropes, 100 meters long with knots every two meters
checking on the depth of the survivor so that he may take steps to
prevent the bends in accordance with the rules of safe ascent from
great depths. These rules are placed in every compartment with in
structions on how to rise from depths of 100 meters. The rules permit the men to determine at what depth 1D use oxygen and where and
how long to stop,
The.escape hatches, which are used for rescuing the crews have lengthened lower eoaming to which thick canvas jackets, reinforced with metal ribs, are attached, which can be lowered down almost to the floor plates inside the submarine. In addition to the escape hatches for rescuing the crews and conning tower of the submarine and the torpedo tubes can be used as airlocks.
For raising submarines with a rescuing ship or cranes, on the outer hull, in the bow and stern of the submarine; there are special fittings for fastening cables and special ring bolts attached to the pressure hull. For getting air into the submarine from the rescuing ship, the submarine has special valves and tubes in its deck, which lead to the compartments. Through these air and liquid food can be delivered to the crew.
Recent inspection of two Soviet submarines in Komsomolsk, on the Amur River in Eastern Siberia (at approximately 50030* North, l37°East) by a U.S. Naval Officer, corroborates the above information.
F. Minor Naval Craft and Auxiliaries
Except in a very few cases, minor craft and auxiliaries of the Soviet Navy consist of the remnants of the old Imperial llavy, which have little or no operational value today, and ships taken over from the merchant marines; very few naval auxiliaries have been constructed under the Soviet Regime.
I. GUHBOATS


KRASKAYA ABKHAZIA Class Amphibious Gunboats (Black Sea) - are among the first gunboats (built 1909) designed for landing operations. They have a draft of 3.3' forward and 10' aft, a length of 198'.

VOROVSKY, Ex-Yacht (Arctic Ocean)

ZKELEZNIAKOV, Ex-Destroyer (Baltic Sea)
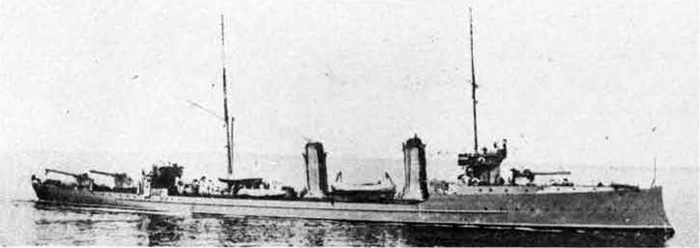
KONSTRUCTOR, Ex-Torpedo Boat (Lake Ladoga)
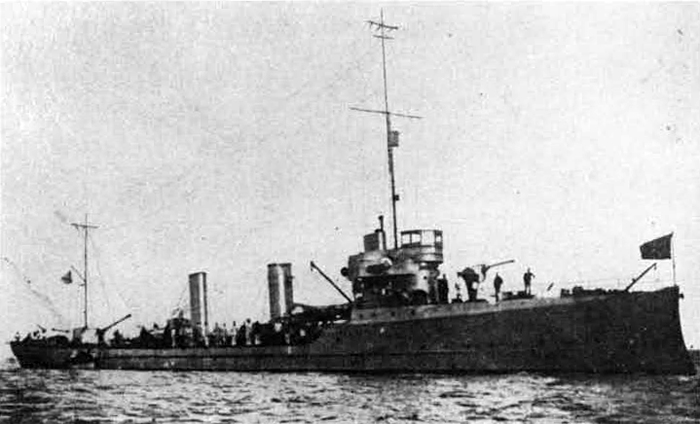
MARKIN Class, Ex-Torpedo Boats (Caspian Sea)
GUNBOATS (Cont.)
II. Minelayers

KRAS1JI AZSRBAIDZKAN Class (Caspian Sea)
ZEYA Class ( Far East)
II. MINELAYERS (Cont.)
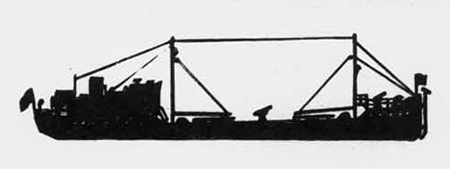
AYAN Class (Far East)
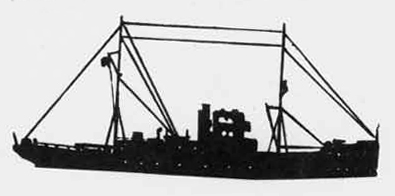
VOROSHILOVSK Class (Far East)
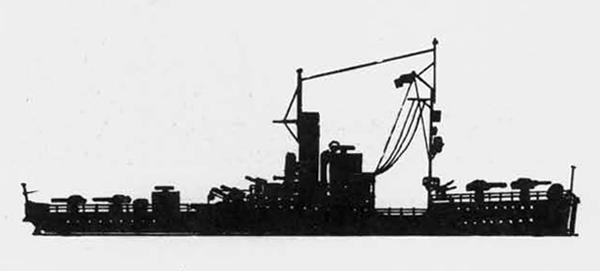
ARGUN Class ( Far East )
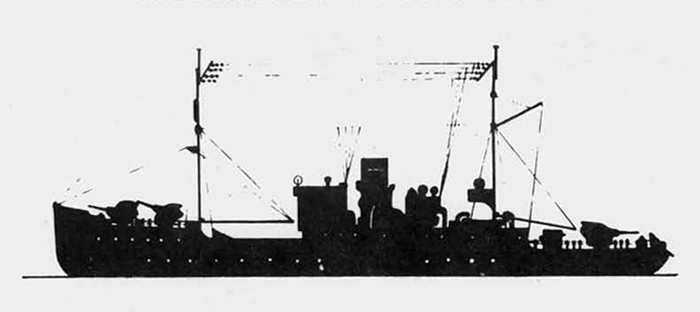
OKEAN Class (Far East)
ABGUN and OKEAN Classes are believed to be former surveying vessels; all other, minelayers shown appear to have been taken over from the Merchant Marine.
III. MINESWEEPERS
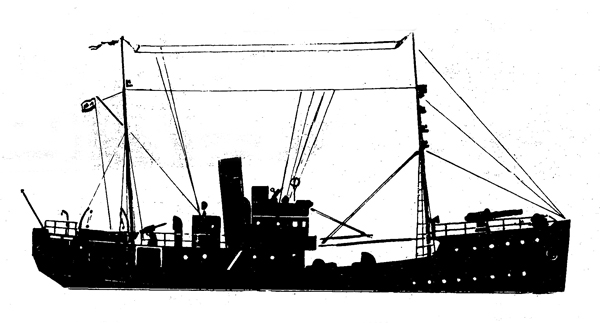
PLASTOON Class (Far East)
BUKSIR Class (Far East)
IV. MOTOR MINESWEEPERS
RIBNY RAZVEDCHIK Class (Far East)
SATURN Glass (Far East)
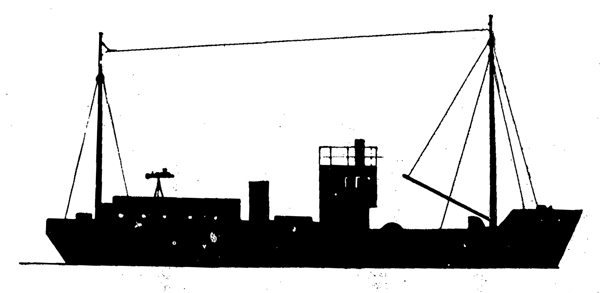
DRIFTER Class (Far East)
BOLSHOI SEINER Class (Far East)
Most minesweepers and motor minesweepers have been taken over from the Merchant Marine and differ considerably in appearance.
The Soviet Northern Fleet has been receiving additional minesweep-ing units from abroad. Even at the beginning of the war, it did not possess a sufficient number of this type of craft, and, due to serious losses, this inadequacy has become worse. At the present time, the 185 foot U.S. minesweepers are being acquired under Lend-Lease for this fleet. Prior to that time, eight former Norweigan whalers, converted to minesweepers (116 feet long), were transferred to it by the British Government. In addition, three British minesweepers, 119 feet long, have been loaned to the Northern Fleet.
Gunnery Training Ship AURORA - former light cruiser (Baltic Sea)
Engineering Training Ship KOMSOMOLETS-former passenger liner (Baltic Sea)
VI. TENDERS
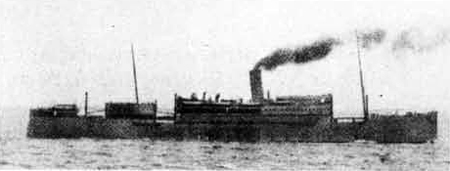
Cadet Training 3hip SVIR-former Dutch passenger liner (Baltic Sea)

Destroyer Tender SERP-I-MOLOT (Baltic Sea)

Destroyer Tender KRASNY GORN (Arctic Ocean)
Submarine Salvage and Repair Ship KOMMUNA (Baltic Sea)
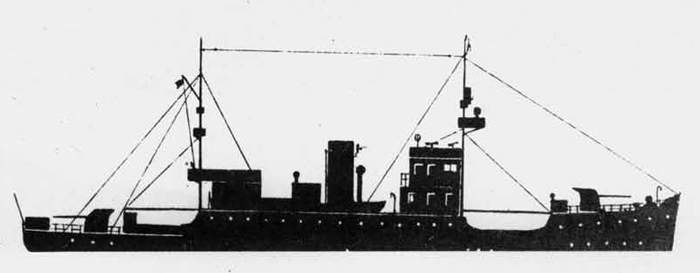
Seaplane Tender PARTISAN Class (Pacific Ocean)
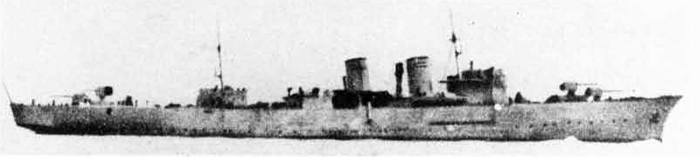
Seaplane Tender 18 MARTA - former Imperial lacht SHTANDART (Baltic Sea)
VII. SUBCHASERS
The MO-IV Class, shown on the next page, appears to be tne prevailing PC design in the Soviet Navy; it is about 30 tons displacement, and has a speed of 25 knots. The silhouette is of a unit in the Far East and the photograph of one in the Arctic.
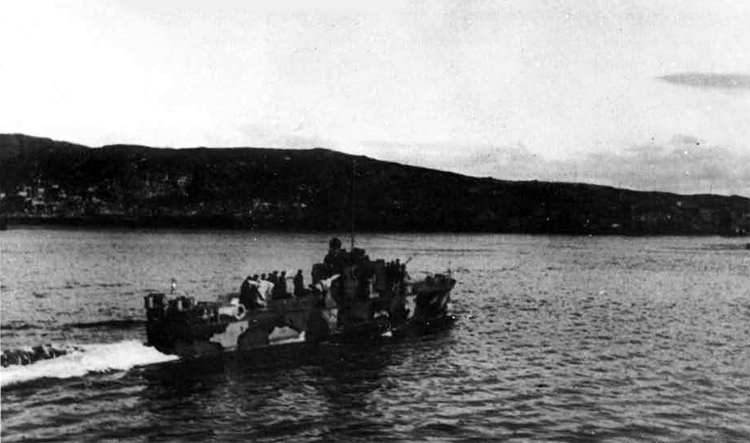

MO-IV Claaa (Arctic Ocean)
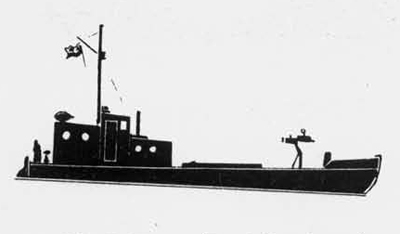
KAVASAKI Class (Pacific Ocean)
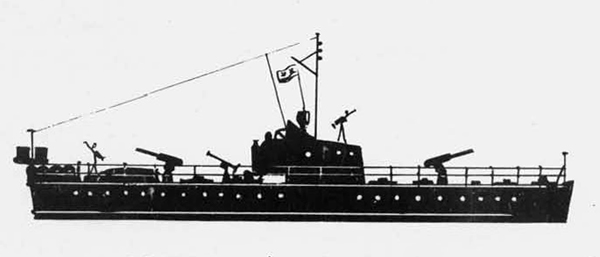
MO-IV Class (Pacific Ocean)
At the present time, the Soviet Northern Fleet is receiving twelve U.S. 110 foot SC's under Lend-Lease; they are all either en route, or will sail very shortly.
VIII. RIVER GUNBOATS
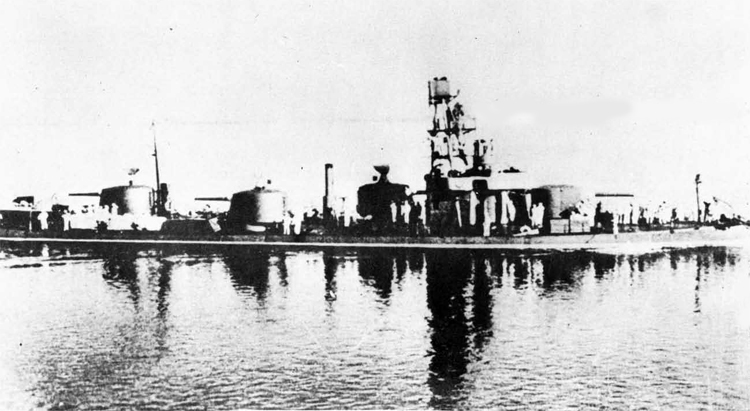
KRASNI VOSTOK Class (Amur River)
IX. ICEBREAKERS
The U.S.S.R. possesses the largest fleet of icebreakers in the world; the Russians consider them as naval auxiliaries.
(a)STALIN CLASS
Especially worthy of note, is this class, composed of three units, which constitute the most powerful icebreakers in the world.
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Dates completed: 1938-1941.
Standard displacement: 11,000 tons.
Length O.A.: 348'.
Beam: 70'
Maximum draft: 32'.
Type of machinery: 3 reciprocating engines.
Horsepower: 10,000.
No. of propellers: 3.
Fuel consumed: Goal.
Full speed: 15 knots.
Cruising speed: 10 knots with a cruising radius of 3,000 miles.
Aircraft normally carried: 3 seaplanes launched by 2 catapults.
ARMAMENT
4 4" guns - 2 forward and 2 aft.
8 Oerlikon guns.
6 12.7 mm. machine guns.
GENERAL
These units can break ice over 6 1/2 ft. thick at an average speed of 1 knot.
In order to break thick ice, the prow of the vessel is run up onto the
ice.
Simultaneously, 1,800 tons of water are pumped into specially constructed
tanks in the prow from the stern—the weight of which presses down and
breaks the ice.
These ships are said to be easily maneuverable, and can turn about in
little more than their own length.
They experience great difficulty in high seas, however; during stormy
weather, a roll of 4-5° is common.
The seaplanes carried are reported to be specially constructed 4-passenger
type for use in the Arctic.
DISTINGUISHING FEATURES
Their construction is unusual; they have a pronounced bridge at the water line and a rounded bottom.
The bow slopes away to almost nothing; this contributes to their unseaworthiness. The STALIN and KAGANOVICH were completed in 1938; the MIKOIAN in 1941.
Ice Breaker MIKOYAN
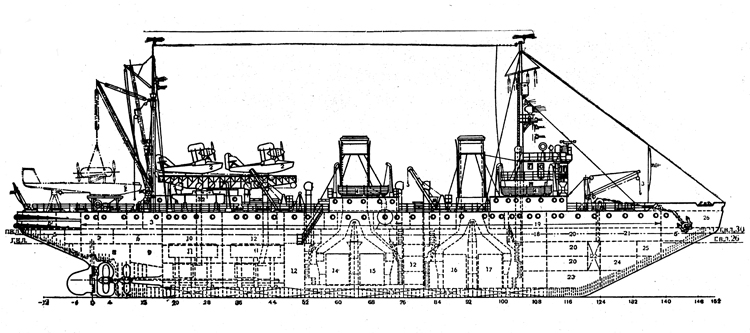
Icebreaker STALIN
1. Heavy Plane. 2. Light Planes. (1&2 replaced by armament) 3. Crew Quarters. 4- Lifeboat. 5. Ballast. 6. Cargo hold or Coal Bunk. 7. Bridge. 8. After-Peak/Ballast of Fresh water. 9. Cargo hold. 10. Machine Storeroom. 11. Machine Compartment. 12. fresh water. 14&15. After-Boiler Compartments. 16&17. Forward Boiler Compartments. 18. Refrigerating Unit. 19. Commanding Officers1 cabins. 20. Pantry & produce. 21. Ship's supplies. 22. Chain case. 23,24,25. Differential Cistern. 26. Ammonal Storage. 27. Listing Cistern. 28. Shaft. 29. After Peak. 30. Ice.

Stern View of Icebreaker - MIKOYAN
(b) Ex NORTWIND
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Date completed: 1943
Normal displacement: 5425.3 tons.
Length: B.P. 250', O.A. 269'.
Beam: 63'6".
Normal draft: 25' 10 1/4".
Number of engines: 6.
Type of machinery: Diesel, 2 cycle opposite Piston Fairbanks Morse.
Horsepower: 4 hour rate 2,000, continuous 1750 per engine.
Fuel: oil fuel and Diesel.
Aircraft normally carried: none installed as yet.
Launching device: one catapult,
ARMAMENT
None installed as yet.
GENERAL
This American icebreaker, which is being fitted out in the U.S. at the present time, will be turned over to the Soviet Navy when completed, under Lend-Lease.
(c) ICEBREAKER KRASSIN
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Date completed: 1917.
Normal displacement: 10,000 tons.
Length O.A.i 323 feet.
Beam: 72 feet.
Normal draft: 25 feet.
Horsepower: 10,000.
Full speed: 14 knots.
Cruising speed: 10 knots.
ARMAMENT
2 3" U.S. guns.
3 .50 cal. colt machine guns.
4 .30 cal. Browning machine guns.
GENERAL
This unit wi3 built for Russia by Great Britain.
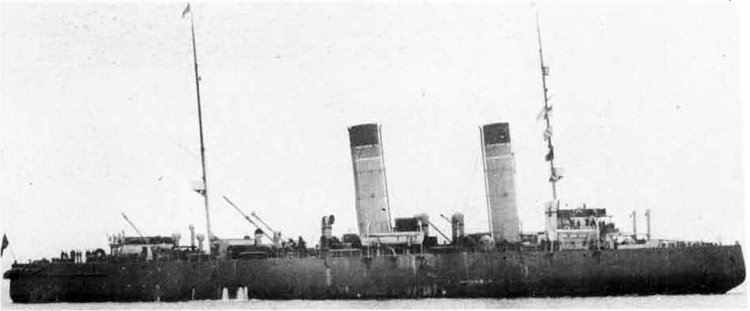
Icebreaker KRASSIN
Icebreaker KRASSIN
(d) ICEBREAKER LENIN
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Date commissioned: 1917.
Displacement: 5,600 tons.
Length O.A.: 264. feet.
Beam: 64. feet.
Maximum draft: 21 feet.
Type of machinery: triple expansion.
Horsepower: 7,500.
Number of propellors: 3.
Number of boilers: 8,
Fuel consumed: coal.
Full speed: 14. knots.
ARMAMENT
1 1.8" gun.
6 anti-aircraft machine guns.
GENERAL
This unit, which was built in England in 1917, is of the type which operates well in broken ice.

Icebreaker LENIN
(e) OTHER ICEBREAKERS
The following are photographs of some of the more important units of the Soviet Icebreaking Fleet.
Icebreaker YERMAK

Icebreaker LITKE (Ex Yacht Earl Grey)
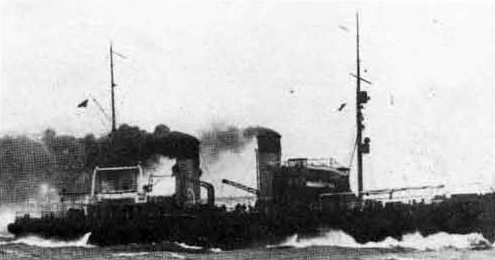
Icebreaker STEPAN MAKAROV

Icebreaker TAIMIR
Icebreaker DEZHNEV
Icebreaker SADKO
Icebreaker KAZAK KHABAROV
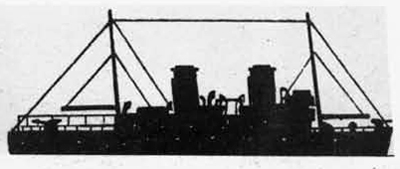
Icebreaker DOBRINYA NIKITICH

Icebreaker DAVIDOV
